Advanced Statistics
Data Elements
Use the Advanced Statistics option to generate statistics and graphs. The graphs can be displayed in Vulcan as well as generated directly in Microsoft Excel.
Instructions
On the Analyse menu, point to Statistics, and then click Advanced Statistics to display the following panel.
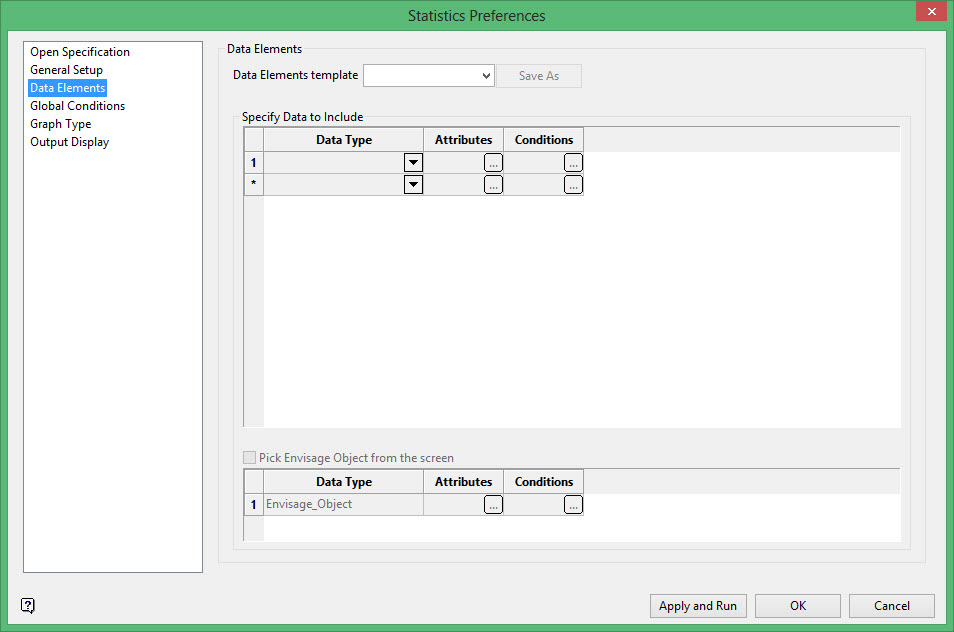
Data Elements template
Enter the name of the template to save to. The current state of the Data Elements section (all data types, attributes and conditions) can be saved to a template. Select the Save As button to save the template.
Specify Data to Include
Data Type
Use the Data Type drop-down list to s elect the data type that you want to calculate statistics on, for example samples database, drillhole database, etc.
Attributes
Click ![]() to edit the attributes for the chosen data type. Once selected, the Data Attributes panel displays. The options displayed through the Data Attributes panel will depend upon the selected data type.
to edit the attributes for the chosen data type. Once selected, the Data Attributes panel displays. The options displayed through the Data Attributes panel will depend upon the selected data type.
Select from the following data types to display the accompanying Data Attributes panel:
-
Samples Database
-
Drillhole Database
-
Map File
-
Block Model
-
Grid Model
Conditions
Click ![]() to edit the conditions for the chosen data type. Once selected, the Data Conditions panel displays.
to edit the conditions for the chosen data type. Once selected, the Data Conditions panel displays.
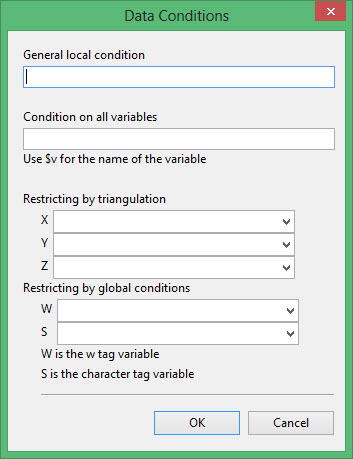
General local condition
This condition is used to limit whole records or blocks in a single database. In the example below, the condition AU1 gt AU5 will select records 2 and 4. A condition of AU1 gt 0 and AU5 gt 0 will select record 2 only.
|
Record Number |
AU1 |
AU5 |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
0.0 |
0.1 |
|
2 |
0.2 |
0.1 |
|
3 |
0.0 |
0.3 |
|
4 |
0.3 |
0.0 |
Condition on all variables
This condition is used to limit certain values of variables. In databases or block models for example, missing values are often indicated with a value of -1 or -99.
In block models, a missing value may occur because there are not enough nearby samples for grade estimation to produce an estimate in a particular block. In databases, a missing value may occur because an interval was not assayed. You want to exclude these values from the statistics as they are outliers and will significantly affect the statistics.
The condition uses the symbol $v to represent all selected data variable names. For example, if the selected data variables are AU and AG and the condition is $v gt 0, then all AU and AG values greater than 0 (zero) will be selected. If the condition is $v ne -1, then all AU and AG values that are '-1' will be ignored ('-1' is generally used for databases, '-99' for block models).
The condition must be true for a value to be selected. Values for which the condition is false are considered missing or invalid. If the variable condition is left blank, then it is considered to be true and all values are considered to be valid.
In the following example, '-1' indicates missing data. A variable condition of $v NE -1 would result in records 1, 2, 4 and 5 being selected in a calculation of the average AU, and records 1, 3, 4 and 5 in the calculation of the average FE. For the generation of scatter plots, however, records 2 and 3 will be ignored because they contain a missing value. This means that only (0.5, 0.2), (0.7, 0.2) and (0.3, 0.3) will be plotted.
|
Record Number |
AU |
FE |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
0.5 |
0.2 |
|
2 |
0.4 |
-1 |
|
3 |
-1 |
0.1 |
|
4 |
0.7 |
0.2 |
|
5 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
Restricting by triangulation
The following drop-down lists allow you to use a triangulation to limit the dataset. Only those samples that fall in the specified triangulation will be used in the analysis. Select from the drop-down list the X, Y and Z coordinate field for each dataset.
Note: For composite databases, specify the mid point coordinates of the samples. For block models specify the centroid coordinates of the blocks to be used.
Restricting by global conditions
Enter, or select from the drop-down list, the W tag and S tag variables to be used as a condition for multiple databases. The W tag is any variable that has a numeric value and the S tag is any variable that has a character value.
Example: A condition of $w eq 2 will select values of 2 for a specified W tag variable.
Related topics

