Data Types
The mapteksdk.data package provides an API that you can use to interact with the objects in the connected application. An object in a project may be a spatial object representing some entity in three dimensional space, such as a line or surface, or it may be something more abstract, such as a colour map.
Primitive types
Spatial objects are composed of lower order structures called primitives. The fundamental primitive is the point. A point is a location in space defined by Cartesian coordinates indicating the distance from the origin along the X, Y and Z axes. All other primitives are based on points. The following table lists the five primitive types:
| Primitive | Definition | Visual representation | See also |
|---|---|---|---|
| Point | A single location in space. |

|
Main topic: Points |
| Edge | A line segment between two points. |
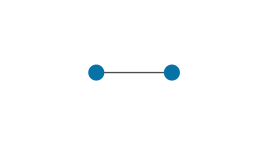
|
Main topic: Edges |
| Facet | A triangle defined by three points. The line segments between each pair of points are also edges. |
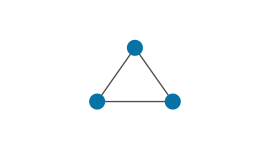
|
Main topic: Facets |
| Cell | A quadrilateral defined by four points. |
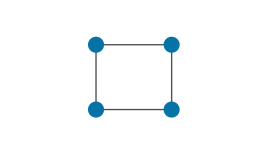
|
Main topic: Cells |
| Block | A cuboid defined by a centroid and a size in each dimension. |
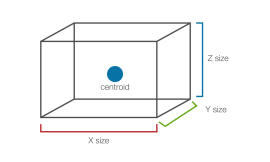
|
Main topic: Blocks |
Spatial object types
Spatial object types can be classified based on the primitive type functioning as the basic “building block” for that type. The following table summarises the main spatial object types that can be accessed via the Python SDK.
| Class | Primitive | Definition | Visual example | See also |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PointSet | Point | Representation of a “point cloud” — an arbitrary set of points in space, with no topological links between points. |
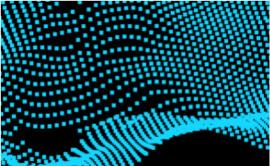
|
Main topic: PointSet Class reference: PointSet |
| Polyline | Edge | A sequence of edges defined by a sequence of points forming an open chain. |
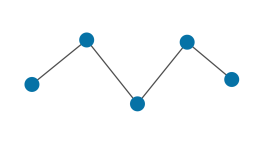
|
Main topic: Polyline Class reference: Polyline |
| Polygon | Edge | A sequence of edges defined by a sequence of points forming a closed chain. |
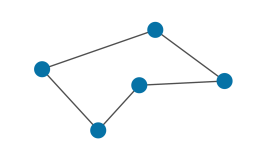
|
Main topic: Polygon Class reference: Polygon |
| EdgeNetwork | Edge | An arbitrary collection of potentially disjoint edges, which may include polylines and/or polygons. An edge network is defined by a set of points and a set of edges connecting points. |
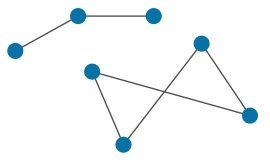
|
Main topic: EdgeNetwork Class reference: EdgeNetwork |
| Surface | Facet | A set of facets typically used to represent a objects with a surface area. Surfaces are also called triangulations, since they are made up of triangular facets. |
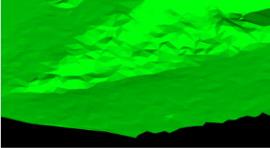
|
Main topic: Surface Class reference: Surface |
| GridSurface | Cell | An alternative to Surface for representing objects with a surface area using a grid of cells rather than facets. |
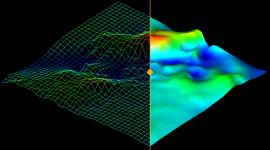
|
Main topic: GridSurface Class reference: GridSurface |
| Scan | Cell | Similar to a point set, but specialised to store point cloud data acquired from a laser scanner. Although visualised as a point cloud, scans store each point internally using spherical coordinates relative to the acquisition origin rather than Cartesian coordinates. |
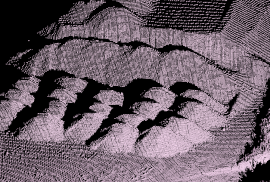
|
Main topic: Scan Class reference: Scan |
| DenseBlockModel | Block | A block model constructed from a three dimensional grid of rectangular prism blocks all of which are the same size and shape. A DenseBlockModel’s extents are always completely filled with blocks. |
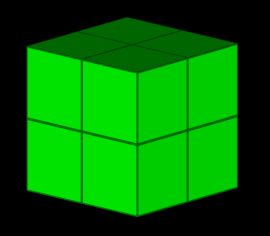
|
Main topic: DenseBlockModel Class reference: DenseBlockModel |
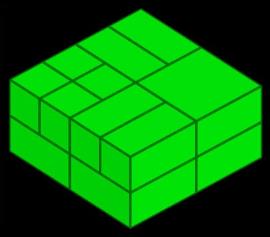
| SubblockedBlockModel | Block | A dense block model that allows blocks to contain smaller blocks, known as subblocks. |
|
Main topic: SubblockedBlockModel Class reference: SubblockedBlockModel |
| Text2D | Point (single) | A two-dimensional object containing custom text. As the text is two dimensional, it will never appear upside down or back to front regardless of the angle it is viewed from. |

|
Main topic: Text2D Class reference: Text2D |
| Text3D | Point (single) | A three-dimensional object containing custom text. This text can appear upside down or back to front depending on the angle from which it is viewed. The size of the text is based on the real-world size, so size is measured in metres |

|
Main topic: Text3D Class reference: Text3D |
| Marker | Point (single) | A three dimensional object that can be used to mark locations. You can give markers a shape from a list of predefined shapes or can use a Surface object to define their shape. |

|
Main topic: Marker Class reference: Marker |
| Drillhole | Point (single) | A representation of a drillhole. A drillhole’s spatial representation is defined in terms of its collar location. Multiple drillholes are collected together in a drillhole database. |

|
Main topic: Drillholes Class reference: Class reference: Drillhole |
Non-spatial object types
Colour maps are non-spatial objects in that they do not have any geometry associated with them. The two kinds of colour maps are described in the table below.
| Class | Definition | Visual example | See also |
|---|---|---|---|
| NumericColourMap | An object that assigns numbers to colours. These maps can be used to colour objects via user-defined properties which are defined on each primitive in an object. |

|
Main topic: Colour Maps Class reference: NumericColourMap |
| StringColourMap | An object that assigns strings to colours. These maps can be used to colour objects via user-defined properties which are defined for each primitive in an object. |

|
Main topic: Colour Maps Class reference: StringColourMap |
