Glossary
Source file: glossary.htm
| Term | Definition | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batter | Refers to the slope of a wall. For example, an excavator digs to a 'batter angle' to achieve a dig wall to the design batter angle. | ||||||||
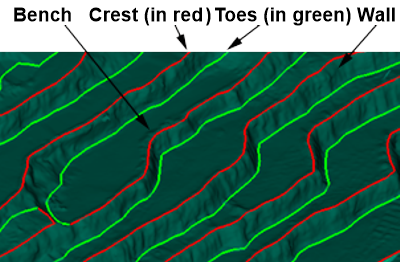
| Bench |
When a high wall becomes too high for safety, a bench is used to act as a buffer for falling rocks. This is where a digging machine (e.g. excavator or dragline) sites while digging material below this level.
|
||||||||
| Crest | The line along the top of a wall. | ||||||||
| Toe | The line along the base of a wall. | ||||||||
| Wall | Steeply angled slope between a crest and a toe. | ||||||||
| Breakline | A line with a series of vertices that defines points of inflection in the topographic surface of the earth (i.e. places where there are sharp changes in the direction of slope on the earth's surface). | ||||||||
| Chainage | Chainage (running distance) is the distance along a curved or straight survey line from a fixed commencing point, similar to mileage. Alternatively: A length as measured by a surveyor's chain or tape. | ||||||||
| Database | Database is another name for the working file for data in Maptek software. All data is contained within the Database file and is not accessible from Windows. More | ||||||||
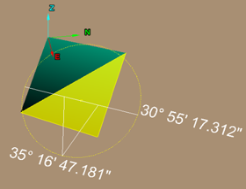
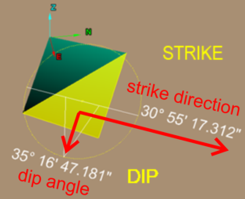
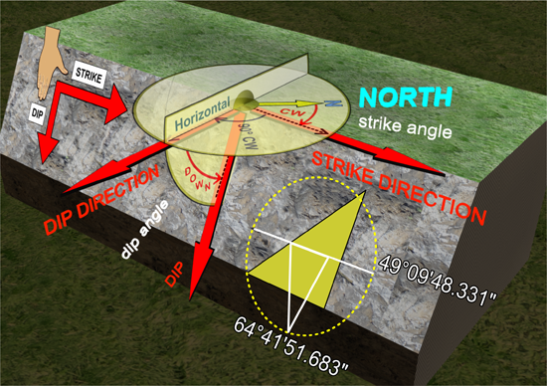
| Dip, Dip Angle, Dip Direction |
|
||||||||
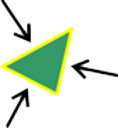
| Edges | Straight lines that join the vertices of a facet form the edges. |
|
|||||||
| Facet | A simple plane represented by a filled polygon with co-planar vertices. It is used as a basic building block to build 3D surfaces in software. Generally, surfaces are made up of a collection of facets joined together to approximate the shape of a real object, or to create a custom or a virtual object. Two common facet types include triangles and quadrilaterals. | ||||||||

|

|
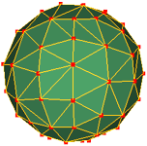
|
|||||||
Sphere
constructed of quadrilateral
facets.  |
Sphere
constructed of triangular
facets.  |
Red
dots = Vertices.
|
|||||||
| Facet network | See Surface. | ||||||||
| Frustum | The part of a solid, such as a cone or pyramid, between two parallel planes cutting the solid, especially the section between the base and a plane parallel to the base. | ||||||||
| Geodesy | The study of the shape of the Earth and the determination of the exact position of geographical points (latitude, longitude and elevation). Geodetic - and activity relating to geodesy. Geodesist - a person undertaking geodetic work. | ||||||||
| Great circle | A great circle of a sphere is the intersection of the sphere and a plane which passes through the centre point of the sphere. | ||||||||
| Plunge | See Trend. | ||||||||
| Project | A project file stores data and results of analyses which can be opened in a project session. The project file (also termed a database file) uses the extension .maptekdb and can't be accessed by other programs. | ||||||||
| Rill | See Windrow. | ||||||||
| Rose diagram | A circular histogram plot that displays directional data and the frequency of each class. | ||||||||
| Stereonet | A stereonet (or stereogram or hemispherical projection) is a way of representing 3-dimensional directions on a 2-dimensional surface. The net is a projection from the point onto the equator. | ||||||||
| Strike | The strike line of a bed, fault, or other planar feature is a line representing the intersection of that feature with a horizontal plane. On a geologic map, this is represented with a short straight line segment oriented parallel to the strike line. Refer to Dip. | ||||||||
| Surface |
|
||||||||
| Trend |
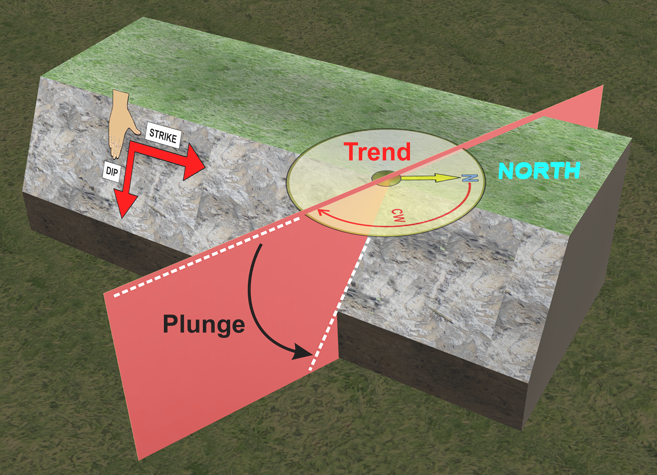
|
||||||||
| Trend and plunge refer to the characteristics of a linear geological feature and are related to the dip and strike of a slope. The trend is the angle to the line of the feature, measured from the North direction. The plunge is the vertical angle dropping from a horizontal line to the feature line where it sits along the slope. Note that the plunge is generally less than the dip of the slope. When the feature runs perpendicular to the strike of the slope, the plunge will be equal to the dip of the slope. | |||||||||
| Triangulation | A surface consisting only of triangle-shaped facets. |

|
|||||||
| Vertices | Vertices are the points that define the corners of a facet. (Singular: Vertex) |
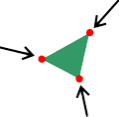
|
|||||||
| Windrow | Loose material that has been pushed to an edge, generally used to prevent vehicles from driving off high walls or outside of designated roads, as well as for establishing boundaries. | ||||||||