Transform
Source file: transform-group.htm
The Transform group hosts tools for repositioning and resizing objects in the view window.
|
|
Freehand Transform (Shift+T, Shift+R) Activate the freehand transform widgets. |
|
|
Translate (Ctrl+R) Move an object linearly in any direction. |
|
|
Scale Resize objects in any direction. |
|
|
Rotate (Ctrl+E) Rotate objects around any axis. |
Freehand Transform
Freehand Transform
The Freehand Transform tools enable you to translate and rotate a selected object for macro adjustments.
The freehand transform tool resides in both the Manipulation group of the Home tab and the Transform group of the Position and Filter tab. You can select the integrated
translate and rotate widget, or either the translate (Shift+T) or rotate (Shift+R) widget individually from the drop-down list. You can also select the Freehand Rotate Scan Bearings tool from this list.
- To turn a freehand transform tool off, click the
 Freehand Transform button.
Freehand Transform button.
|
|
|
Freehand transform tools: Combined (left), Translate (middle). Rotate (right). |
When launched, the transform tool appears at the centre of rotation with its axes, planes and rings aligned with the view window axes. To reposition it, set a new centre of rotation. See Set centre of rotation.
Operate the freehand transform tools, as follows:
-
Select the objects to be moved.
-
Hover the mouse over the control element of the tool for the required transformation:
-
To translate in along an axis (X, Y or Z), hover over that axis.
-
To translate across a plane (XY, XZ or YZ), hover over that plane.
-
To rotate, hover over a ring.
-
-
Drag the highlighted control with the middle mouse button.
While dragging, distances or angles are displayed.
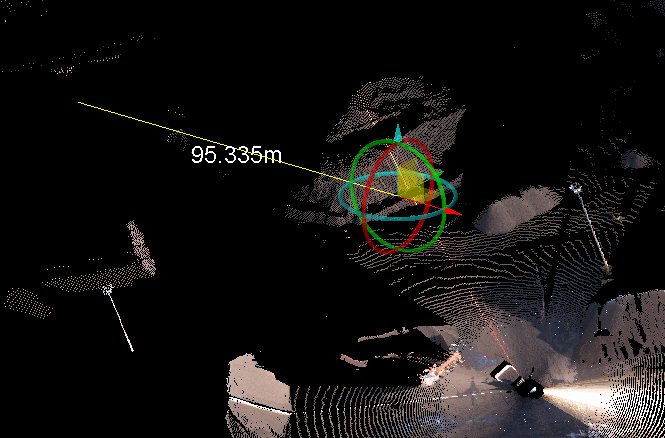
Translation along an axis.
Translation along a plane.
Rotation about an axis.
-
Release the mouse button when the objects are in position.
You can also set a precise one-dimension translation distance and rotation angle:
-
Middle click on a handle then enter a value.
-
For a two-dimension transformation, repeat with the next handle.
The ![]() Freehand Rotate Scan Bearings tool enables you to rotate individual scans
Freehand Rotate Scan Bearings tool enables you to rotate individual scans ![]()
![]() around their origins. When launched, the tool appears as a white sphere inside a cyan ring at the origin of each selected scan. That is, there will be as many instances of the tool as selected scans. Only one instance will be active at any moment. The active tool will also have a larger outer ring in the x-y plane of the corresponding scan. The outer ring is the rotation handle.
around their origins. When launched, the tool appears as a white sphere inside a cyan ring at the origin of each selected scan. That is, there will be as many instances of the tool as selected scans. Only one instance will be active at any moment. The active tool will also have a larger outer ring in the x-y plane of the corresponding scan. The outer ring is the rotation handle.
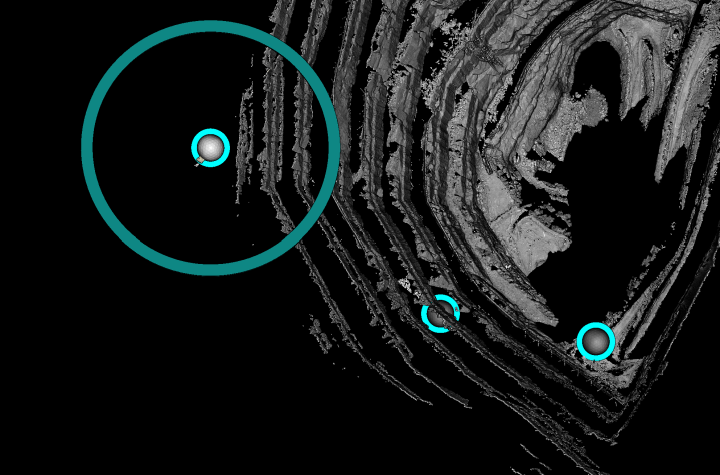

Note: The inner ring aids visibility as the tool may be obscured by, or blend in with, objects in view.
Tip: If the tool is concealed, zoom out to locate it. The tool remains the same size in view, regardless of the zoom level.
-
To rotate a scan, drag the outer ring of the tool with the middle mouse button.
-
To rotate another scan, select that scan and repeat.
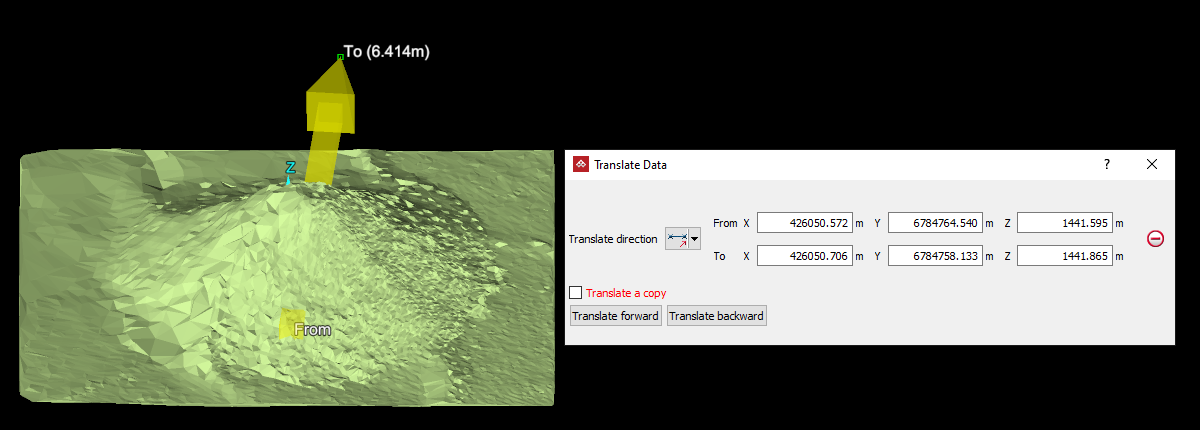
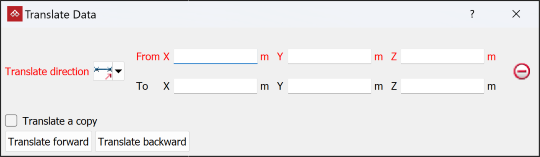
Translate
Translate
The Translate tool (Ctrl+R) enables you move or shift objects in any direction, as follows:
-
On the Edit tab, in the Transform group, click
 Translate or in the
Position and Filter tab, in the Transform group, click
Translate or in the
Position and Filter tab, in the Transform group, click  Translate.
Translate. -
Select the method of defining the Translate direction from the drop-down list.
The panel will change to request additional inputs according to the selected Translate direction type. The Translate direction options are:

Two points
Define the translation by specifying two points.
Two points and distance
Define the direction by specifying two points and then define the distance to translate along that direction separately.

Facet and distance
Pick as facet and then specify a distance to translate along the normal of that facet.

Axis aligned and distance
Specify an axis and how far you want to move in that direction.

Bearing, inclination and distance
Specify a bearing, inclination, and distance to translate.

Action plane axis and distance
Specify direction by choosing an axis of the current view's action plane (horizontally, vertically, or out of the action plane in its normal direction.) and then provide a distance to translate.
Tip: Right-click on the input fields to display a context menu with additional basic options, including Selection centre and Zero (or origin).
-
Select the Translate a copy option to allow you to produce a copy of the selected objects located at the nominated direction and distance from the source.
-
Select the object to be translated in the project explorer and make sure that no other objects are highlighted.
-
Click Translate forward to perform the translation process. Use Transform backward to retrace the path back to the start position.
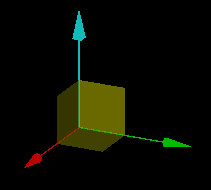
The direction vector guide
The direction vector guide is a visual aid
that indicates the how the selected object will be translated. Its appearance depends on the translation direction method chosen, but always includes an arrow showing the direction and distance of the translation.
|
|
|
Direction vector using the Two points direction method. |
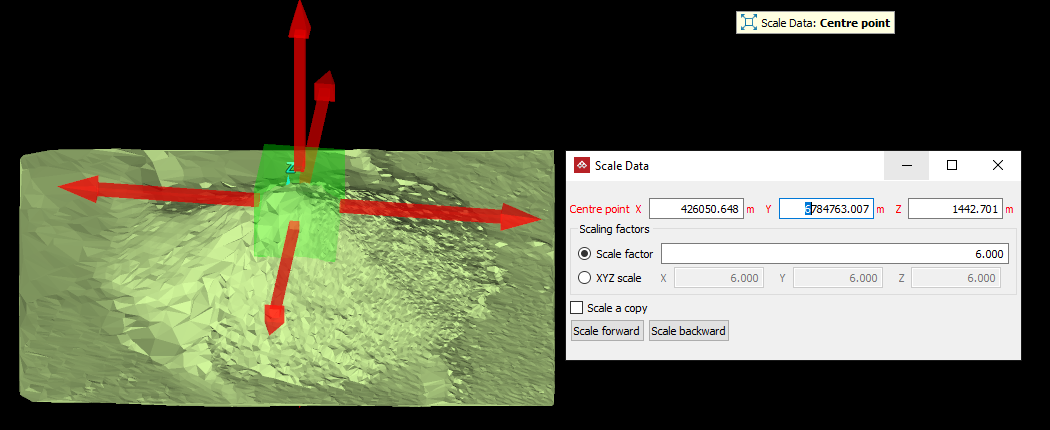
Scale
Scale
The Scale
tool allows you to resize objects in any direction, as follows:
-
On the Edit tab, in the Transform group, click
 Scale, or in the
Position and Filter tab, in the Transform group, click
Scale, or in the
Position and Filter tab, in the Transform group, click  Scale.
Scale.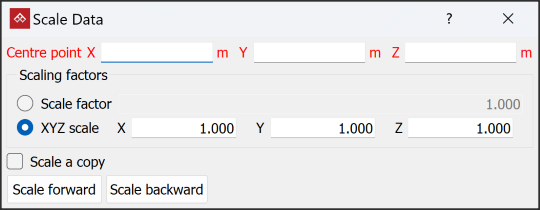
- Select
a Centre point
about which the object is scaled.
Tip: Right-clicking on Centre point field will display a context menu with additional basic options.
-
Enter a Scale factor to scale the object equally in all directions.
Or
Select XYZ scale and enter factors for each of the X, Y and Z directions to scale the object disproportionately.
Tip: To scale scans horizontally, enter the scaling factor for X and Y, and set Z =
1.0. -
Select Scale a copy to duplicate the original object and scale the new copy each time Scale forward or Scale backward is selected.
-
Select the object to be scaled in the project explorer and make sure that no other objects are highlighted.
- Click Scale forward to increase the object size by the scale factor, or click Scale backward to decrease the object size.
Note: Scaling removes photographic data from scans.
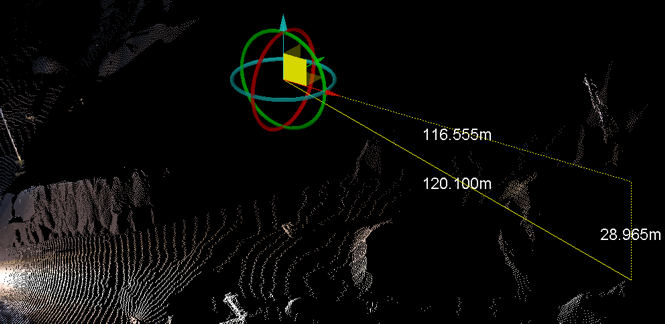
The scaling vector guide
The scaling vector guide is a visual aid
that indicates the how the selected object will be resized. The guide consists of a green cube representing the original size of the selected object, and red arrows indicating the projected scaling in each direction.
|
|
|
The scaling guide where a single Scale factor is to be applied in all directions. |
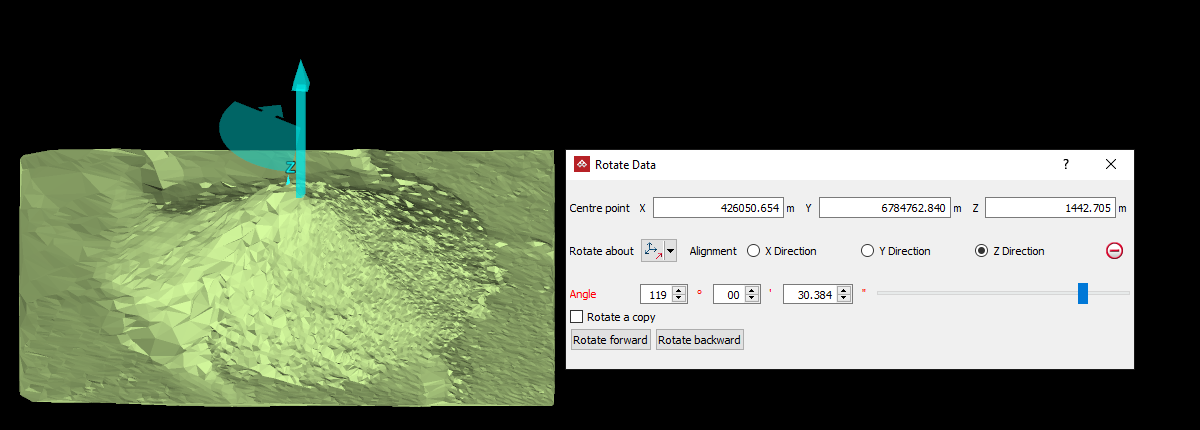
Rotate
Rotate
The Rotate tool (Ctrl+E) allows you to rotate data around the three axes (X, Y, Z), or around a user-defined axis, as follows:
-
On the Edit tab, in the Transform group, click
 Rotate, or in the
Position and Filter tab, in the Transform group, click
Rotate, or in the
Position and Filter tab, in the Transform group, click  Rotate.
Rotate.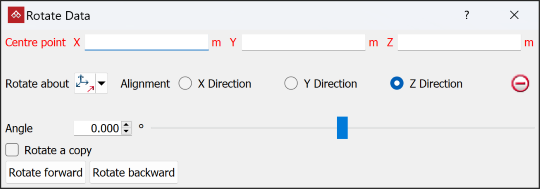
- Select a Centre point of rotation. The centre of rotation can be selected in the view window or entered in the panel.
-
Select the method of defining the rotation axis from the Rotate about drop-down list.
-
Select the object to be rotated in the project explorer and make sure that no other objects are highlighted.
-
Enter a rotation Angle and use the Rotate forward and Rotate backward buttons to rotate clockwise and anti-clockwise.
-
Select Rotate a copy to rotate a duplicate of the original object each time Rotate forward or Rotate backward is selected.
Tip: Right-clicking on Centre point fields will display a context menu with additional basic options.
The panel will change to request additional inputs according to the selected Rotate about type. The Rotate about options are:
|
|
Two points Rotate around an axis defined by two points. |
|
|
Facet Rotate around an axis perpendicular to a facet. |
|
|
Axis aligned Rotate about X, Y or Z. |
|
|
Bearing and inclination Rotate about an axis defined by a bearing and inclination angles. |
|
|
Action plane axis Rotate about the action plane of active view. |
Tip: With Rotate a copy active, select the new copy of the object to create another copy rotated further around the axis.
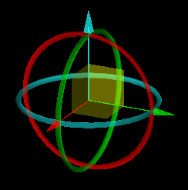
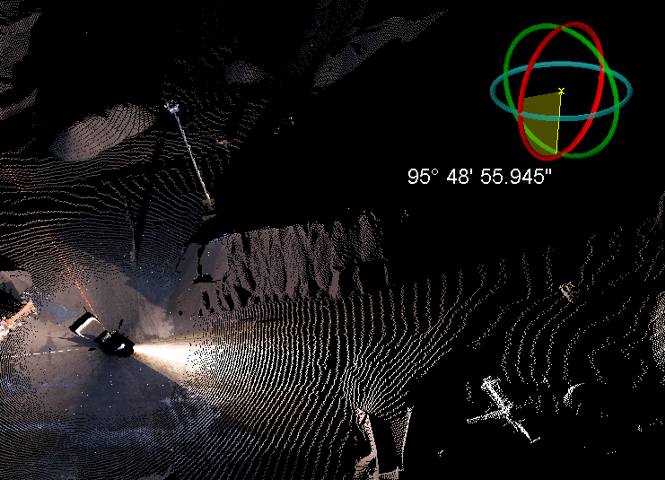
The rotation vector guide
The rotation vector is a visual aid
that indicates the how the selected object will be rotated. It appears as a sector with an arrow indicting the direction of rotation and a straight arrow indicating the axis of rotation.
|
|
|
The rotation vector guide using the Axis aligned rotation method, rotating about the Z axis. |