Apply Image to Object
These instructions explain methods for applying imported images to the surface of objects using Two-point or Multi-point methods.
The import process will end with panels for applying the image to an object. There are two methods available for aligning the image onto the surface of the object:
- Two-point method
- Multi-point method
Two-point method
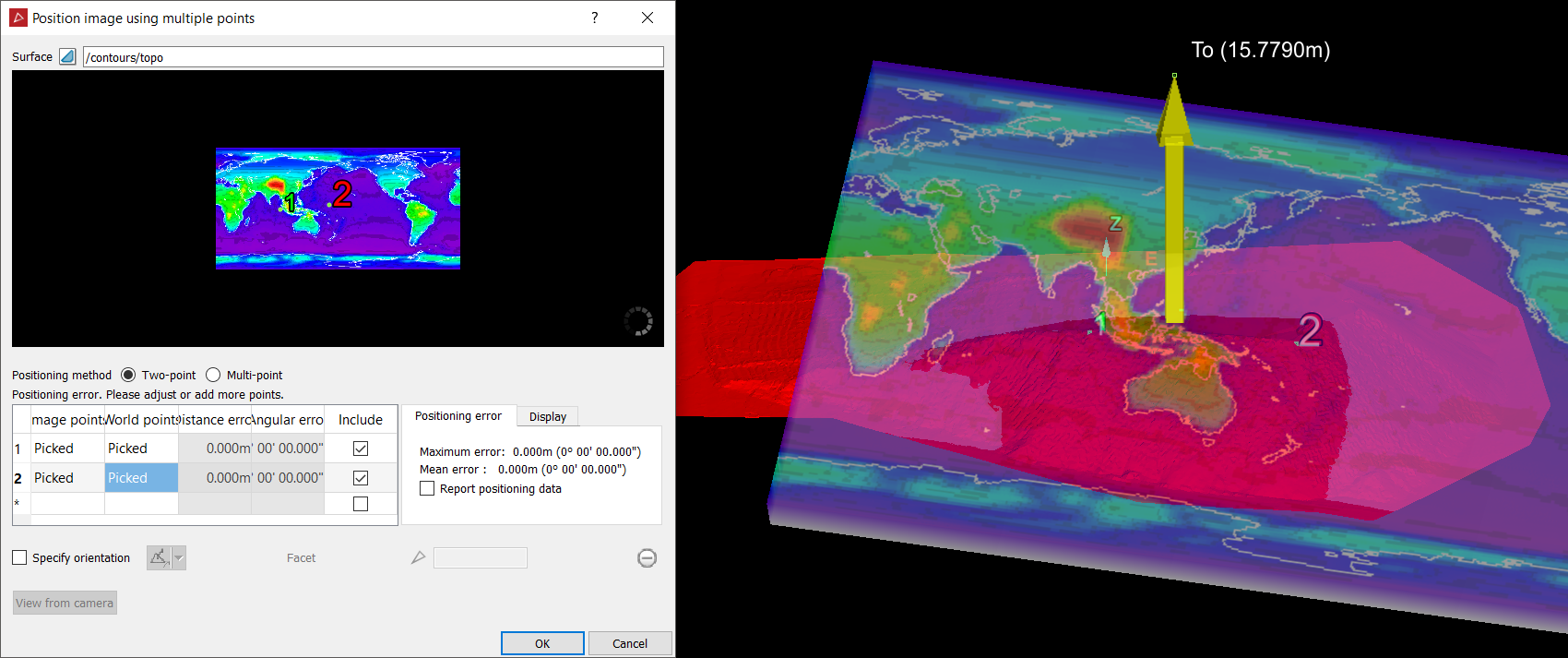
Two points positioning uses two representative point pairs on the input image and aligns them onto two points in the 3D view selected by the user. This approach maps the input image straight onto the object as if it was illuminated by a projector. There a options to assist placement and orientation of the input image during the mapping process. A coordinates table lists the corresponding image points with respect to their equivalent points on the surface in the 3D view window. These can be manually edited or automatically entered by selecting points on either the image or surface.
-
Import the image by dragging it into a blank view window.
The Import image dialog will open.
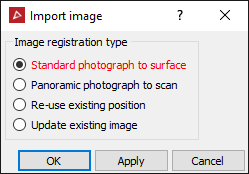
-
Select the Standard photograph to surface radio.
The Position image using multiple points panel will open.
-
Drag and drop the surface to map the image onto into the Surface field.
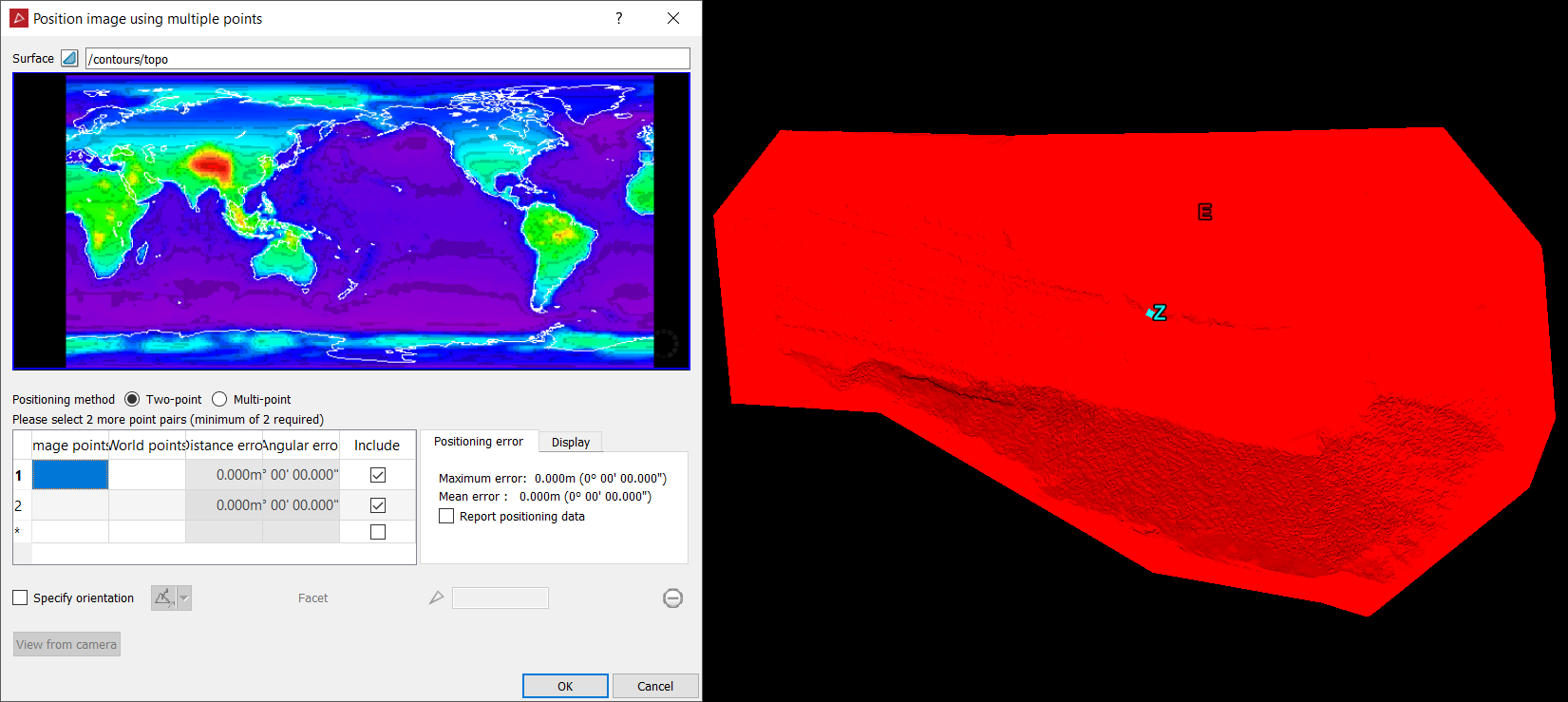
-
Select Two-point for the Positioning method.
-
Click into the first row in the Image points.
-
Click on the image where point 1 is to be positioned.
-
Click on the surface for the corresponding point 1 position.
The cursor will now jump to the point 2 field.
-
Click on the image where point 2 is to be positioned.
-
Click on the surface for the corresponding point 2 position.
A filtered version of the image will be applied to the surface.
-
Specify orientation provides other methods to apply to the mapping of the image.
The initial position of the reference points 1 and 2 will always remain fixed.
To specify the orientation use one of the following options:
-
 Two points: You can create a vector, which will swivel the image around the reference
points
Two points: You can create a vector, which will swivel the image around the reference
points -
 Facet: This will align
the mapping image with the plane of a selected facet.
Facet: This will align
the mapping image with the plane of a selected facet. -
 Axis aligned: This aligns
the mapping image with either the X,Y or Z axis.
Axis aligned: This aligns
the mapping image with either the X,Y or Z axis. -
 Bearing and inclination: This creates a vector using bearing and orientation directions,
which will result in swivelling the mapping image around the reference
points.
Bearing and inclination: This creates a vector using bearing and orientation directions,
which will result in swivelling the mapping image around the reference
points. -
 Action plane axis: The active view aligns the mapping image with either the
X or Y axis.
Action plane axis: The active view aligns the mapping image with either the
X or Y axis.
-
Click OK to complete the mapping process.
Multi-point method
Multi-points mapping applies a camera lens algorithm to the input image and attempts to undo the lens distortion, then apply the image onto a surface. You must select at least eight matching point pairs corresponding between the input image and the surface to be mapped onto. The algorithm will benefit from more points to improve accuracy. A coordinates table lists these corresponding values, which can be manually entered or points can be directly selected on the image and surface. Positioning error gives an indication of the variation between the actual points selected by the user and the estimation of points determined by the algorithm. Display options allow the user to see the difference between actual selected points and the algorithm mapping of these points, allowing for visual fine tuning of the positioning of these points.
-
Select Multi-point for the Positioning method.
-
Click into the first row in the Image points.
-
Click on the image where point 1 is to be positioned.
-
Click on the surface for the corresponding point 1 position.
The cursor will now jump to the point 2 field.
-
Click on the image where point 2 is to be positioned.
-
Click on the surface for the corresponding point 2 position.
-
Continue selecting points in the image and the corresponding points on the surface for the rest of the six point pairs.
-
Click OK to complete the mapping process.
Tip: Press the scroll wheel and move the mouse to pan around. Scroll up or down to zoom in and out in the image.
The Display options provides a visual guide to the algorithm process and allows comparison between your inputs and equivalent points determined by the algorithm.