Results
This section allows users to specify the location of the output fault surface triangulation.
Fault Surface Features
The output fault surface triangulation name is preset as Fault_<Fault name>.00t. User can select the directory where this file will be stored and also specify a colour to the resulting triangulation.
Make Smooth Surface
When the amount of data points is small, the resulting fault surface may contain relatively rough turns that one would hardly expect in a fault surface.
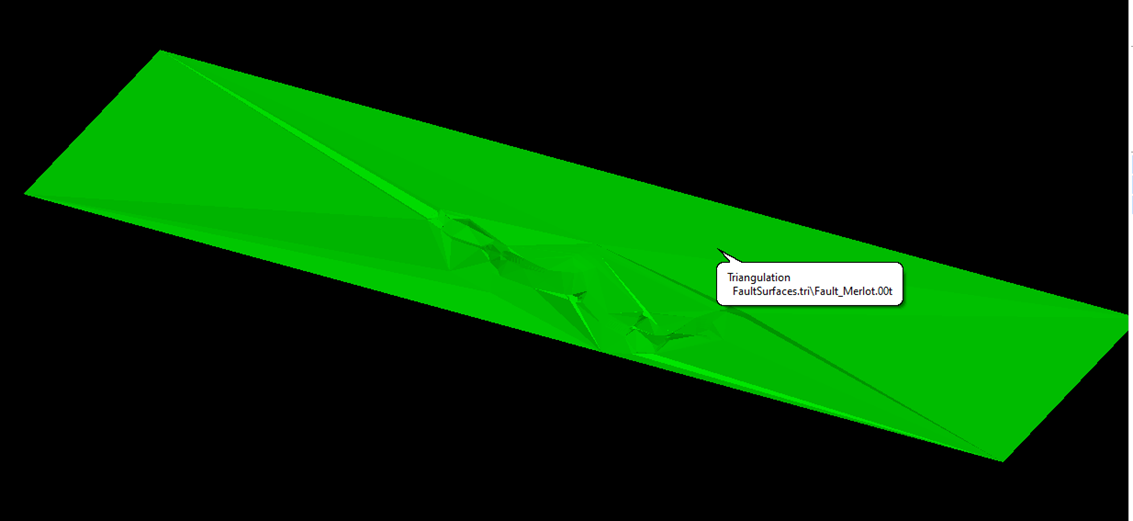
Figure 1: Rough turns in resulting fault surface
This option provides the choice of smoothing the resulting surface using some of the Grid Calc tools.There are two smoothing methods from Grid Calc available here: Triangulation and Inverse Distance. These methods make surface much smoother.
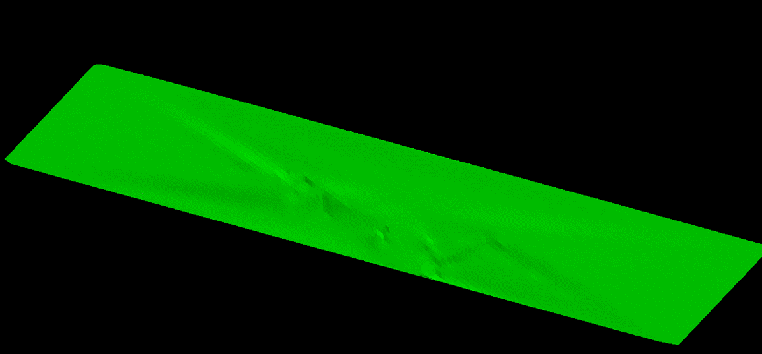
To know more about these methods, see Modelling Method and Parameters.
Snap triangulations to input data
Selecting this option preserves the positioning of input points.
Maximum triangle side length
Enter the maximum length for a triangle side. The points evaluated within a triangle with a side length greater than the specified length will have a data mask value of 0.
Spine Surface
Select this option if you want to produce smooth surfaces without any smoothing when interpolating within the triangles. Breaklines are recognised.
Save Fault Data Points
By choosing this option, users can also save the points of the resulting triangulation in a designated layer of the currently open design database with a designated colour.
Note: The unsmoothed version of the fault surface of a point having directional information define a flat pseudo-circular area around it. The radius of the flat area is defined by the proximity of other points making the surface but is limited by 50 units.
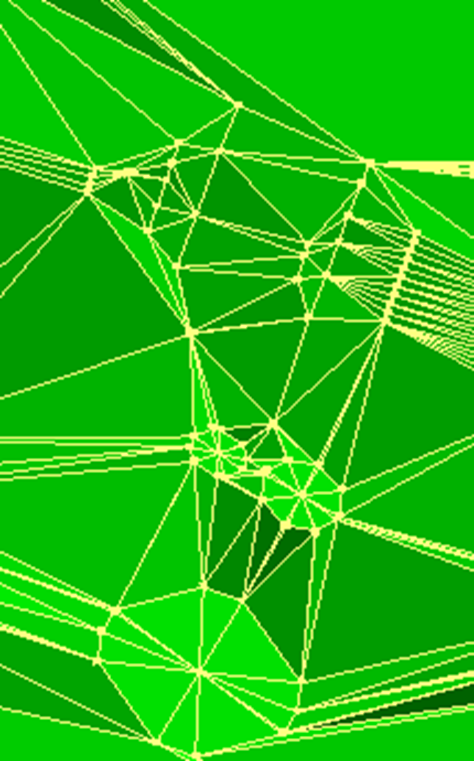
Figure 2: Flat pseudo-circular area around the unsmoothed fault surface
Related Topics

