Mining
There are five separate sections in the Mining tab:
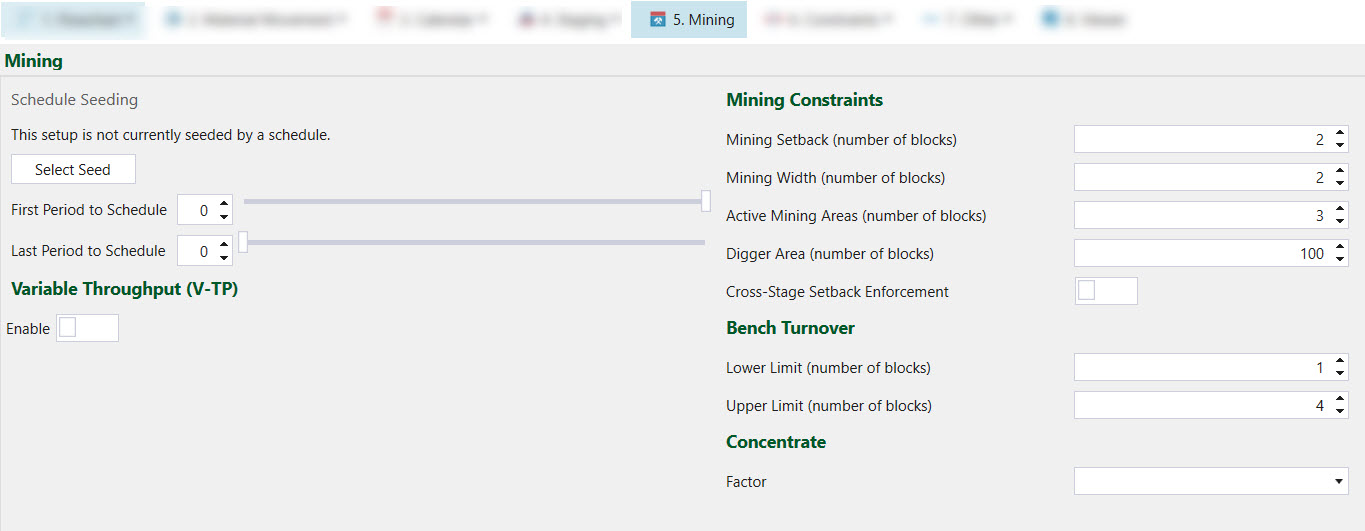
Schedule Seeding
Evolution allows for the use of seeding, which is the generation of newer schedules from previously created schedules.
Variable Throughput (V-TP)
The Variable Throughput option is used to base the the mill capacity on total crushing hours available in a period and not an ore tonnage. Therefore, select the material type from the model, and enter the processing rate (t/hr) for each material type. Enabling this option will modify the Calendar tab. This will require you to enter a utilisation rate, an operating efficiency and any delay hours for the mill.
Mining Constraints
The following constraints are specified in this section:
- Mining Setback (number of blocks)
- Mining Width (number of blocks)
- Active Mining Areas (number of blocks)
- Digger Area (number of blocks)
- Cross-stage setback enforcement
These constraints are considered hard.
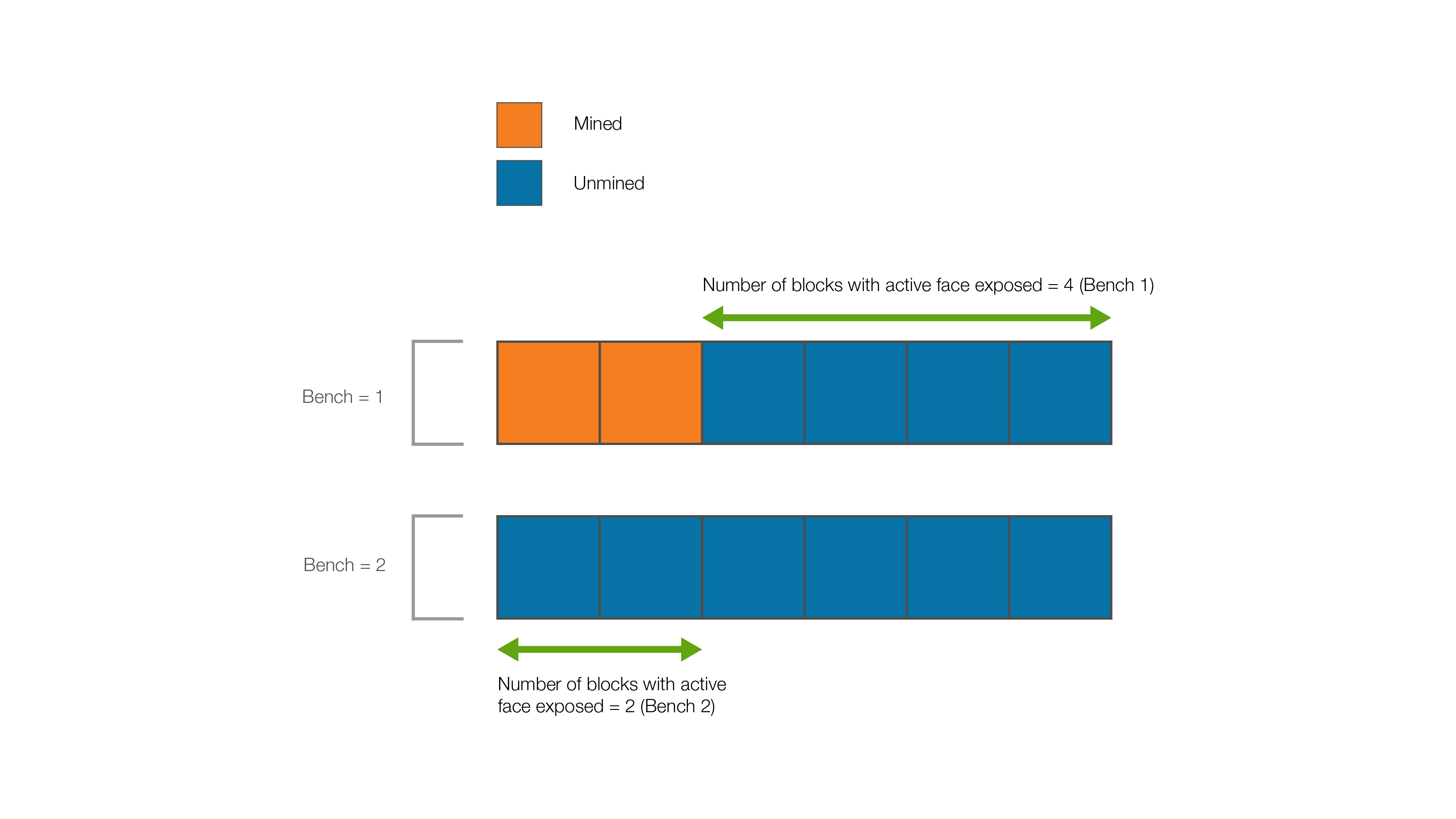
Mining Setback
The mining setback is the minimum number of blocks that are required to be exposed in a bench once mining in that bench takes place. Consider the following example.
Worked Example: Mining setback = 3
As the mining setback is set to 3, the only option in this situation is to mine an extra block in Bench 1. When this block is mined, the number of active faces in Bench 2 will be 3. This means Evolution will choose between either mining the top bench entirely or begin mining Bench 2. Partial mining cannot occur, because it has been specified that the active face of at least three blocks need to be exposed once mining in that bench takes place.
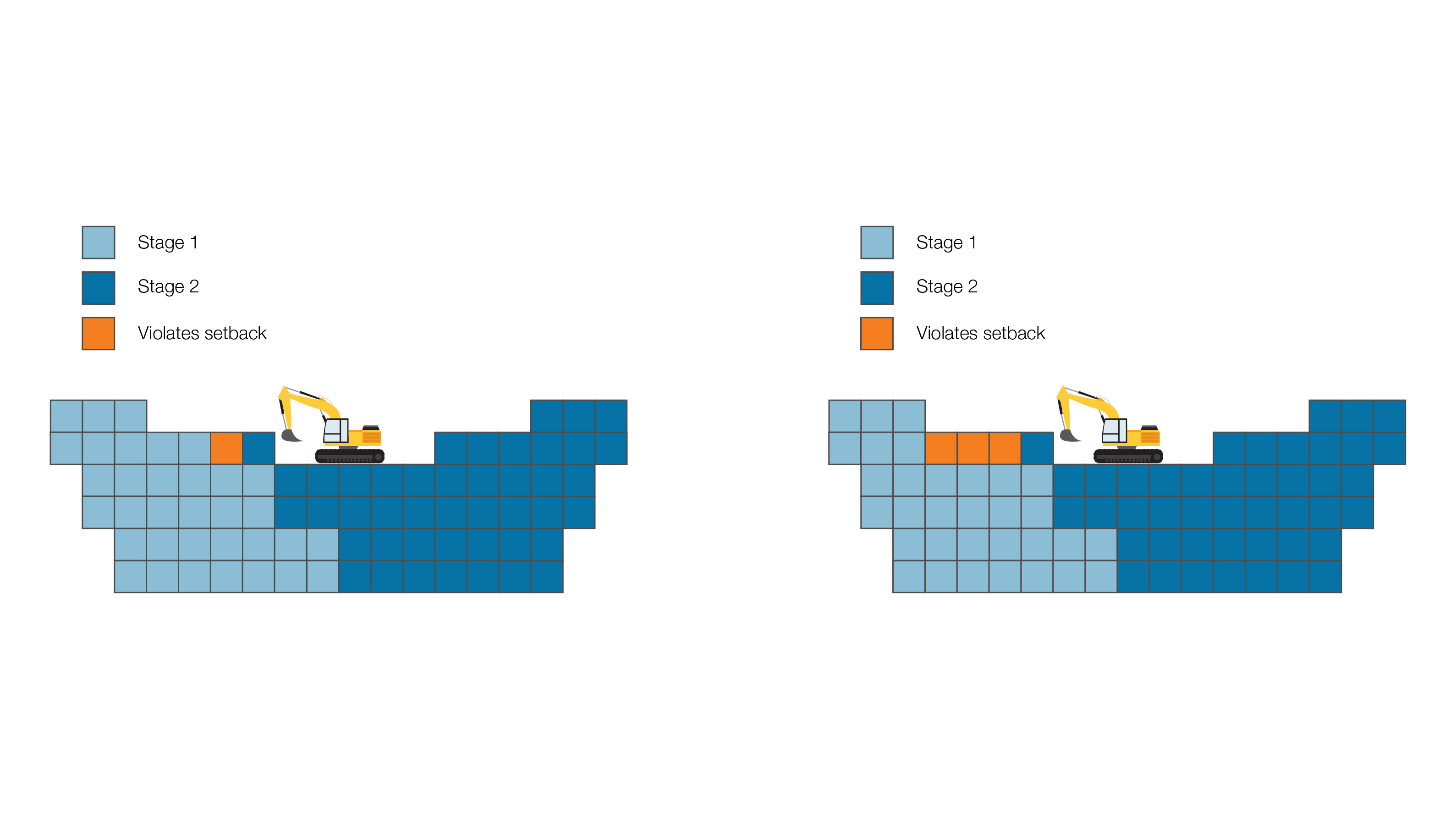
Cross-stage setback enforcement
This option enforces the mining setback rule within stage boundaries.
In the diagrams, below the mining setback is set at 3. In the top diagram, as the cross-stage setback enforcement option has been disabled, mining can only occur one stage at a time. In the bottom diagram, the cross-stage setback enforcement option has been enabled, therefore benches can be mined across stage boundaries. The red blocks are available to mine in terms of the cross-stage setback enforcement constraint, but cannot be mined as the mining setback will be violated.
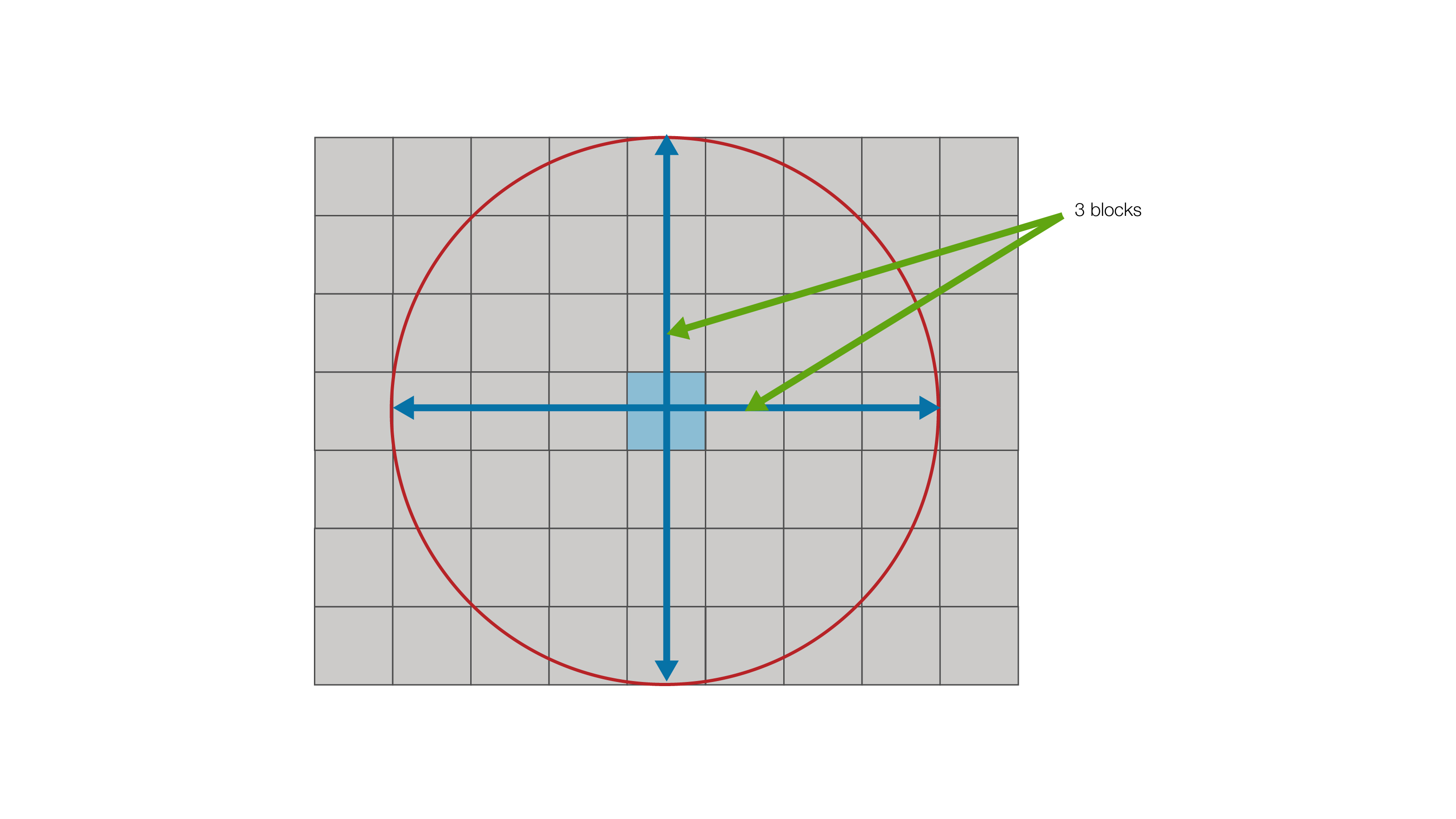
Mining Width
The Mining Width is the minimum space required to access a new bench. It is specified in terms of number of blocks. The mining width is the product of the size of the block and the number of blocks and is applied as a radius.
Active Mining Areas
In Origin Blocks, a digger is moved to a location, and then allowed to mine within a given radius. The active mining areas are the number of areas where the blocks are being mined at a given time.
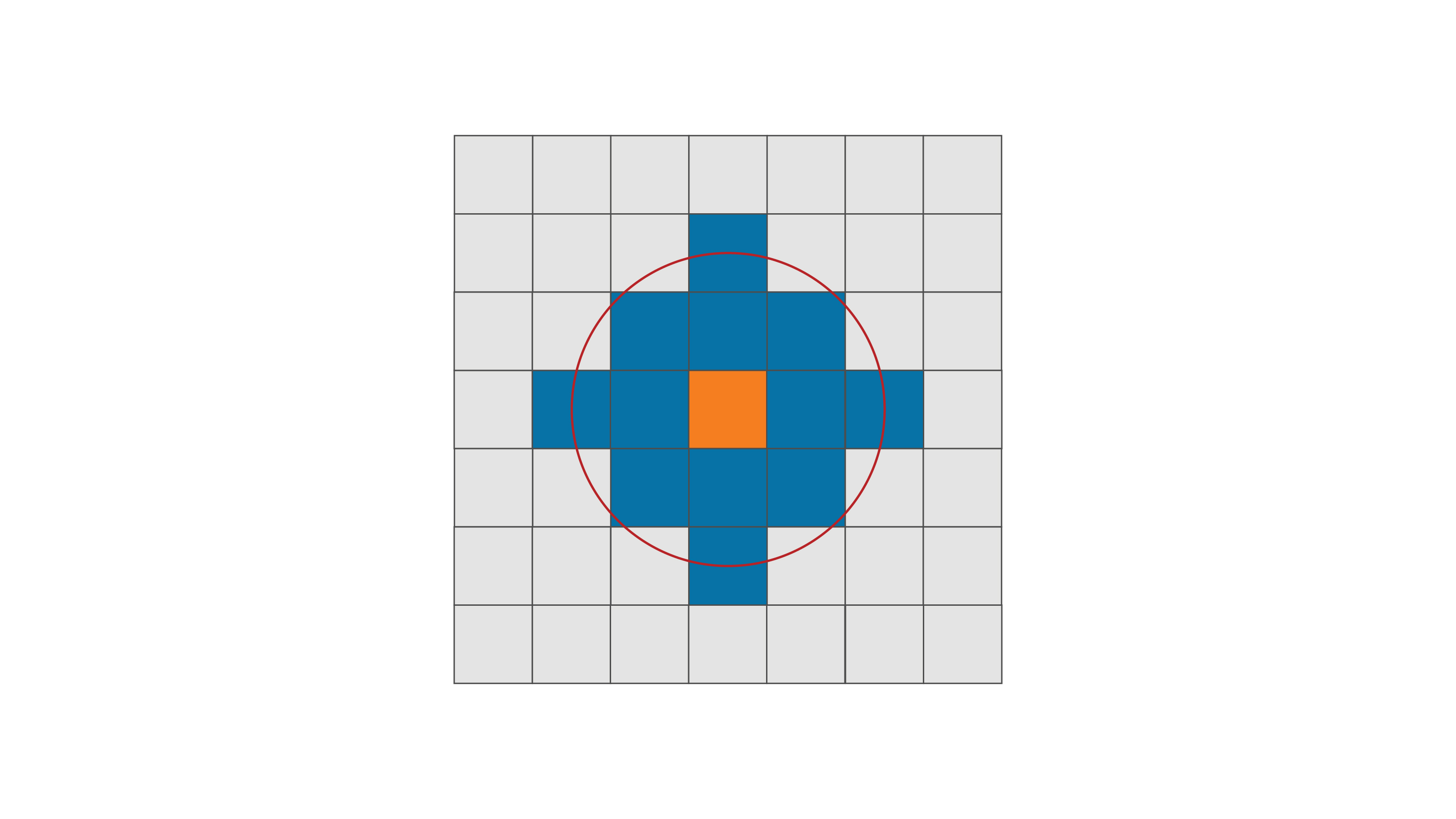
Digger Area
The digger area is the number of blocks to be mined from an active area before the digger is available to be moved. This setting ensures the mining sequence can be practically achieved without requiring the mining fleet to be constantly relocated.
Bench Turnover
The bench turnover inputs control how each bench within a stage is developing vertically. To develop the schedule in large flat benches lower values should be entered ie 1-2, whereas to increase the vertical advance, larger numbers can be entered, ie 10-100.
Concentrate
The concentrate factor is used in an equipment (truck hours) schedule when the mill is targeting an item other than tonnes. The concentrate model input item is used to back calculate the ore tonnes by multiplying the scheduling item * concentrate factor to ensure the cycle times of the truck are based on ore tonnes.