Quick Start
This quick start guide will orient you to the basics of GeoSpatial Manager, including concepts, basic manipulation of the as-built model, and several key tools.
Overview
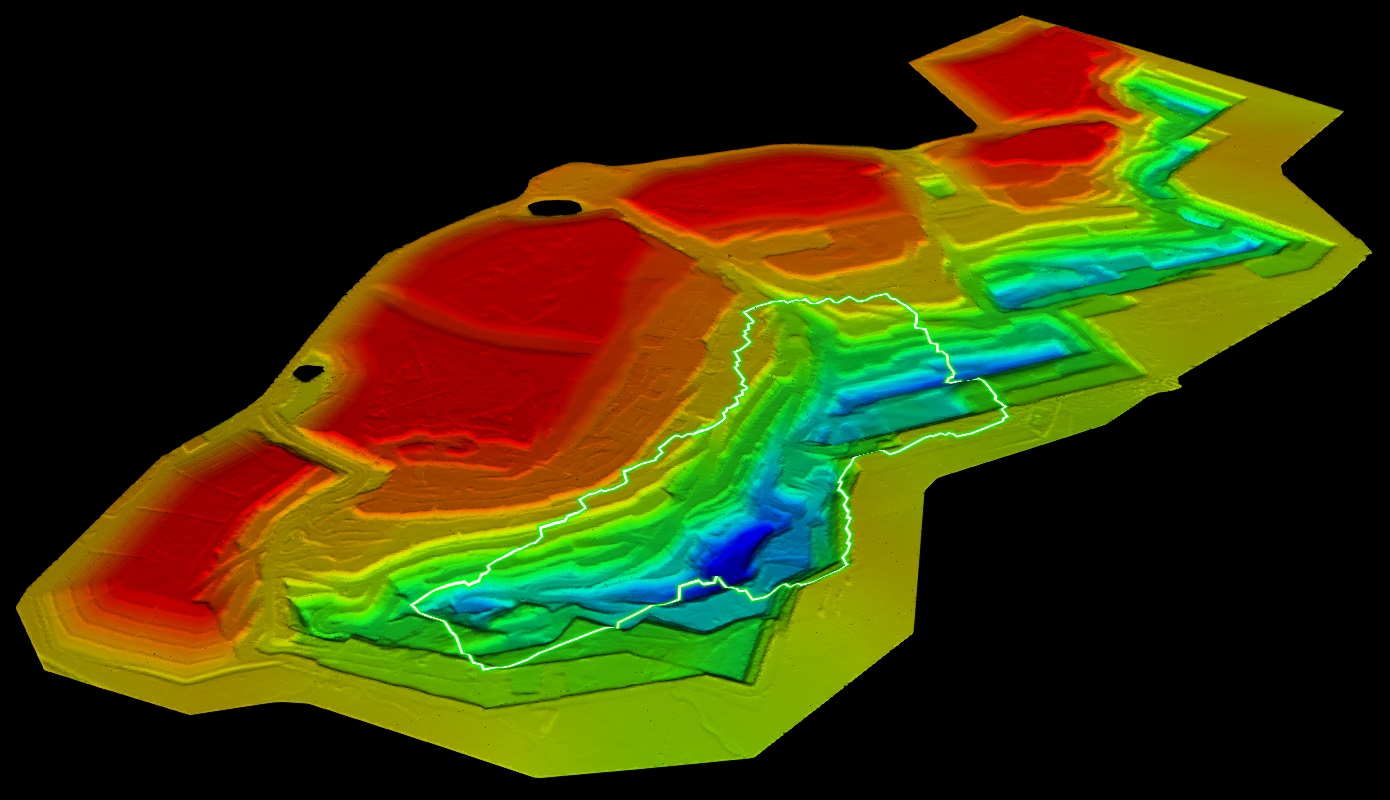
GeoSpatial Manager is the single source of truth for your digital as-built surface model. Users with upload permissions (typically surveyors) upload regular updates in the form of as-built surfaces that might cover only a portion of the site. GeoSpatial Manager incorporates each of these partial source surfaces into a single overall model. The model keeps track of the acquisition date and time of each source surface so that users can view the overall as-built surface for any given point in time between the initial and most recent surface uploads. All users see and query the same model. Each source surface remains identifiable and retrievable for download. Source surfaces can also be deleted so that they no longer contribute to the as-built model. GeoSpatial Manager automatically and dynamically updates the as-built model in response to uploads and deletions so that the model always represents the best available information.
|
|
|
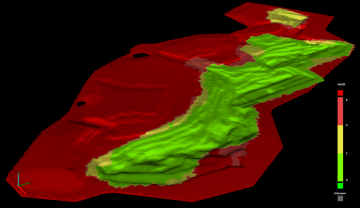
Example of an as-built model viewed in GeoSpatial Manager. The model is composed of many source surfaces, one of which is highlighted. |
User interface
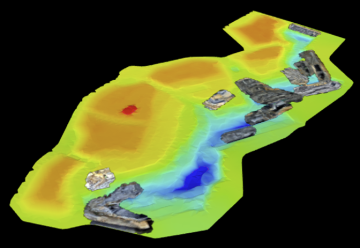
The image below shows the main user interface elements of the GeoSpatial Manager ![]() Home page.
Home page.
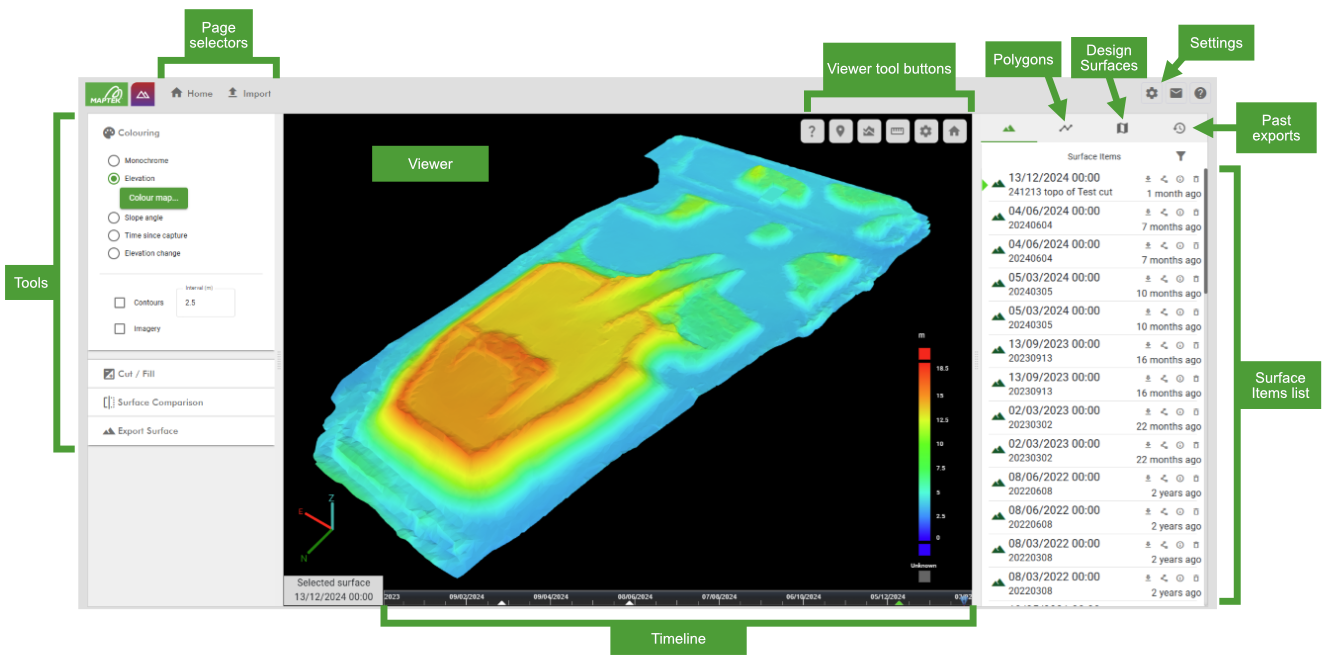
| Page selectors | Switch between the |
| Viewer | View and interact with the as-built model in 3D. See Panning, zooming, and rotating on this page for the main manipulation controls. |
| Viewer tool buttons | Access tools for controlling the view and performing simple surface queries. |
| Timeline | Use the timeline to set the selected surface, or define time ranges for tools that require it. See Selecting a surface in the timeline on this page for more information on using the timeline. |
| Tools |
Change the surface visualisation, generate cut and fill reports, view the as-built in cross-section, and export the as-built surface. See Changing the surface visualisation and Analysing the as-built model on this page for more information on these tools. |
| Surface Items list |
View and manage the list of imported source surfaces contributing to the as-built model. See Source surfaces and the Surfaces list on this page for more information. |
| Polygons list | View and manage polygons and polygon sets used to identify areas of interest or as input for certain tools. See Creating polygons on this page for information on creating polygons. |
| Design Surfaces list | View and manage design surfaces for comparison with as-built surfaces. See Surface Comparison for details on comparing as-built and design surfaces. |
| Past Exports list | View a list of surface files that have been exported for use in other applications. |
| Settings | Configure site settings, coordinate systems, users and roles, and other settings. See Site Settings for more information. |
Interacting with the as-built model
The as-built model is displayed in an interactive 3D viewer. GeoSpatial Manager handles large, detailed surfaces easily. It does this by dynamically adjusting the level of detail shown based on the current view of the data, allowing smooth and responsive interaction.
Panning, zooming, and rotating
You can pan, zoom, and rotate your view of the as-built surface using the following controls, depending on whether you are using a mouse or a touch screen.
| Operation | Mouse | Touch |
|---|---|---|
| Pan | Left click + drag | One finger drag |
| Zoom |
Right click + drag, or |
Two finger pinch |
| Rotate |
Middle click + drag, or |
Two finger drag |
The pan, zoom, and rotate operations are all based on the position of the mouse cursor on the screen (or the position of your fingers on a touch screen). This means, for example, that when zooming in, the view will keep the point under the mouse cursor as the focal point; when rotating, the view will rotate around the point under the mouse cursor. The following animation demonstrates panning, zooming, and rotating by positioning the mouse, clicking the left, right, or middle mouse buttons respectively, and dragging.
Source surfaces and the Surfaces list
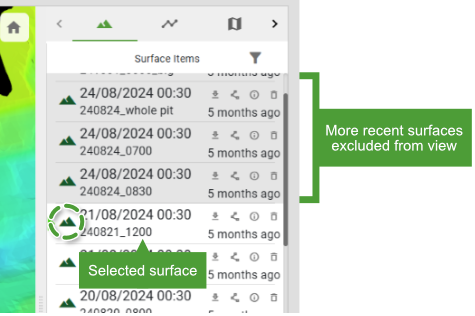
The uploaded source surfaces contributing to the as-built model are listed in the Surface Items list in the right-hand pane in descending chronological order; that is, the most recent source surface appears at the top of the list.
-
Hover over a source surface in the list to show its boundary polygon in the as-built model.
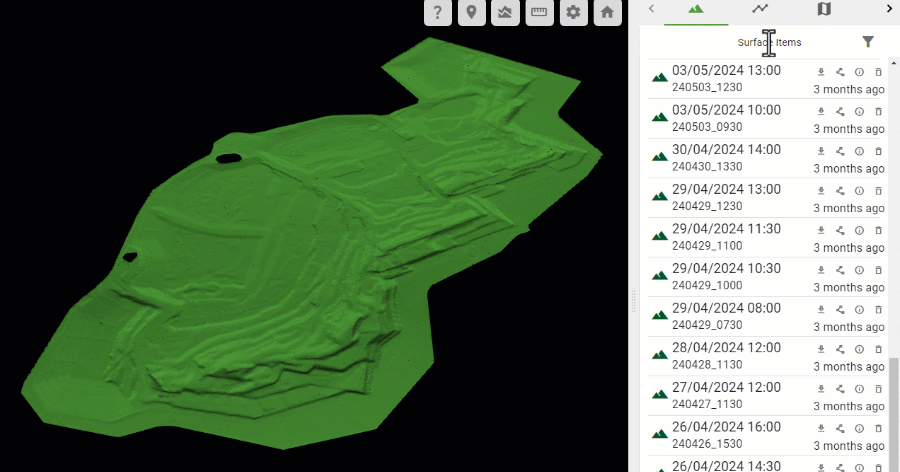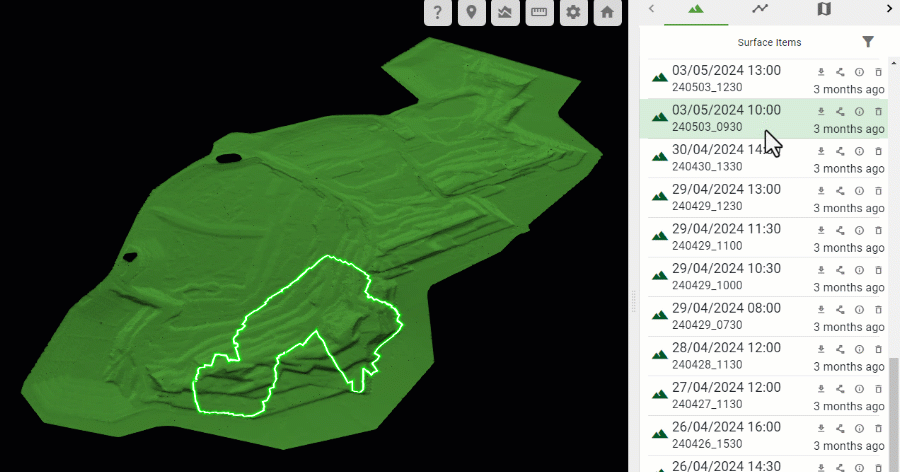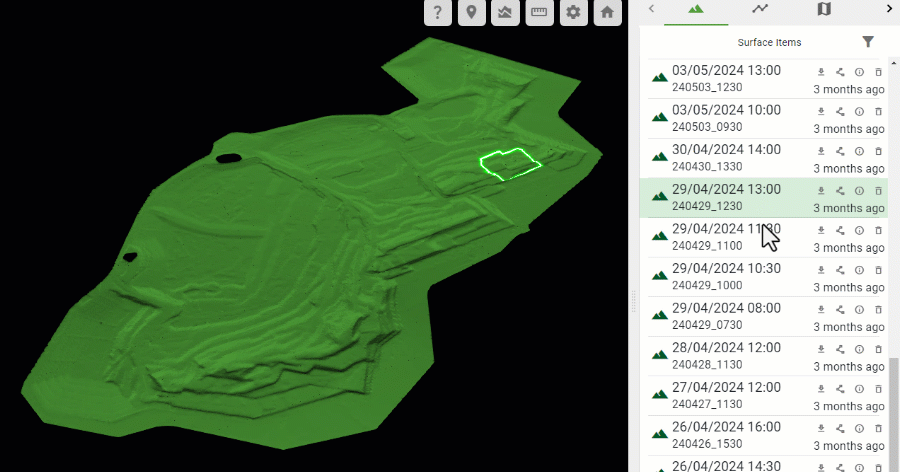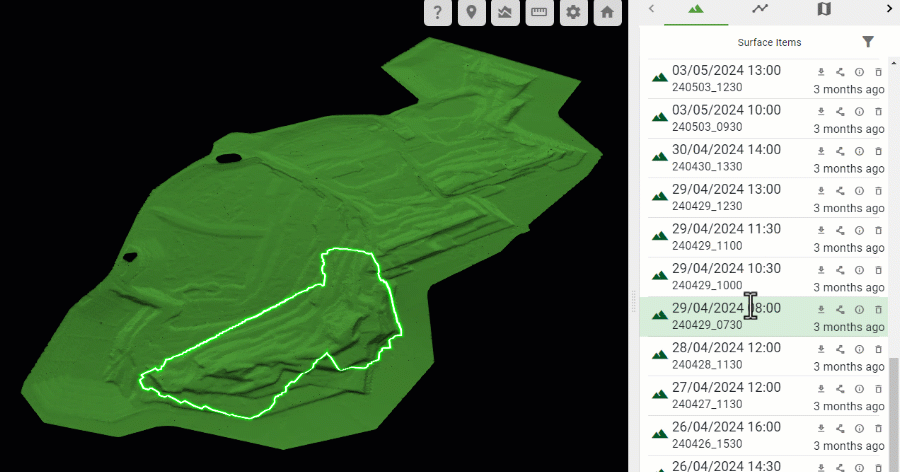
-
Perform actions on individual surfaces in the list using the tool buttons, including
 (Download surface) and
(Download surface) and  (Generate polygon).
(Generate polygon).
See Managing Surface Items for more information about the surfaces list.
Selecting a surface in the timeline
GeoSpatial Manager can display the as-built surface for any point in time between the oldest source surface and the most recent source surface. The timeline located at the bottom of the viewer represents each uploaded source surface with a triangle. The green triangle represents the currently selected surface. The surface in the viewer is a model built from the combination of all source surfaces from the oldest to the selected surface.

-
Click on the timeline to pick a point in time and select the closest source surface. A blue position marker indicates the point in time that was picked. The date and time of the selected surface are shown in the bottom-left corner of the view. The viewer will automatically update to show the as-built at that point in time.
-
Hover over the timeline and use the mouse scroll wheel to zoom the timeline in or out. Alternatively, right-click on the timeline and drag the mouse left or right for finer control.
-
Hover over the timeline and middle-click on the timeline and drag the mouse left or right to shift the timeline backward or forward.
The current selected surface is also indicated in the surfaces list with a green triangle.
The animation below demonstrates clicking various points on the timeline to show the progression of a mining operation over time.
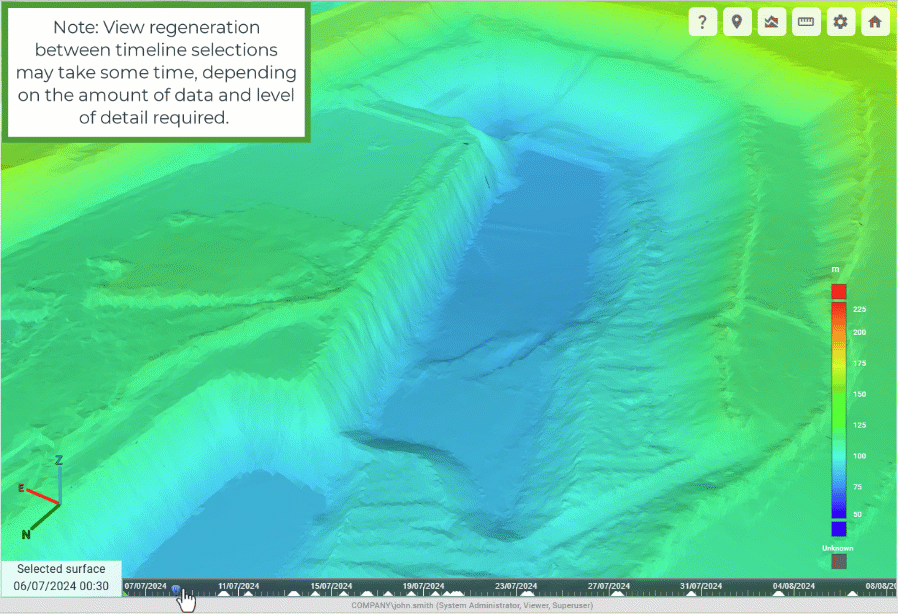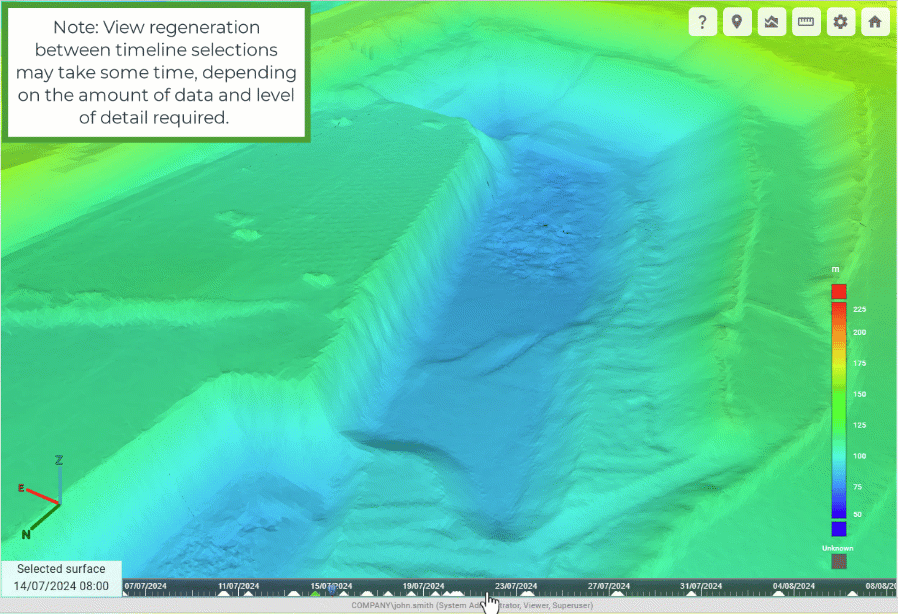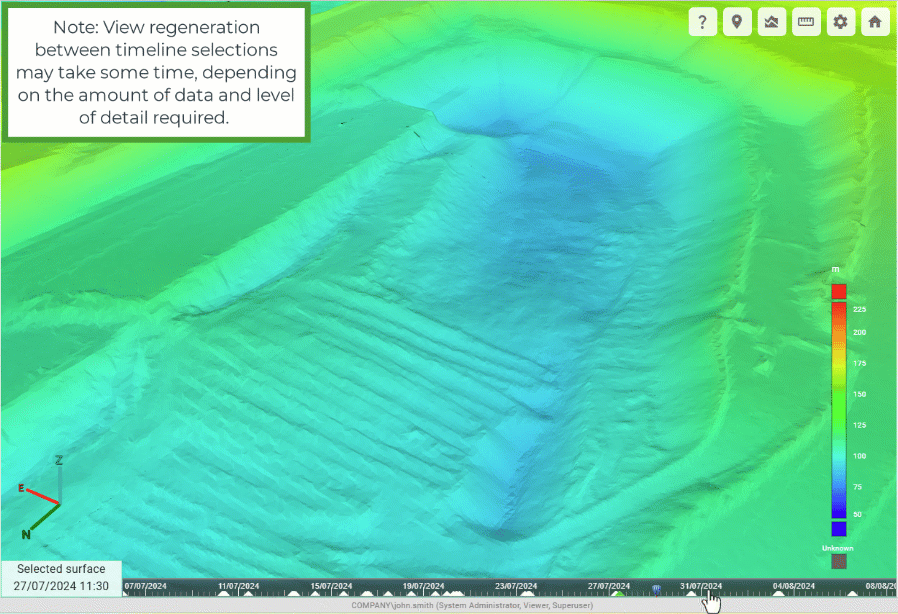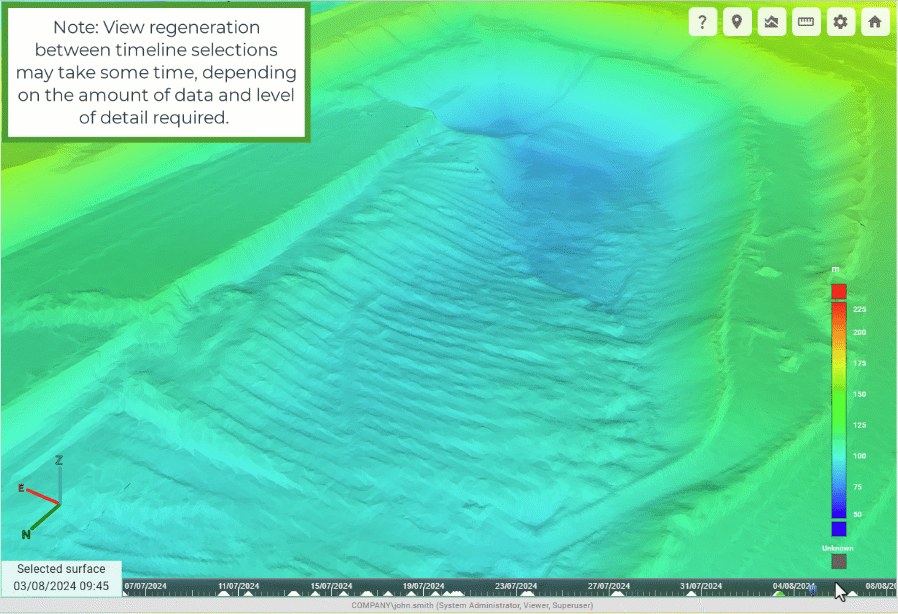
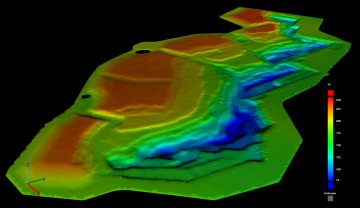
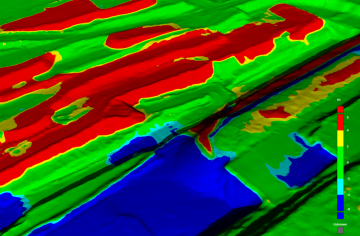
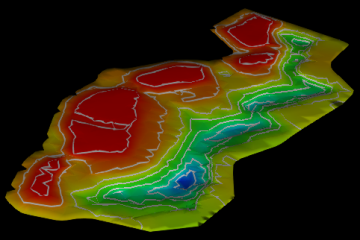
Changing the surface visualisation
You can change the visualisation of the surface model using the ![]() Colouring tool group located in the left pane.
Colouring tool group located in the left pane.
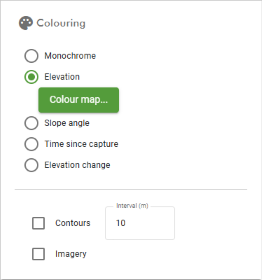
The table below summarises each colouring tool. See Colouring for detailed instructions on the colouring tools, including how to configure colour maps for options that use them.
|
Monochrome |
Apply a single colour uniformly to the surface.
|
|
Elevation |
Colour the surface by elevation according to a configurable colour map.
|
|
Slope angle |
Colour the surface by slope angle according to a configurable colour map.
|
|
Time since capture |
Colour the surface based on the time elapsed since the latest data capture. This is useful to quickly identify which parts of the surface have not been updated recently and may require resurveying.
|
|
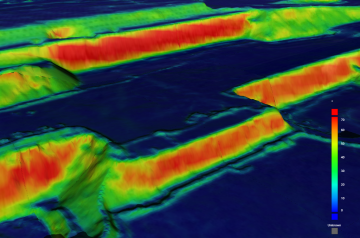
Elevation change |
Colour the surface by the change in elevation over a specific time period or deviation from a selected design surface. This colouring option is useful to quickly visualise which parts of a site have been subject to the most activity.
|
|
Contours |
Apply contour lines to the surface at specified intervals.
|
|
Imagery |
Display imagery on the surface (requires an imagery provider).
|
Analysing the as-built model
GeoSpatial Manager contains several tools to help you analyse and understand your data. Most of these tools operate on an area of interest defined by a polygon, so we will first look at how to create polygons in GeoSpatial Manager.
Creating polygons
There are three ways of creating polygons in GeoSpatial Manager: by digitising points on the surface in the viewer, by generating from a surface boundary, or by importing from file. Manage polygons and polygon sets in the ![]() (Polygons) list in the right-hand pane.
(Polygons) list in the right-hand pane.
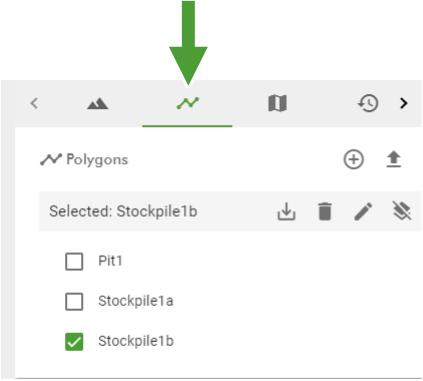
The animation below shows how to create a new polygon by digitising point on the surface. Start by switching to the ![]() (Polygons) list and clicking the
(Polygons) list and clicking the ![]() (Draw polygon) button. Instructions appear on the screen.
(Draw polygon) button. Instructions appear on the screen.
You can view any saved polygon by making sure its checkbox is selected in the ![]() (Polygons) list.
(Polygons) list.
See Polygons for more detailed instructions on polygons, including generating from surface boundaries, importing from file, and combining into polygon sets.
Cut and fill tool
The ![]() Cut / Fill tool allows you to calculate surface volumes and tonnages in relation to elevation, date range or a design surface. See Cut / Fill for detailed instructions on calculating cut and fill.
Cut / Fill tool allows you to calculate surface volumes and tonnages in relation to elevation, date range or a design surface. See Cut / Fill for detailed instructions on calculating cut and fill.
Surface Comparison tool
The ![]() Surface Comparison tool allows you to view the parts of the surface behind an intersecting vertical plane. You can opt to display the surface at a single point in time, or compare the surface between two points in time.
Surface Comparison tool allows you to view the parts of the surface behind an intersecting vertical plane. You can opt to display the surface at a single point in time, or compare the surface between two points in time.
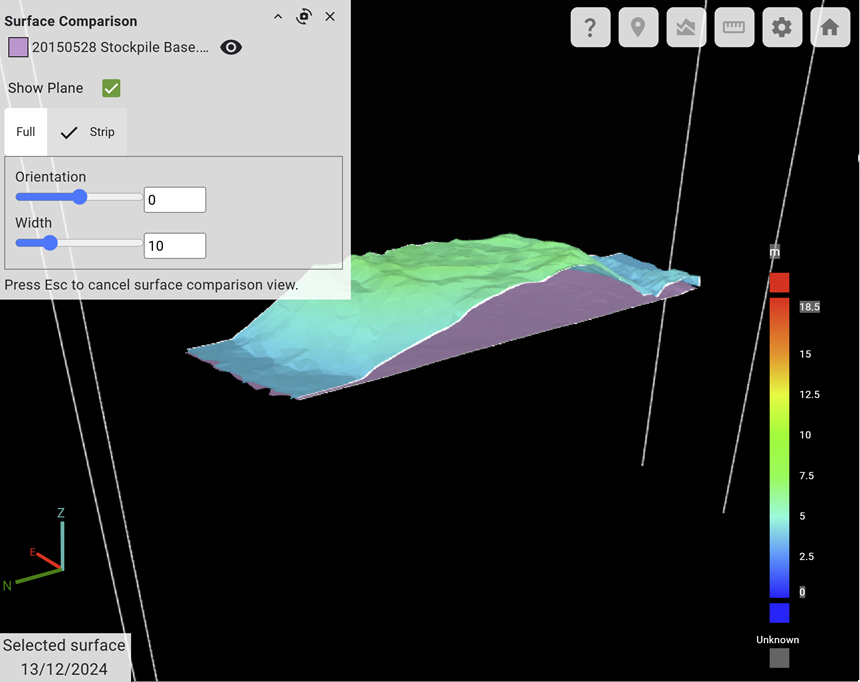
To use the surface comparison tool, on the ![]() Home tab, expand the
Home tab, expand the ![]() Surface Comparison tool. The Surface Comparison panel will open in the viewer and the cross-section plane outline will be displayed.
Surface Comparison tool. The Surface Comparison panel will open in the viewer and the cross-section plane outline will be displayed.
(Optional) You can constrain the view to a smaller area by selecting a polygon. You can also compare the surfaces to a design surface.
See Surface Comparison for more detailed instructions on using the cross-section tool.
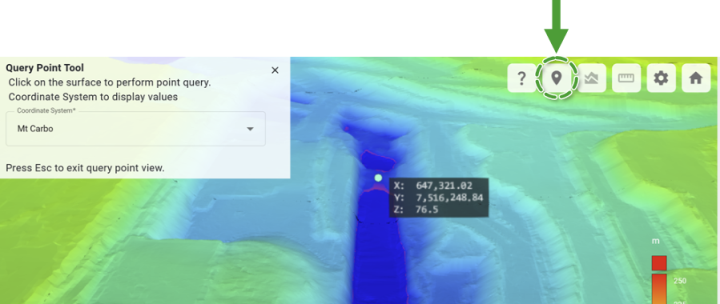
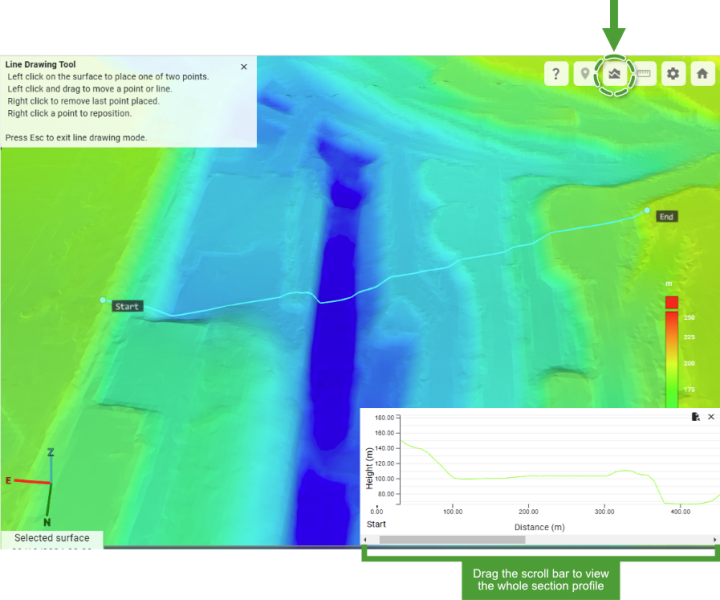
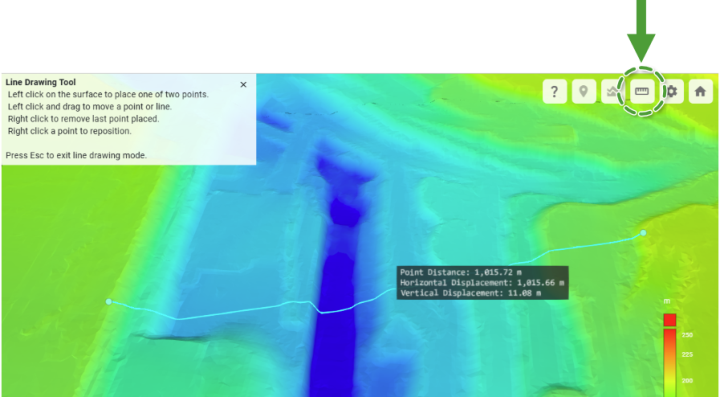
Point, cross-section, and distance queries
The viewer supports a couple of simple queries based on the geometry of the surface model. These queries are available from the tool buttons located in the top-right corner of the viewer and are described below.
|
|
Query Point Query the location of a point clicked on the surface.
|
|
|
Cross Section Generate a cross-section chart to view the elevation profile between two points clicked on the surface. Export the chart as an SVG file (
|
|
|
Distance Query Query the distance and horizontal/vertical displacement between two points clicked on the surface.
|