Multiple Object Filter
Filtering Multiple Objects
Use the Multiple Object Filter option to filter duplicate objects from layers. Matching objects can be recognised using any combination of point and/or object attributes, such as point or object name, point sequence etc.
The selection of objects to compare is made in the usual way, in one layer or across a number of layers. You can also specify the action to be taken with the duplicate objects, they can be deleted or you can move all of the unique objects to a new layer.
Instructions
On the Design menu, point to Layer Edit, and then click Multiple Object Filter to display the Multiple Object Filter panel.
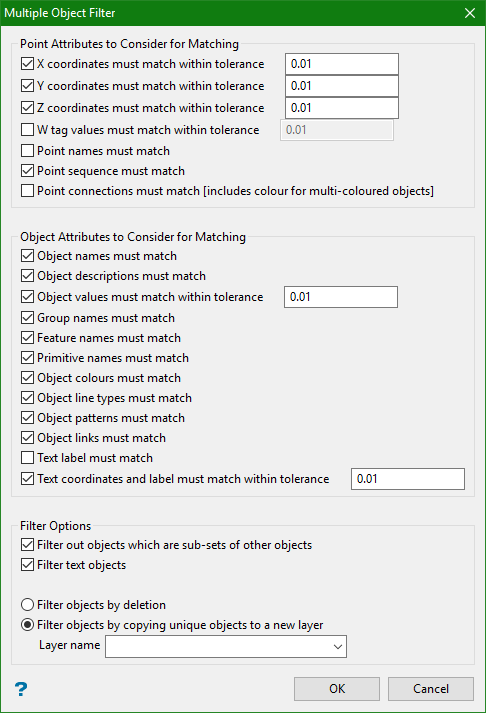
This panel allows you to specify the criteria for the duplication.
Point attributes to consider for matching
X, Y and Z coordinates and W tag values must match in tolerance:
This value will determine the maximum distance points can be apart and still be considered to be duplicates. It is possible to select only one value.
Example: You might enable the X coordinate must match check box and no other point attribute option, this will mean that points with the same coordinate (or in the X coordinate tolerance) will be considered duplicates even if the Y and Z coordinates are different. If your layer does not contain points with W tags, then this check box will be shaded, i.e. disabled.
Point names match
Select this check box if you want points with the same name to be considered duplicates.
Points sequence must match
Select this check box if you want points with the same, digitised, sequence to be considered duplicates.
Point connections must match
This option is only applicable if you have selected Point sequence must match.
Select this check box if you want the point connections to match. Point connections can be of two types a 'move to' point or a 'drawn to' point. When creating points if you move to a space and then create the point this is a 'move to' point. However, if you are in the process of creating an object (for example, a line or a polygon) and you draw a line and then create a point this is a 'drawn to' point. Generally when you are digitising points you are producing 'move to' points and when digitising objects the first point is a 'move to' point and the remainder are 'drawn to' points. To determine the type of points in your object you must use the Analyse > Detail > List option. This allows you to display an object's details.
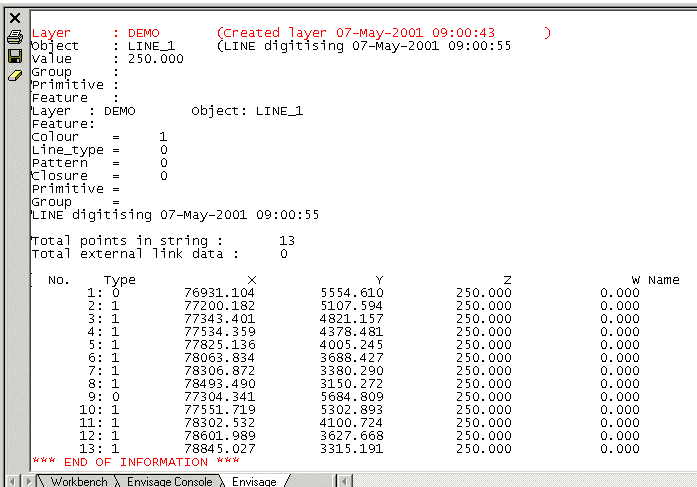
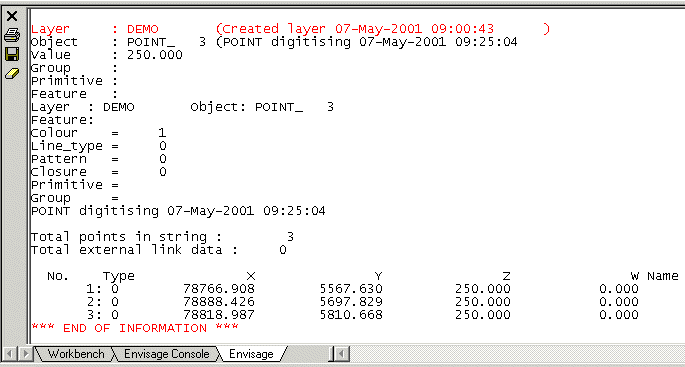
The connection information is contained in the Type column of a detail list. 'Move to' points have the value 0 and 'drawn to' points have the value '1'. For example, in the above list point 1 is 'move to' point and the remainder are 'drawn to' points.
Hence if you have selected this option, points must have the same digitised sequence and the same type of connection.
Object attributes to consider for matching
Object names must match
Select this check box if you want objects with the same name to be considered duplicates.
Object descriptions must match
Select this check box if you want objects with the same description to be considered duplicates.
Object values must match
Select this check box, and enter a value for the tolerance, if you want objects with the same value (or in the tolerance) to be considered duplicates.
Group, Feature and Primitive names must match
Select this check box if you want objects, that have the same group, feature or primitive names to be considered duplicates.
Object colours, line types or patterns must match
Select this check box if you want objects that have the same attributes to be considered duplicates.
Object links must match
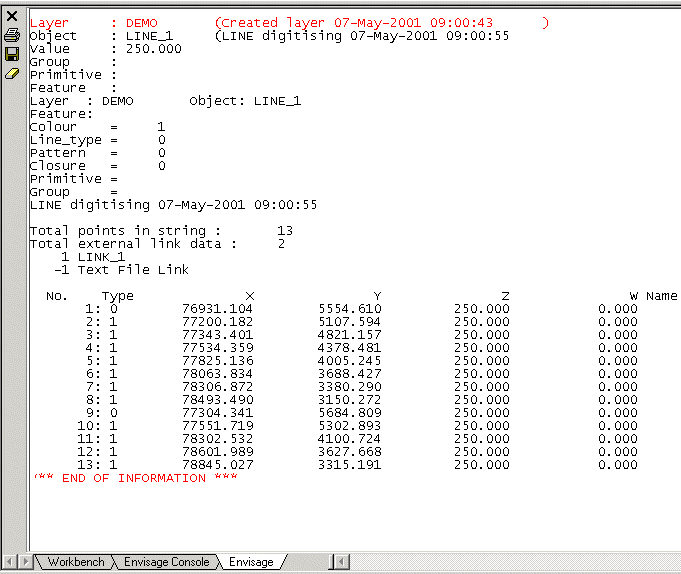
Select this check box if you want objects that have the same link data to be considered duplicates. For more information on Object Link Data refer to Analyse > Attribute Data. The Analyse > Detail > List option displays a list of the details, including the object's links.
Example: In the list above the object has no external link data, however, the object from the list below has two external links. For this object to be considered a duplicate of another the information in the external link field must match.
Filter out objects which are subsets of other objects
Select this option to filter objects that are a part of another object.
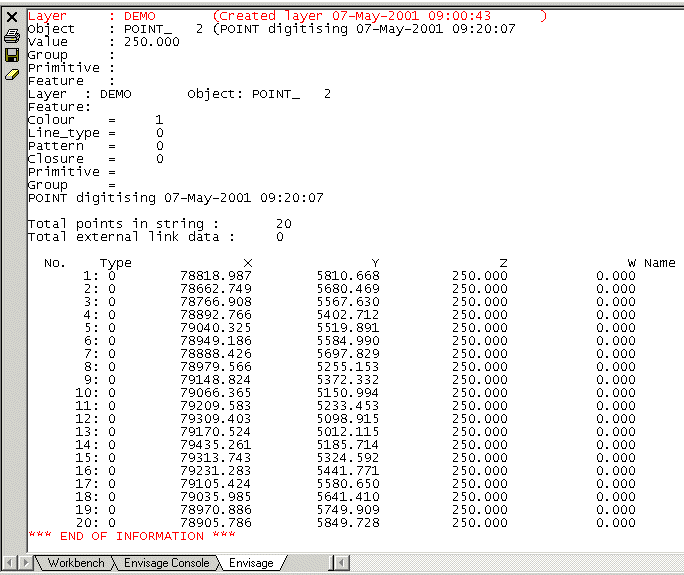
Example: From the two lists below it is clear that POINT_3 is a subset of POINT_2. Hence the object POINT_3 will be filtered out.
Filter objects by deletion
Select this option to remove the duplicate objects from the layer.
Filter objects by copying the unique objects to a new layer
Select this option to create a new layer that contains the unique objects from the current layer. The current layer will remain unchanged. Enter a name for the new layer.
Click OK.
After you have selected your method of determining if objects are duplicates you must select the data that you want to filter. That is, do you want to remove duplicate objects from an object, group, feature or layer.
From the Multiple Selection box choose what you want to have filtered.
Pick from the screen an item in your chosen filter object. For example, of you have selected object then click on the object that you want filtered. It is possible to select more than one object, feature or group. Once you have selected these items, right-click to exit the selection mode.
The Multi Filter dialog box is then displayed. You can choose to filter objects, continue selection or abort. If you choose to filter objects, the objects will be deleted or the unique objects copied to a new layer depending upon your earlier choice. A message displays on the screen informing you of the number of objects that were kept and the number of objects present originally.
Use the Save option (under the File > Layers submenu), or select the Save button from the Standard toolbar, to save the recently made changes.

