Structural Data
Structural data can be loaded into Vulcan GeologyCore from a variety of sources:
-
Extracted from a drillhole database
-
Imported from a Vulcan geotechnical database
-
Imported from CSV files
-
Manually entered on screen
-
Extracting structural data from a drillhole database.
-
Vulcan Isis drillhole databases (*.isis)
-
Vulcan ODBC link drillhole databases (*.dsf)
-
Comma-separated values (CSV) files (*.csv)
-
Import from a Vulcan geotechnical database.
Structures may be imported into Vulcan GeologyCore directly from a Vulcan Geotechnical database.
Use the Home > Data > Project option to browse for a geotechnical database.
-
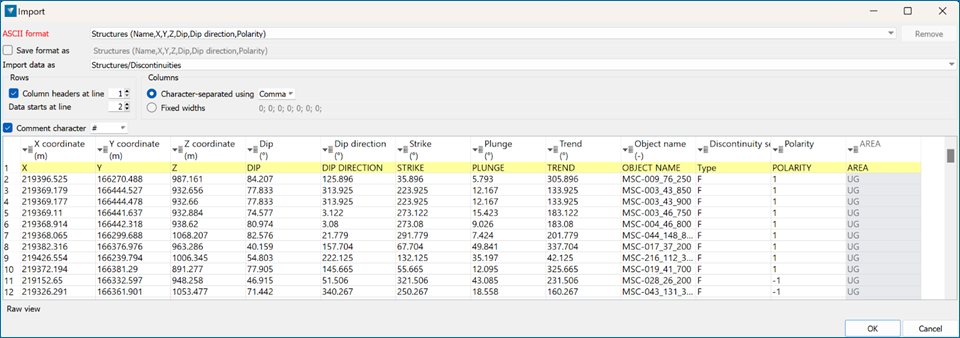
Import from CSV files containing coordinate and structural orientation information.
Use Home > Data > Import option or drag and drop the file onto the screen to import as ASCII.
Choose to import data as Structures/Discontinuities and match the columns.
Note: To organise the dataset by structural type, set the Type field to Discontinuity Set.
-
Manually entered on screen.
Oriented Structure
Use the Oriented Structures option on the Modelling ribbon to manually create a structure.
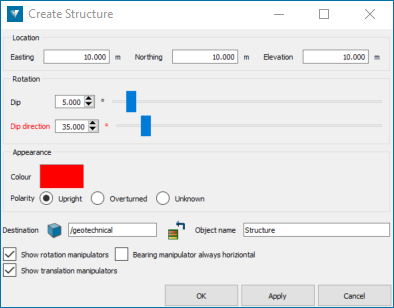
Adjust the orientation of the structure by either:
-
Specifying the structure location (Easting, Northing, Elevation)
-
Entering the Dip value or adjusting the sliders (Measured dip angle: 0°-90°)
-
Entering the Dip direction value or adjusting the sliders (Bearing or Azimuth of the dip: 0°-360°)
-
Adjusting the onscreen dynamic controls (rotation and translation manipulators)
Polarity
The polarity of the structure will be used to define the top and bottom in surface generation. Use the Edit Polarity option to adjust the polarity.
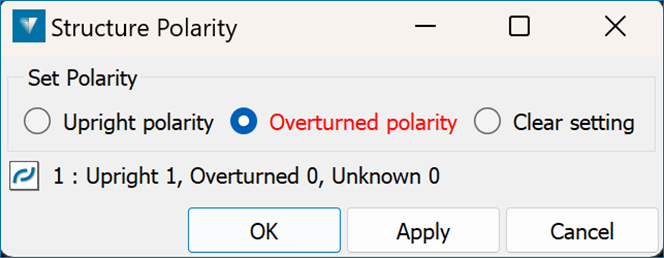
Before adjusting the polarity:

After adjusting the polarity:

-
Structural data, for use in geological modelling, can be extracted from drillhole databases that contain Alpha and Beta measurements and/or Dip and Dip direction.
1.1 Import drilling database into Vulcan GeologyCore
Drillholes are the main data source for generating geological models. You can load drillhole information into Vulcan GeologyCore from a variety of sources, including:
See Import Drilling Database into Vulcan GeologyCore.
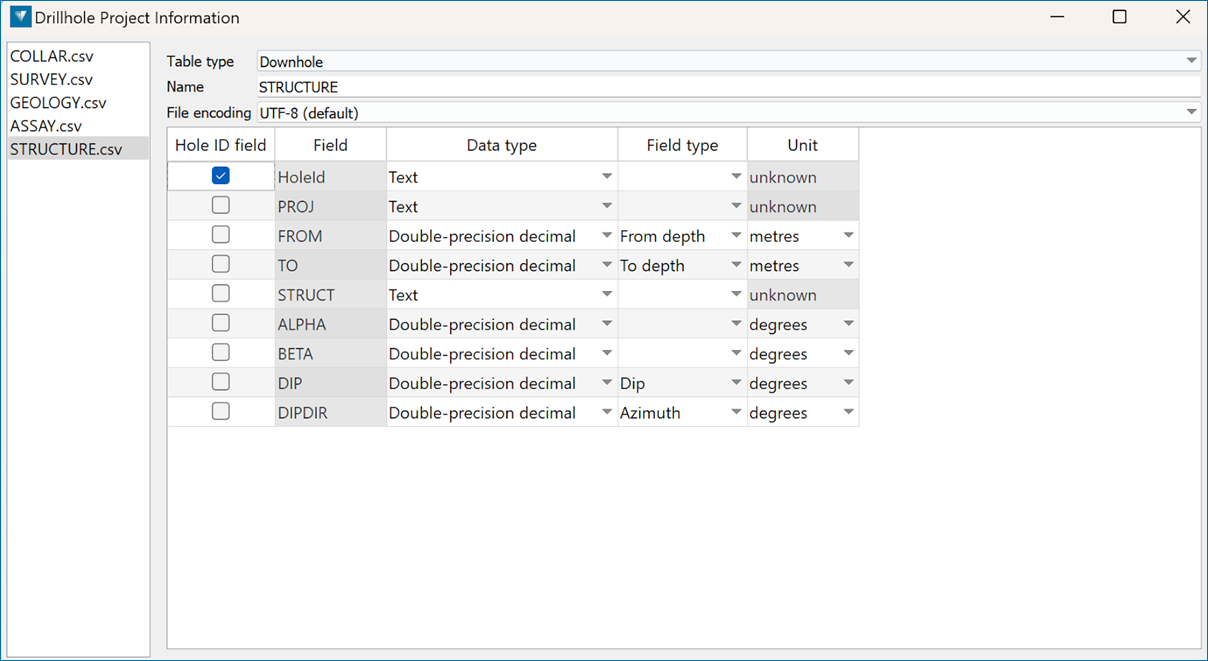
Note: Make sure that alpha, beta, dip, and dip direction have their data type set as single or double precision and a valid angle unit applied.
1.2 Extract structural data from drilling database
Converting and editing structural data is controlled from the Modelling ribbon.

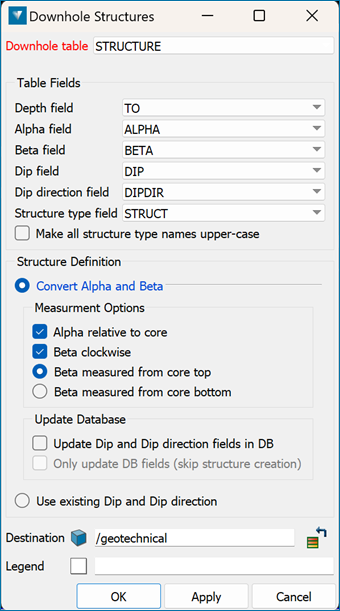
Use the Downhole Structures option to convert the orientation measurements from the drilling database to structures.
1.3 Select the drillhole database containing the structures as well as the structural table and fields
Select to either convert alpha and beta measurements to dip/dip direction or to use existing dip/dip direction measurements from the database.
Structures will be extracted to the geotechnical container, organised by drillhole database name and structure type. Structures are displayed as 3D oriented discs.
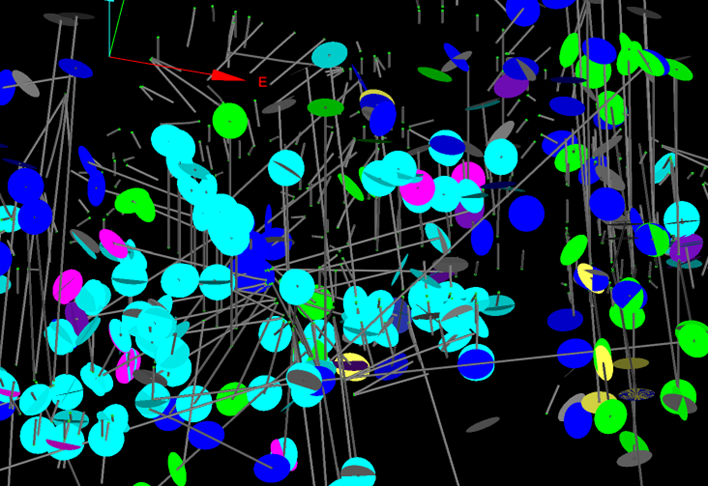
Table Fields
A structural file contains six columns representing STRUCT , DEPTH , ALPHA , BETA , DIP, and DIPDIR values. DIP and DIPDIR columns need to exist in the structural file, but they should not contain any values. This option will calculate the true dip and dip direction of the logged structures from the value in the ALPHA and BETA columns.
Convert alpha and beta
Select this option to convert the alpha and beta angles. If this option is not selected, then the measured alpha and beta angles will be used to calculate the dip and dip-direction of the structure.
Alpha relative to core
Alpha angles are always less than or equal to 90.
Select the Alpha relative to core check box if you want the alpha value to be the angle between the core axis and the structure. If the Alpha relative to core option is checked, the alpha angle is measured between the core axis and the structure. Therefore, for vertical core, the alpha for a horizontal structure would be 90 and the alpha for a vertical structure would be 0. If the Alpha angle is measured relative to the core axis, the angle would be complementary to the apparent dip angle of the structure in the core.
Leave the Alpha relative to coreoption unchecked, and the alpha angle will be measured between a plane 90 from the core and the structure. Therefore, for vertical core, the alpha for a horizontal structure would be 0 and the alpha for a vertical structure would be 90.
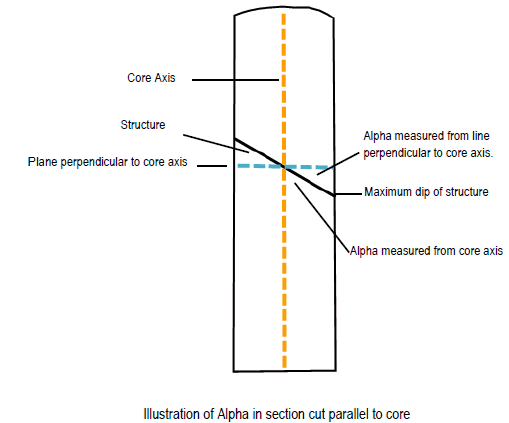
Fig. Alpha angle explained
Beta clockwise
Check the Beta clockwise check box to treat the beta angles as being clockwise from the core axis. It is recommended to check the Beta clockwise check box if the beta value corresponds to the angle between the reference line and the bottom of the structure. This is measured in a clockwise direction when looking along the core in the direction of drilling, from a reference line on the top of the hole/core.
Therefore, for a vertical hole, a beta value of 0 indicates a dip direction of 0°, while a beta value of 90 indicates a dip direction value of 90°. If the Beta clockwise check box is not checked, then the beta angles will be measured in an anticlockwise direction.
Note: The Beta clockwise and Alpha relative to core check boxes can only be used when converting alpha and beta angles.
Beta measured from core top and Beta measured from core bottom
These options allow you to specify whether the reference line for Beta angles is at the top or bottom of the core. Select the Beta measure from core top option to confirm you want to have the measurement begin at the core top. If a measurement from the bottom of the core is preferred, select the Beta measured from core bottom option.
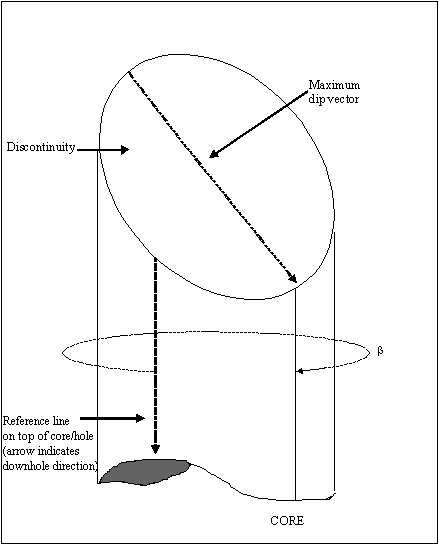
Fig. Beta/Sectional View
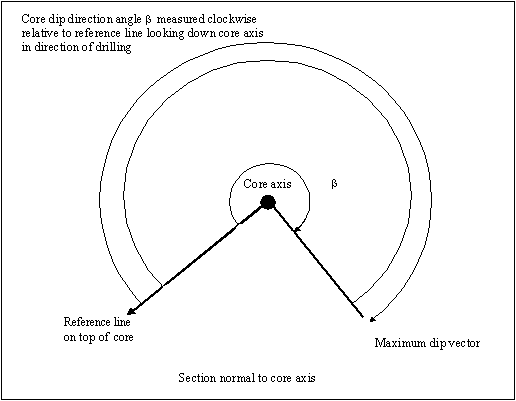
Fig. Beta/Plan View
If an existing legend is not supplied, colours will automatically be assigned for the structural types found in the database.