New
Source file: create-new-photogrammetric-reconstruction.htm
To create a photogrammetric reconstruction, click on the ![]() New button on the Photogrammetry ribbon tab, then follow the steps below.
New button on the Photogrammetry ribbon tab, then follow the steps below.
-
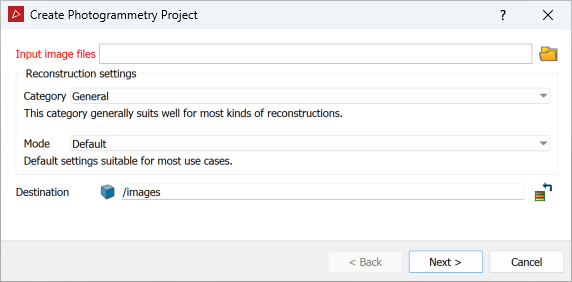
Add the required image files to the Input image files field. You can do this in either of the following ways:
-
Drag them in bulk from a Windows file explorer to the Input image files field.
-
Click the
 button and navigate to the image folder, select the image files and click OK.
button and navigate to the image folder, select the image files and click OK.Tip: In the search field of the file selection dialog, type kind:image to find and list all images in the chosen location and its subfolders.
Note: You cannot perform photogrammetry on a single file; you need to select at least two files. Typically one would use at least ten, and often more than 100.
-
-
Choose the reconstruction settings:
-
Select the reconstruction category according to the descriptions:
General This category generally suits most kinds of reconstructions well. Aerial/Nadiral Use this category when you are reconstructing a top-down view scenario, typically a UAV drone-acquired dataset. Urban Use this category when reconstructing buildings, façades or scenarios that are shot in an urban setting. You can use this category for small objects instead of the Surface scan category if you are mixing different types of photos, especially if the whole dataset is not shot from the same distance. Surface scan Use this category when you are reconstructing surfaces close up (e.g. terrain or ground). Vertical structure Use this category when you are reconstructing telecommunication towers or other thin vertical structures from drones. -
Select the mode, depending on the required level of detail:
Fast Reduced resolution, bundle adjustment iterations and number of keypoints: faster than default. Default Default settings suitable for most use cases. Deep Increased bundle adjustment iterations, number of keypoints and camera matches. Slower than the default setting, this mode should be used when you are losing cameras in Default mode.
-
-
Optionally, choose the output container by dragging it in from the project explorer. By default the output will be placed in a container named for the folder of the source images, inside the images container
 .
. -
Click Next >.
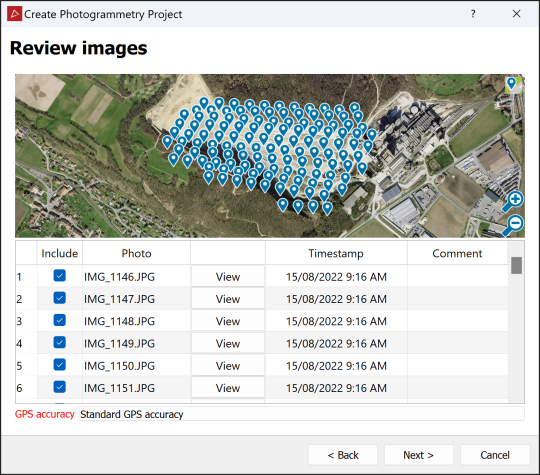
The images will be listed in the next panel and those with GPS data will be marked on a satellite image of the area.
-
Review the images by clicking View alongside a photo to see it in the image viewer.
-
Select GPS accuracy option that best matches the accuracy of the GPS metadata in the image files.
Note: If no images containing GPS information are selected, the Review Images page will not show either the map view or the GPS accuracy options.
-
Deselect any images that are not required to exclude them.
-
Click Next >.
-
If any of the selected images contain GPS information, you will have the option of batch processing the remaining photogrammetry tools, excluding Register Reconstruction. Select the tools you wish to run. If you need to do further registration of the images, leave these unselected.
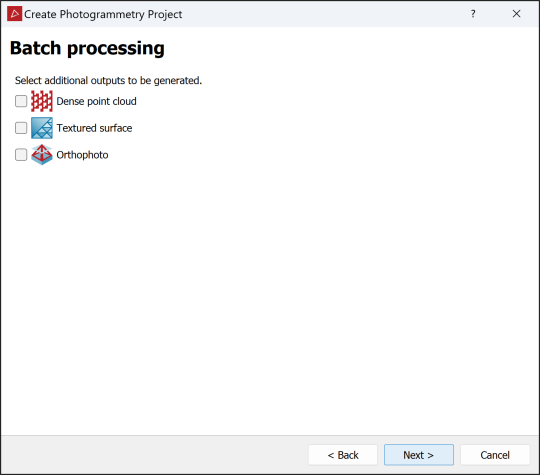
Tip: Because these stages must be completed sequentially, you only need to select the one to be processed last.
-
Click Next >.
-
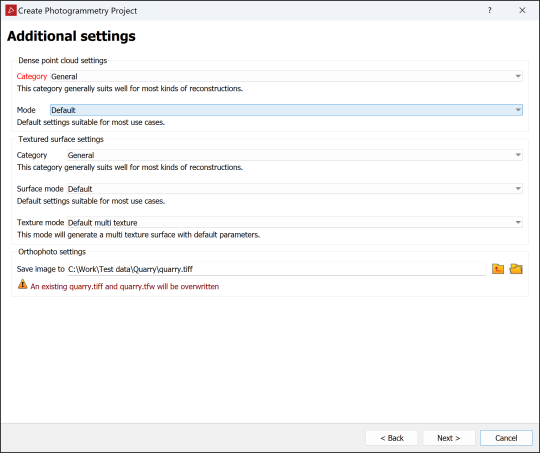
If you selected any additional outputs on the batch processing page, the Additional settings page will appear. Here you will need to select category and mode settings for each selected stage, and a folder and name for the orthophoto image.
-
Click Next >. The tool will run, generating a sparse point cloud and storing it in the chosen output container, then proceeding with the selected batch processes.
