Create a DomainMCF Model
The tools for working with DomainMCF are all located on the DomainMCF ribbon tab.
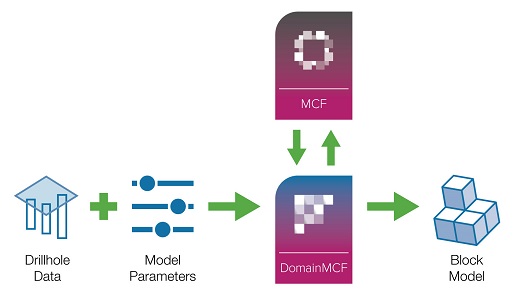
DomainMCF models are generated by bundling your input data and model parameters into processing units called Jobs. When you start a job, the data is uploaded to the Maptek Compute Framework (MCF) for processing in the cloud. The MCF uses machine learning techniques to predict domain boundaries based on the input data and generates a block model. When processing is complete, you can download and view the model in Vulcan GeologyCore.
Get started using DomainMCF modelling by following these steps:
-
Launch the DomainMCF Jobs tool.
The DomainMCF Jobs tool allows you to manage all of your DomainMCF jobs.
To launch the tool, click
 DomainMCF Jobs on the ribbon.
DomainMCF Jobs on the ribbon.The DomainMCF Jobs panel appears.
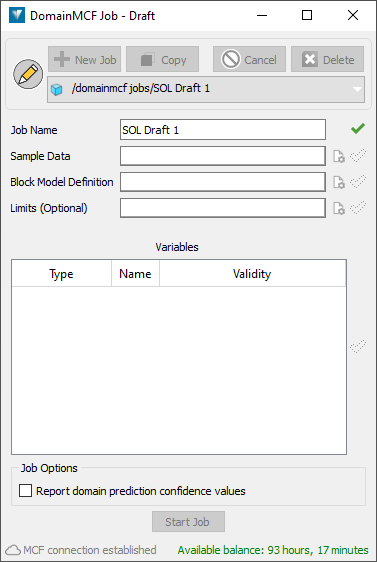
From this panel you can configure and submit new jobs, as well as view summaries of previous jobs.
-
Configure a job.
A DomainMCF job starts off as draft, which means it has not been submitted for processing yet.
The first time you open the DomainMCF Jobs panel, a new draft is created for you ready to fill out. Subsequently, if there are existing jobs in the list, you’ll need to start a new job by clicking
 New Job.
New Job.One you have a draft job, you need to supply a set of inputs. Each input has a status icon next to it, as follows:
Input incomplete 
Input complete 
Input complete with warnings 
Input invalid Configure the inputs as follows:
-
Optionally rename the job in the Job Name field.
-
Specify the sample data.
The sample data is a set of points that provide the known domain values. DomainMCF uses these known points to build a model, which is then used to estimate the domain at any given point within the block model extent.
In the Sample Data field, specify either:
-
One or more drillhole databases
 . Vulcan GeologyCore will automatically extract the sample points from the drillholes as interval midpoints. If you specify a database, all drillholes in the databases specified will be used.
. Vulcan GeologyCore will automatically extract the sample points from the drillholes as interval midpoints. If you specify a database, all drillholes in the databases specified will be used. -
A set of sample points
 .
.You can generate a set of sample points by running the
 Extract Points option on a drillhole selection. Do this if you wish to model multiple domain fields in the same model, or use grade to help predict domains.
Extract Points option on a drillhole selection. Do this if you wish to model multiple domain fields in the same model, or use grade to help predict domains.
-
Select the drillholes you’d like to extract the sample points from.

Selecting drillholes in the project explorer 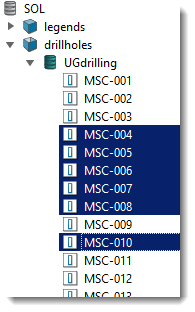
- Shift + Click defines a range
- Ctrl + Click adds/removes a single item
- Ctrl + Shift + Click adds a range
To select all drillholes in a database, click on the drillhole database
 . Hold Ctrl to select multiple databases. If multiple databases are selected, they must have the same schema.
. Hold Ctrl to select multiple databases. If multiple databases are selected, they must have the same schema.
To select a subset of drillholes, use the following controls:
-
Click on a drillhole item
 to start the subset selection.
to start the subset selection. -
Hold Shift and click on a drillhole item
 to select the range of items from the last clicked item.
to select the range of items from the last clicked item. -
Hold Ctrl and click on a drillhole item
 to add or remove that item from the selection.
to add or remove that item from the selection. -
Hold Ctrl + Shift and click on a drillhole item to add the range of items from the last clicked item to the selection.
Tip: Type into the Filter field at the top of the project explorer to display only objects matching the given string.
Selecting drillholes in the view window 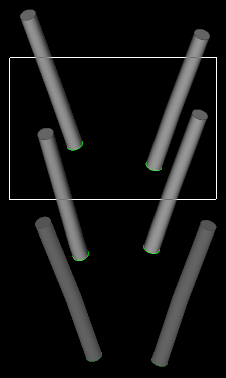
- Shift + Click adds drillholes
- Ctrl + Click removes drillholes
To select all drillholes in the view, press Ctrl + A.
To select a subset of drillholes, use the following controls:
-
In the selection toolbar located at the top of the project explorer, make sure the selection mode is set to objects
 . If selecting a region, choose Rectangle
. If selecting a region, choose Rectangle  , Polygonal Lasso
, Polygonal Lasso or Freehand
or Freehand  Selection Mode.
Selection Mode. -
Hold Shift and draw a region to add multiple drillholes within a region.
-
Hold Ctrl and draw a region to remove multiple drillholes within a region.
-
Hold Shift and click on a drillhole to add a single drillhole.
-
Hold Ctrl and click on a drillhole to remove a single drillhole.
-
On the ribbon, go to DomainMCF > Sample Points >
 Extract.
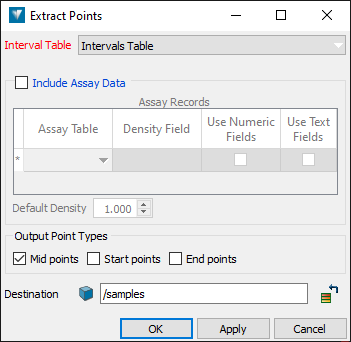
Extract.The Extract Points panel appears.
-
Choose the drillhole database table defining the intervals from the Interval Table drop-down. The table should usually be Intervals Table.
-
If you wish to model multiple domain fields, or use grade to help predict domains, select the Include Assay Data checkbox.
In the Assay Records table, select the table and field for variables you want to include.
Numeric fields will use a mass weighted average if density is supplied, otherwise the value will be weighted by length. Text fields use a majority code when intervals from the selected table do not match exactly to the sample intervals.
Note: DomainMCF requires complete records for modelling. Ensure that any additional domains or grade are fully sampled.
-
Under Output Point Types, select the point types you’d like to extract and include in the sample point set. The default and recommended point type is Mid points.
-
Optionally change the output destination container to store the sample points. The default destination is the samples container
 .
. -
Click OK or Apply to extract the points.
You can view the generated sample points by dragging them from the project explorer into a view window.

-
-
Combine multiple point sets

 .
.You can correlate and combine multiple sample points by running the option
 Correlate and Combine points. Use this option when you have multiple point sets that you wish to upload to the DomainMCF.
Correlate and Combine points. Use this option when you have multiple point sets that you wish to upload to the DomainMCF. 
-
On the ribbon, go to DomainMCF > Sample Points >
 Combine.
Combine.The Correlate and Combine Points panel appears.
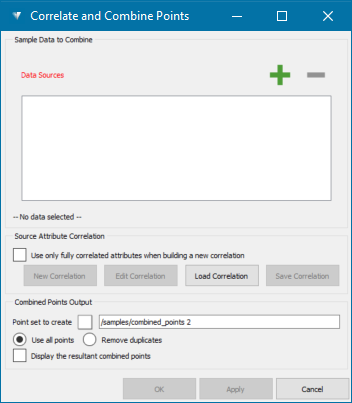
-
Add sample data sources from which the combined point set is to be created.
To add samples, select the data sets from the samples container
 in the project explorer and drag it on to the Data Sources area, or click on
in the project explorer and drag it on to the Data Sources area, or click on  Add button on the panel. Use Ctrl + Click to select multiple samples.
Add button on the panel. Use Ctrl + Click to select multiple samples.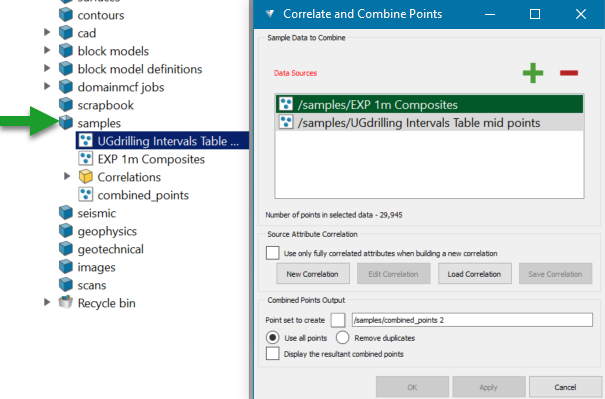
Important! At least two data sources must be selected. The order of the selection is important because the data source sitting at the top of the selection (first data source coloured in green) will define the structure of the resultant point set. The attributes of the first data source will define the initial list of attributes to be added to the combined point set. The list may be changed and/or added to, but it is better to use the data set with the most number of attributes as the first data source.
-
Set up a new correlation to link the fields between the point sets. You can create a new correlation or load an existing correlation. Optionally, you can select the option Use only fully correlated attributes when building a new correlation to use only those attributes for which there is a representative in each source.
-
New Correlation - Use this option to create a new correlation for the selected sample data sets.
-
Edit Correlation - Use this option to edit the current correlation for the selected sample data sets.
-
Load Correlation - Use this option to load an existing correlation which matches, or can be made to match, the selected sample data sets.
-
Save Correlation - Use this option to save the current correlation for future use.
Note: Any fields that have different names can be manually matched up. However, validity warnings will be displayed if data types (eg. text and integer) are found for the data sources.
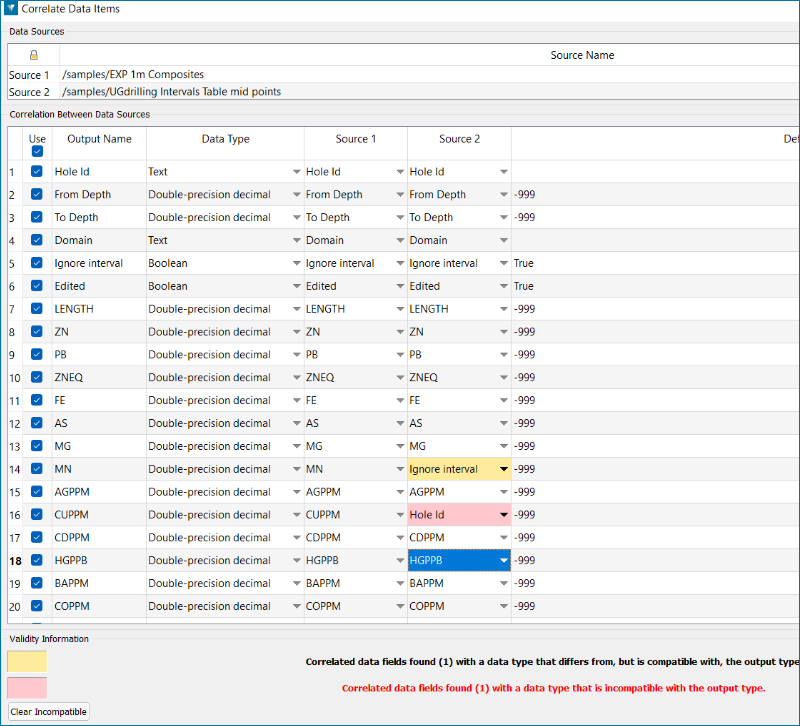
- Yellow warning indicates differing but compatible data types (eg. a numeric can be saved into a text field)
- Red warning indicates a data incompatibility (eg. trying to save text into a numeric field)
ddd -
-
Under Combined Points Output, set the name of the resultant point set to be created in the Point set to create field. The default naming convention is /samples/combined_points, where samples is the output destination container to store the combined sample point.
-
Choose whether or not to remove duplicate points from the resultant point set.
Use all points - Select this option to use all points in the resultant point set irrespective of whether the points are duplicated or not.
Remove duplicates - Select this option to remove the duplicated points in the resultant point set.
-
Click OK or Apply to generate the resultant point file that can be uploaded to the DomainMCF.
-
-
-
Specify a block model definition.
A block model definition contains the physical configuration of the desired block model, including its origin, extent, orientation and block size constraints, as well as the names of the variables you want to model.
You can either supply an existing block model definition, or let Vulcan GeologyCore generate one for you based on your sample data.
-
To use an existing block model definition
 , drag it from the project explorer into the Block Model Definition field. Block model definitions are stored in the block model definitions container
, drag it from the project explorer into the Block Model Definition field. Block model definitions are stored in the block model definitions container  by default. To import a block model definition from a Vulcan block model definition file (*.bdf), go to Home > Data >
by default. To import a block model definition from a Vulcan block model definition file (*.bdf), go to Home > Data >  Import.
Import. -
To generate a block model definition from your sample data, simply click
 to the right of the Block Model Definition field. The generated block model definition will be created in the block model definitions container
to the right of the Block Model Definition field. The generated block model definition will be created in the block model definitions container  , named after the job name, and suffixed with “BDF”.
, named after the job name, and suffixed with “BDF”.
Note: DomainMCF accepts regular block models (having all blocks the same size), and sub-blocked block models with a parent to sub-block ratio of ½, ¼, ⅛ or 1/16. Imported block model definitions will be rounded to the nearest size compatible with DomainMCF.Whether you supply an existing definition or generate one, you can inspect and modify the parameters by clicking
 to the right of the Block Model Definition field.
to the right of the Block Model Definition field. Expand for detailed instructions on how to modify the block model definition.
Expand for detailed instructions on how to modify the block model definition.
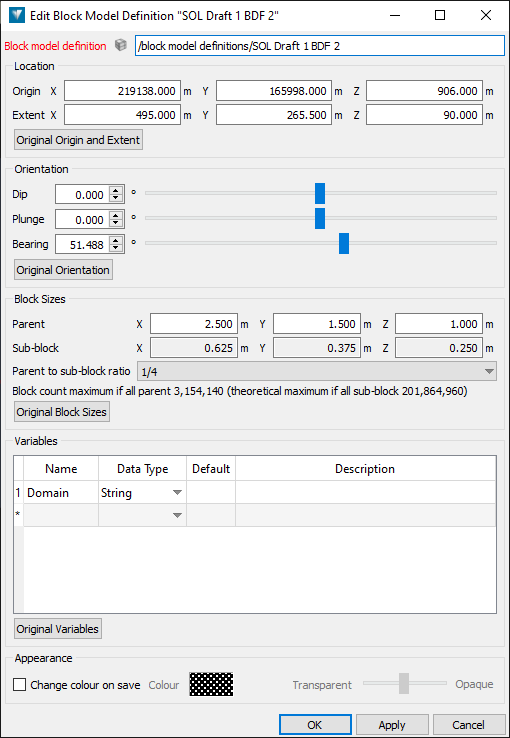
You can change the block model parameters as follows:
-
Under Location, define the location of the block model in space, in terms of the following:
-
Origin X, Y, Z—the reference location from which the extent of the block model is defined.
-
Extent X, Y, Z—the volume of space limiting the size of the block model.
Click Original Origin and Extent to reset the fields to their initial value.
-
-
Under Orientation, define the angular measurements expressing the orientation of the block model in space, in terms of Dip, Plunge and Bearing.
Click Original Orientation to reset the fields to their initial value.
-
Under Block Sizes, configure constraints on the size of individual blocks within the resulting model. The extent must be an exact multiple of the block size.
-
Parent X, Y, Z—the maximum size of a parent block in each dimension.
-
Sub-block X, Y, Z—the minimum size of a sub-block in each dimension. Configure the sub-block size by setting the Parent to sub-block ratio. Choose from the following values: ½, ¼, ⅛, 1/16 or Make all blocks the same size.
Click Original Block Sizes to reset the fields to their initial value.
-
-
Under Variables, specify the variables to be modelled. At a minimum, you will want to specify Domain as a variable to model.
Click Original Variables to reset the variable list to the initial list.
-
Under Appearance, select the Change colour on save checkbox to apply a specific colour and translucency to the block model definition object. This affects the visualisation of the object when viewed in a view window.
-
Click OK or Apply to update the block model definition.
-
-
Optionally specify limits to constrain the size and shape of the realised block model.
Drag and drop into the Limits (Optional) field either:
-
Two surfaces
 , representing top and bottom topographic surfaces.
, representing top and bottom topographic surfaces.Vulcan GeologyCore will automatically detect which surface is the top and which is the bottom surface—but you can also edit this classification manually by clicking
 to the right of the field. The realised block model will be confined to the region between the two surfaces.
to the right of the field. The realised block model will be confined to the region between the two surfaces. -
A single solid
 . The realised block model will be confined to the region inside the solid.
. The realised block model will be confined to the region inside the solid.Specifying a convex hull is a good way of limiting the generated model to the volume covered by the sample data.
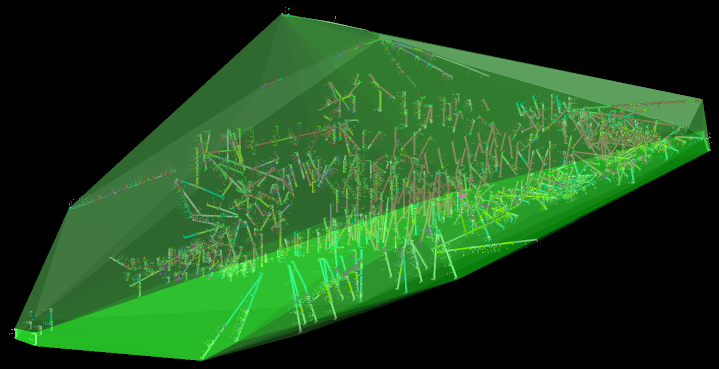
 Expand for detailed steps on how to generate a convex hull.
Expand for detailed steps on how to generate a convex hull.
-
Select your sample data. This could be sample points, drillholes, or any other data type.
-
On the ribbon, select DomainMCF > DomainMCF Modelling >
 Hull.
Hull.
The Hull panel appears.
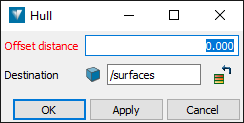
-
In the Offset distance field, optionally enter a positive distance to offset the hull from the data.
-
Click OK or Apply.
The convex hull is generated as a surface
 in the specified destination folder
in the specified destination folder  (/surfaces by default).
(/surfaces by default).
-
-
Once all the inputs are valid
 , the Start Job button becomes enabled, meaning you can submit the job for processing.
, the Start Job button becomes enabled, meaning you can submit the job for processing.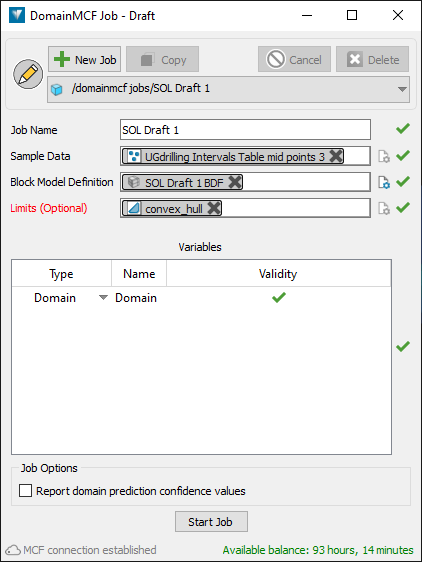
-
-
Run the job.
-
To submit your job for processing, click Start Job.
A panel appears asking you to confirm the job.
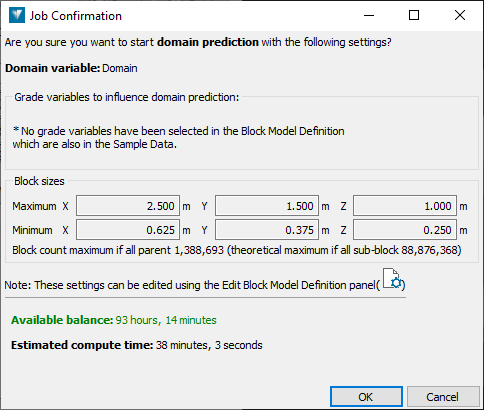
Note the Available balance of processing time you have left, and the Estimated compute time for the job.
-
Click OK to proceed.
Your job begins uploading to the MCF server for processing, and the DomainMCF Job tool displays a summary of the job details.
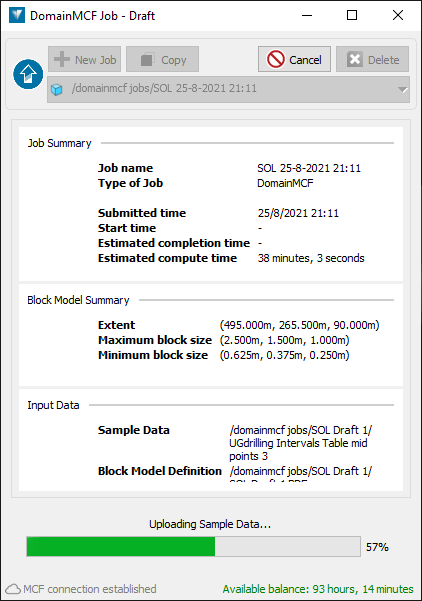
-
-
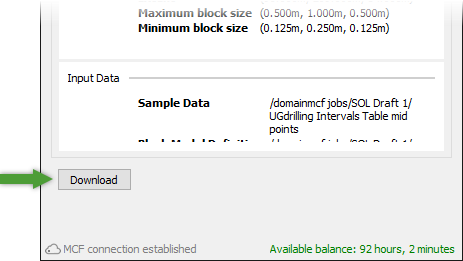
Download and view the result.
When processing is complete, click Download to download the resulting block model, which will be stored in the block models container
 .
.
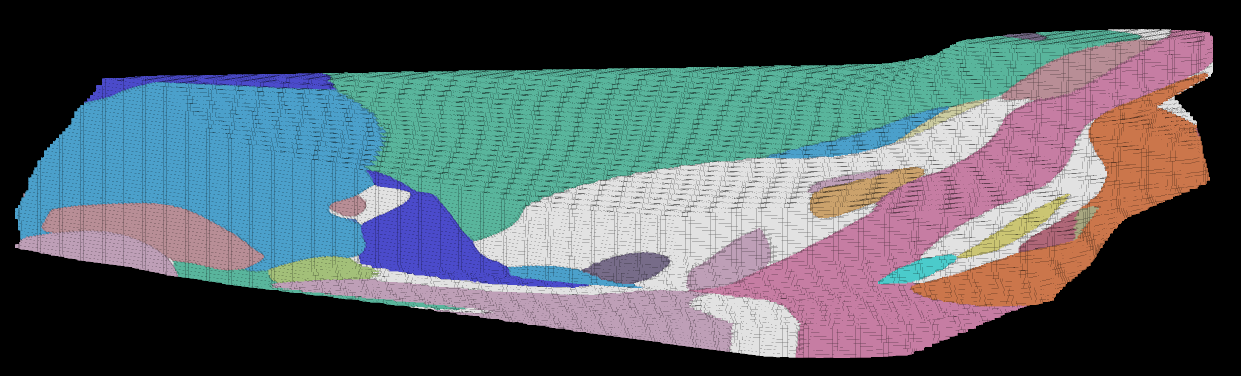
After downloading, click View Block Model to load the block model into a new view window.
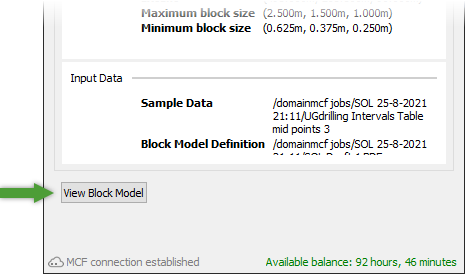
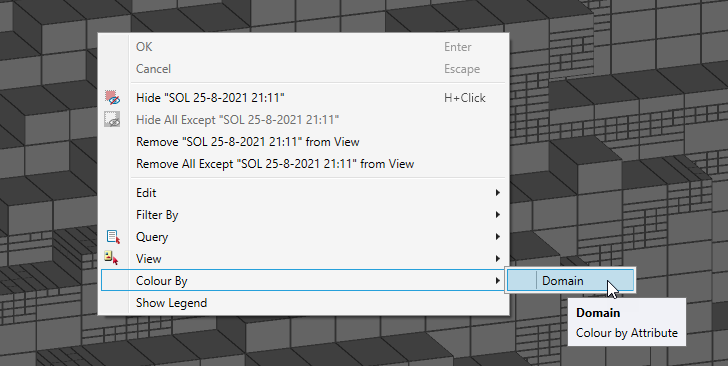
To colour the block model, right-click on it in the view, and in the context menu select Colour By > Domain.
|
Step 5: Validate the Model
|