DGD Reading & Writing
Layers and objects in a DGD (design database) can be manipulated without Vulcan being opened. The following examples illustrate how to do this.
Topics:
Modules to import
Import the following libraries:
from maptek import vulcan import numpy as np import pandas as pd
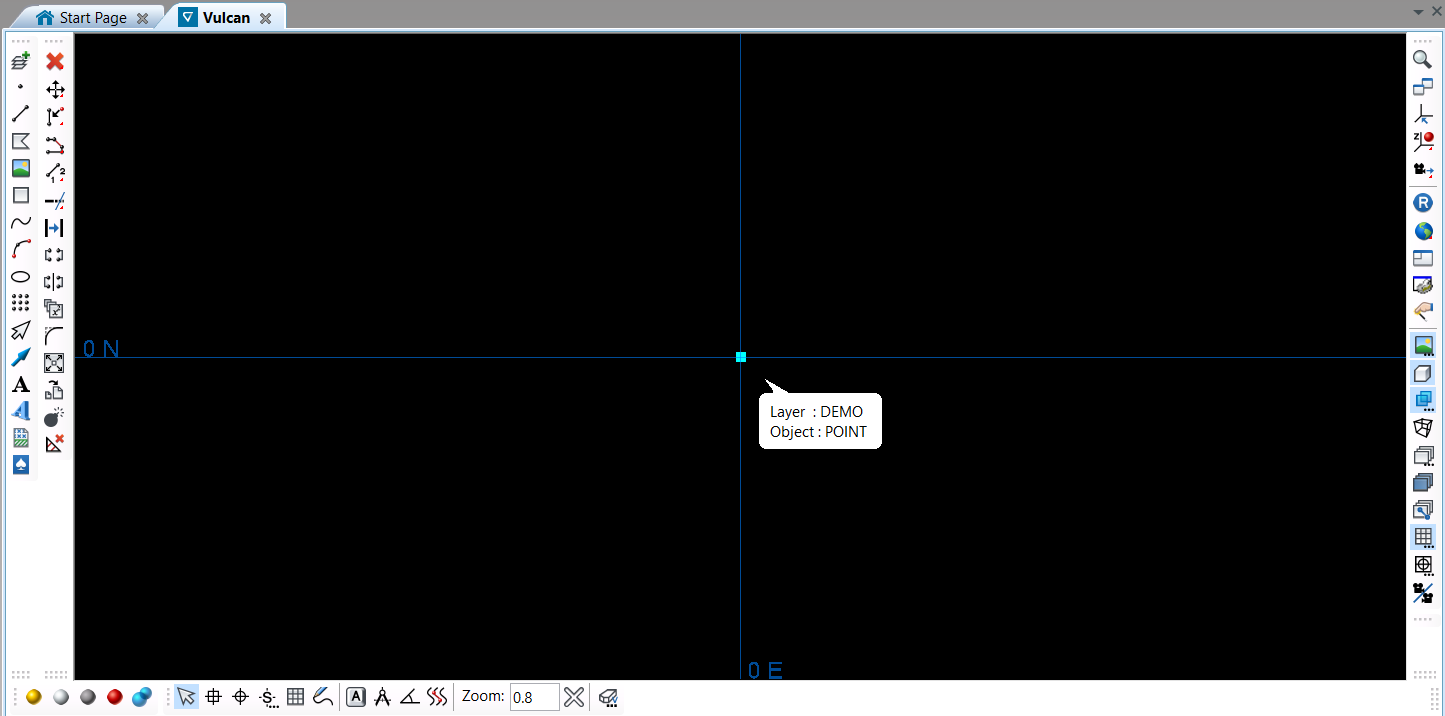
Create a DGD
Creates a dgd, adds a layer called DEMO and then adds a single point at location 0,0,0. The colour of the object can be changed using the set_colour() method with an integer. The integer represents the colour number in the Vulcan scd colour palette.
from maptek import vulcan
with vulcan.dgd('pydemo.dgd.isis', 'create') as dgd:
layer = vulcan.layer('DEMO') # create a new layer called DEMO
obj = vulcan.polyline([0,0,0]) # add a single point
obj.name = 'POINT' # change the name of the point to "POINT"
obj.set_colour(1) # change the colour to colour 1
layer.append(obj) # add to the layer
dgd.append(layer) # add the layer to the dgd
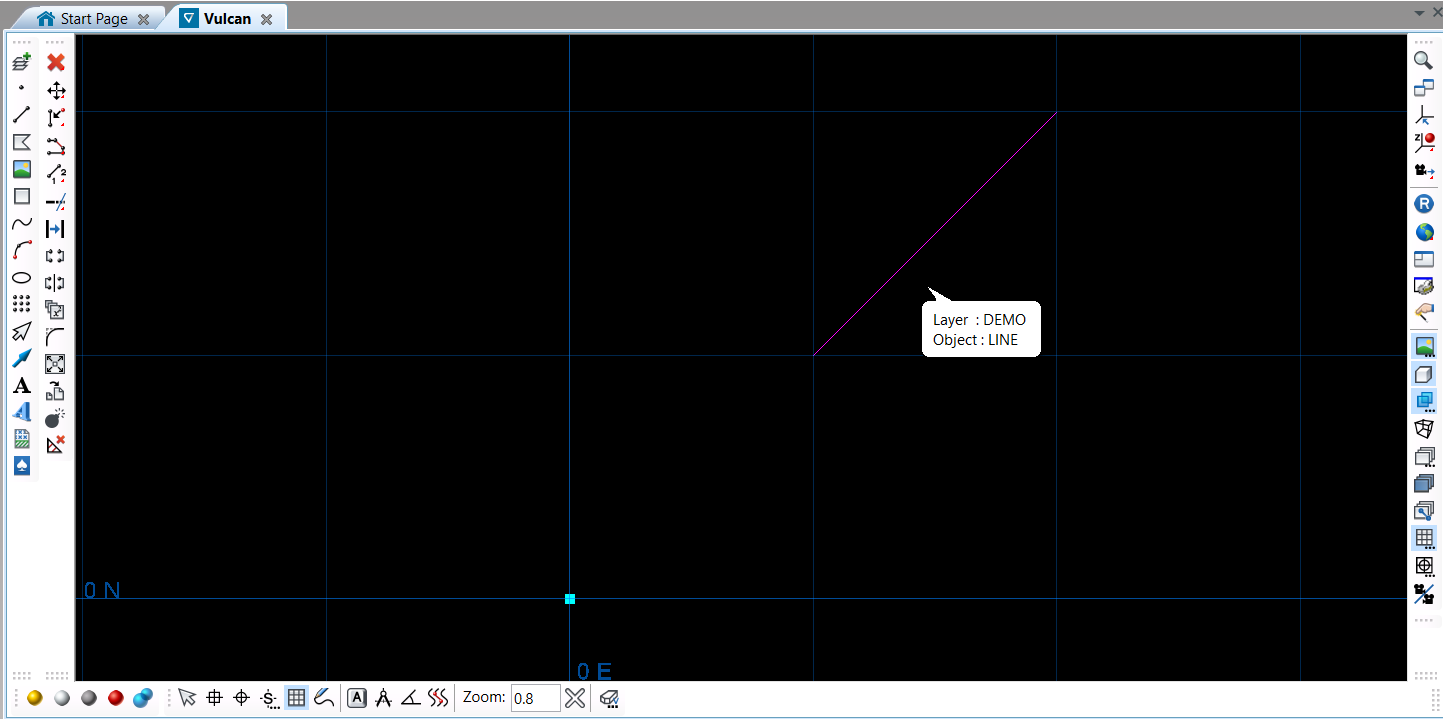
Open existing DGD and add data
This example opens the dgd and layer created previously and adds a line. The line consists of two points with a line between them created using the set_connected() method.
from maptek import vulcan
# open dgd in write mode
with vulcan.dgd('pydemo.dgd.isis','w') as dgd:
layer = dgd.get_layer('DEMO') # get the "DEMO" layer
# create a diagonal line
obj = vulcan.polyline([[5,5,5],[10,10,10]])
obj.name = 'LINE'
obj.set_colour(3)
# set the line as connected so it appears as a line
obj.set_connected()
layer.append(obj)
dgd.save_layer(layer) # save the modified layer
Create a closed polygon
Open an existing dgd and layer and add a closed polygon in the shape of a square. This example illustrates the use of the set_closed() method to close a polygon.
from maptek import vulcan
with vulcan.dgd('pydemo.dgd.isis','w') as dgd:
layer = dgd.get_layer('DEMO') # get the "DEMO" layer
obj = vulcan.polyline([[5,0],[7,0],[7,2],[5,2]])
obj.name = 'SQUARE'
obj.set_colour(5)
obj.set_connected()
obj.set_closed()
layer.append(obj)
dgd.save_layer(layer)

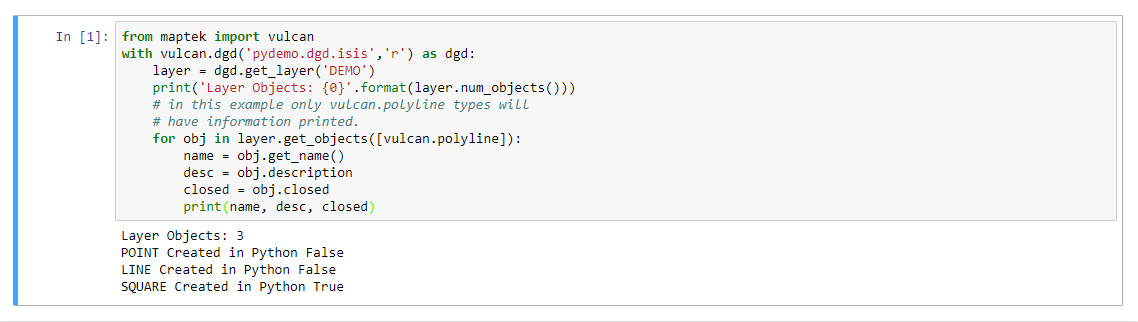
Get object details
This example illustrates how to get details for each object in a layer.
from maptek import vulcan
with vulcan.dgd('pydemo.dgd.isis','r') as dgd:
layer = dgd.get_layer('DEMO')
print('Layer Objects: {0}'.format(layer.num_objects()))
# in this example only vulcan.polyline types will
# have information printed.
for obj in layer.get_objects([vulcan.polyline]):
name = obj.get_name()
desc = obj.description
closed = obj.closed
print(name, desc, closed)
Reading from a DGD
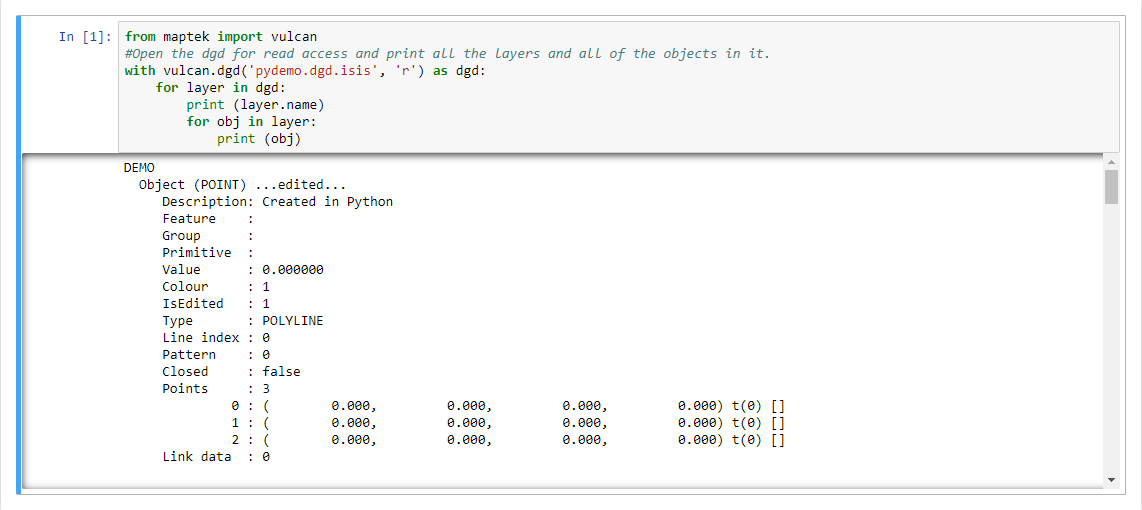
from maptek import vulcan
#Open the dgd for read access and print all the layers and all of the objects in it.
with vulcan.dgd('pydemo.dgd.isis', 'r') as dgd:
for layer in dgd:
print (layer.name)
for obj in layer:
print (obj)
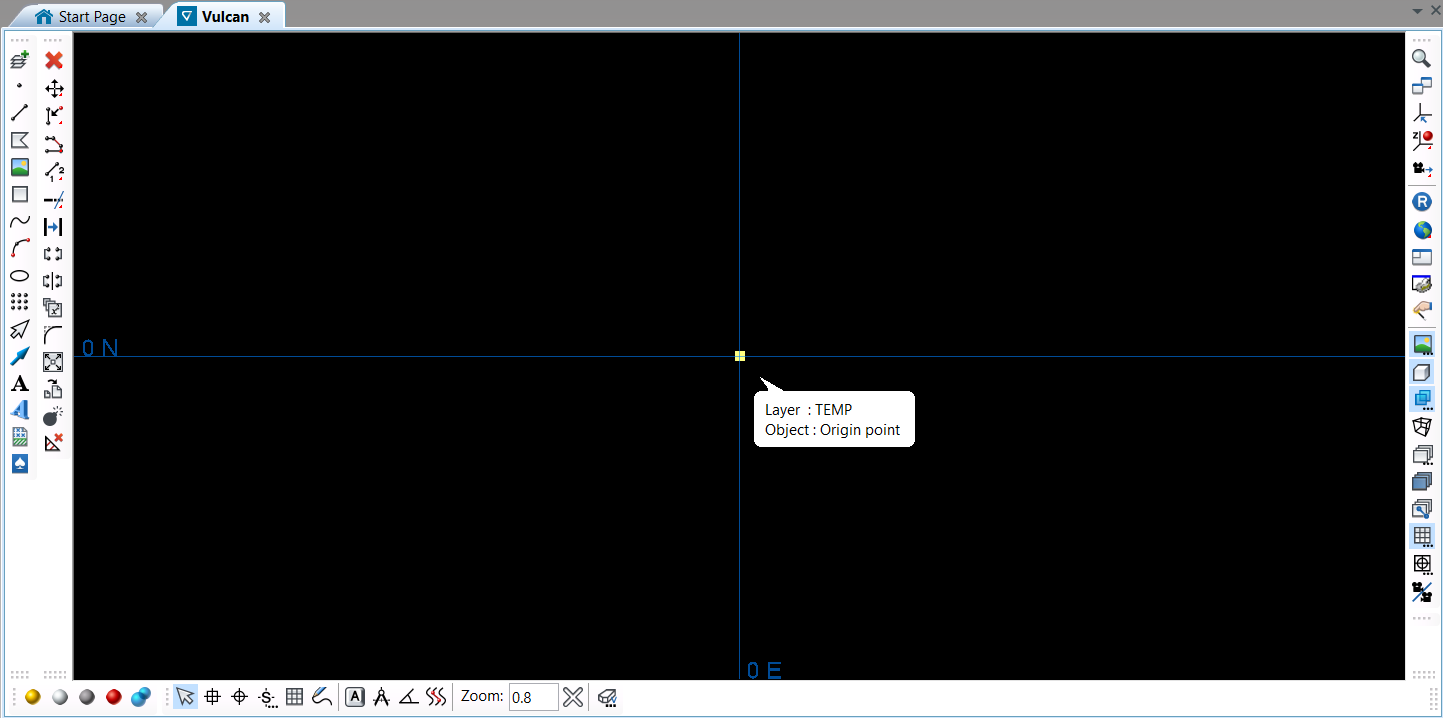
Editing objects in a DGD
from maptek import vulcan
# Open the dgd for write access
with vulcan.dgd('pydemo.dgd.isis','w') as dgd:
my_layer = None
# Find the layer we want
lyr_name = "TEMP"
# If it exists, modify an object in it
if dgd.is_layer(lyr_name):
my_layer = dgd.get_layer(lyr_name)
idx = len(my_layer)-1
print(idx)
if idx >= 0:
obj = my_layer[idx]
obj.name = "LastObject"
my_layer[idx] = obj
dgd.save_layer(my_layer)
# If the layer doesn't exist, make one and add it.
else:
my_layer = vulcan.layer(lyr_name)
obj = vulcan.polyline([0,0,0])
obj.name = "Origin point"
my_layer.append(obj)
dgd.append(my_layer)
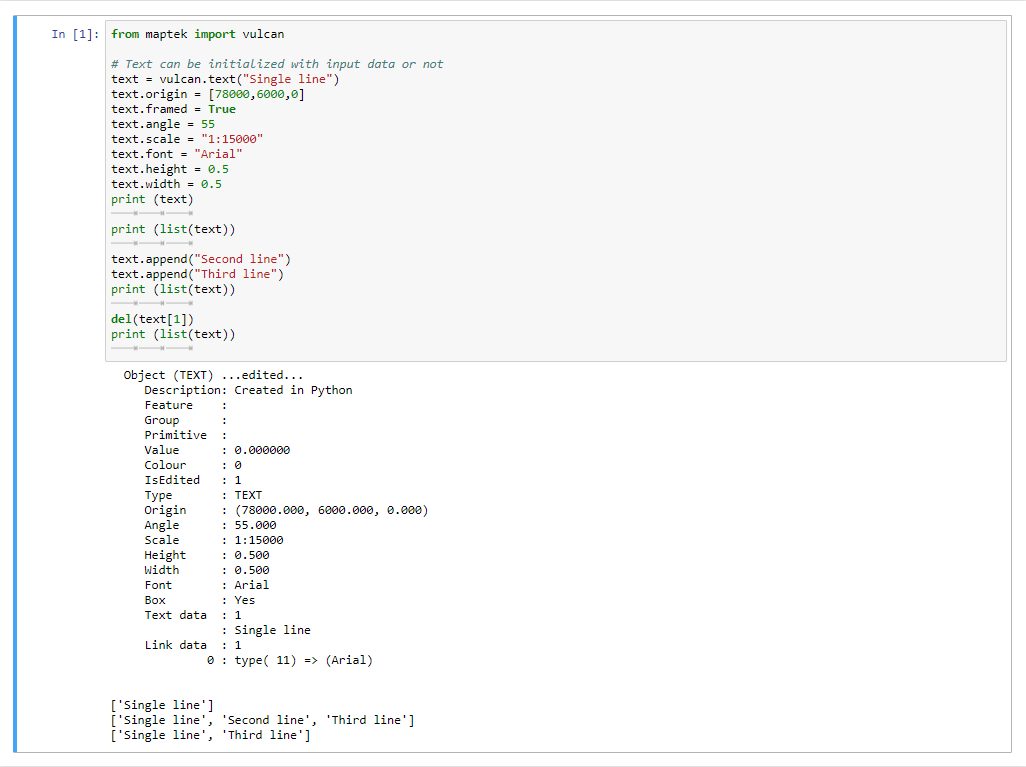
2D Text Manipulation
from maptek import vulcan
# Text can be initialized with input data or not
text = vulcan.text("Single line")
text.origin = [78000,6000,0]
text.framed = True
text.angle = 55
text.scale = "1:15000"
text.font = "Arial"
text.height = 0.5
text.width = 0.5
print (text)
print (list(text))
text.append("Second line")
text.append("Third line")
print (list(text))
del(text[1])
print (list(text))
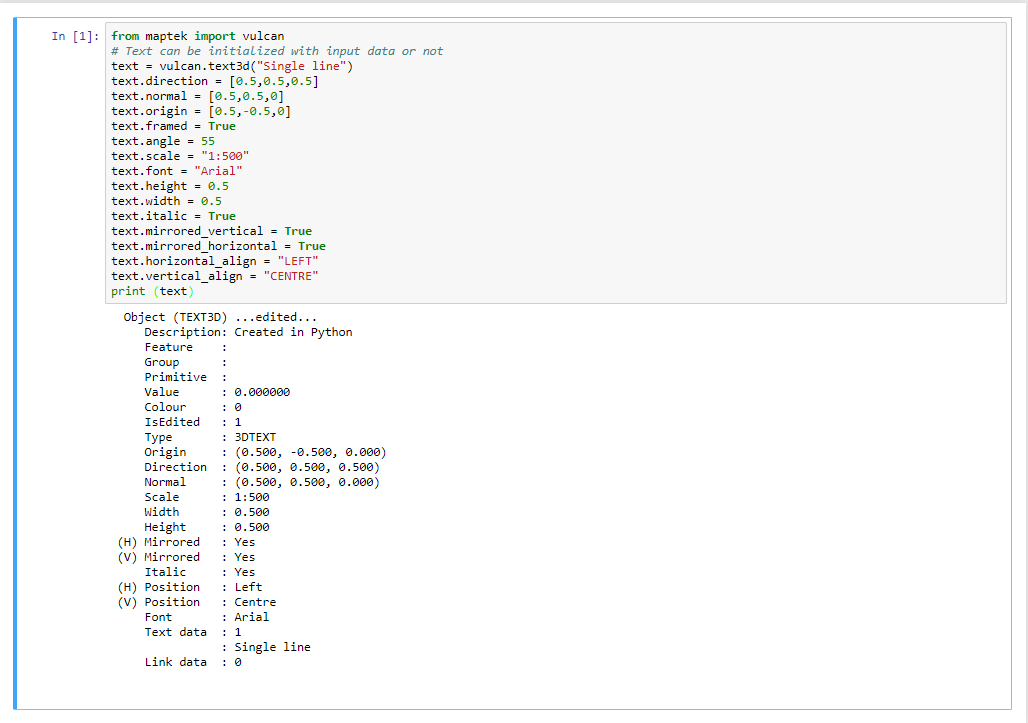
3D Text Manipulation
from maptek import vulcan
# Text can be initialized with input data or not
text = vulcan.text3d("Single line")
text.direction = [0.5,0.5,0.5]
text.normal = [0.5,0.5,0]
text.origin = [0.5,-0.5,0]
text.framed = True
text.angle = 55
text.scale = "1:500"
text.font = "Arial"
text.height = 0.5
text.width = 0.5
text.italic = True
text.mirrored_vertical = True
text.mirrored_horizontal = True
text.horizontal_align = "LEFT"
text.vertical_align = "CENTRE"
print (text)
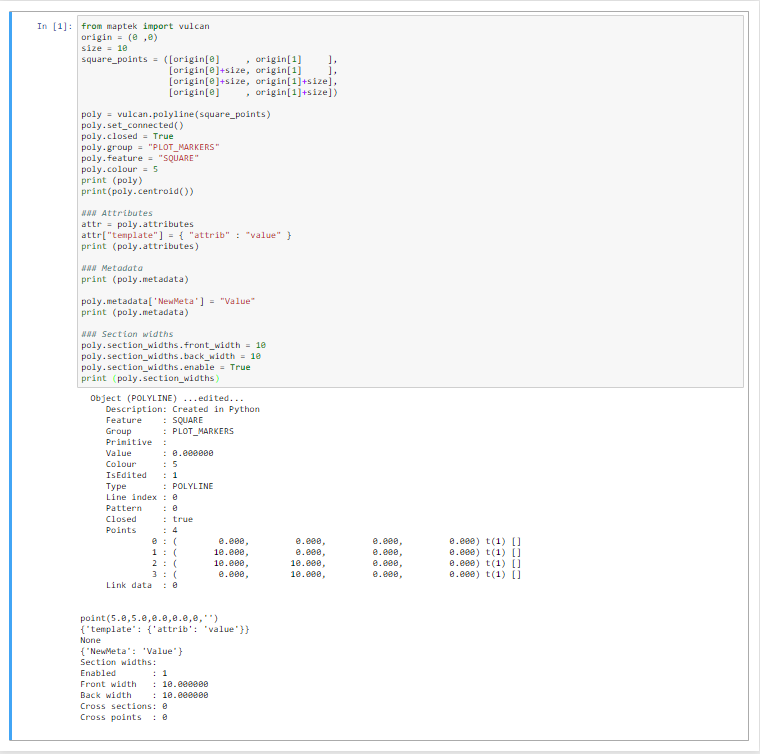
Polyline Manipulation
from maptek import vulcan
origin = (0 ,0)
size = 10
square_points = ([origin[0] , origin[1] ],
[origin[0]+size, origin[1] ],
[origin[0]+size, origin[1]+size],
[origin[0] , origin[1]+size])
poly = vulcan.polyline(square_points)
poly.set_connected()
poly.closed = True
poly.group = "PLOT_MARKERS"
poly.feature = "SQUARE"
poly.colour = 5
print (poly)
print(poly.centroid())
### Attributes
attr = poly.attributes
attr["template"] = { "attrib" : "value" }
print (poly.attributes)
### Metadata
print (poly.metadata)
poly.metadata['NewMeta'] = "Value"
print (poly.metadata)
### Section widths
poly.section_widths.front_width = 10
poly.section_widths.back_width = 10
poly.section_widths.enable = True
print (poly.section_widths)
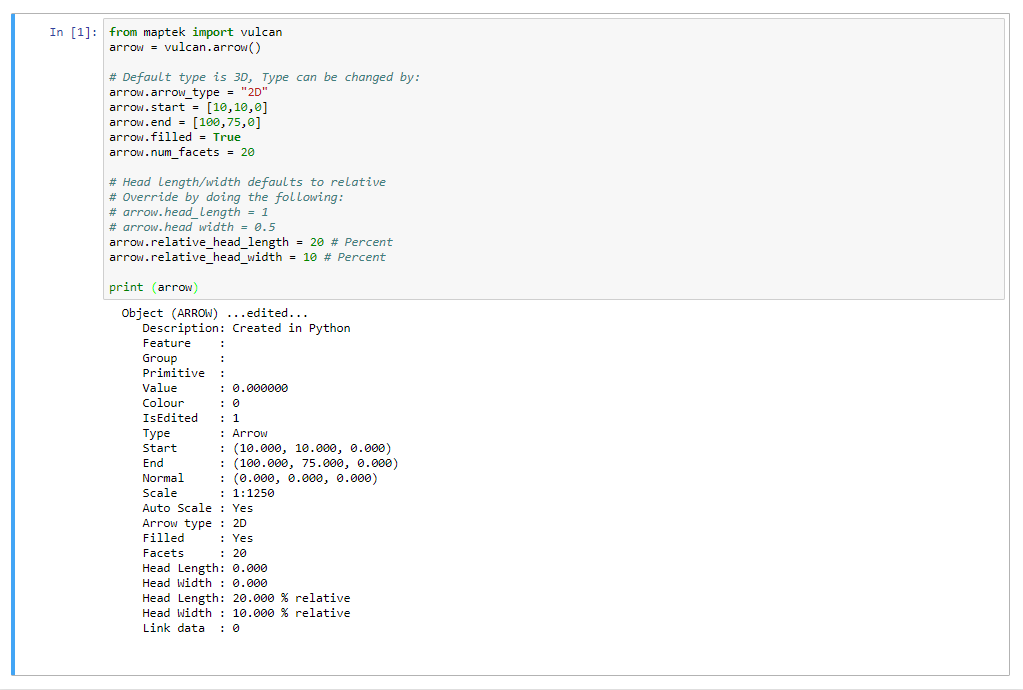
Arrow manipulation
from maptek import vulcan arrow = vulcan.arrow() # Default type is 3D, Type can be changed by: arrow.arrow_type = "2D" arrow.start = [10,10,0] arrow.end = [100,75,0] arrow.filled = True arrow.num_facets = 20 # Head length/width defaults to relative # Override by doing the following: # arrow.head_length = 1 # arrow.head width = 0.5 arrow.relative_head_length = 20 # Percent arrow.relative_head_width = 10 # Percent print (arrow)