Constraints
Source file: epoch-setups-constraints.htm
Constraints allow you to guide or limit the schedules that Evolution can produce.
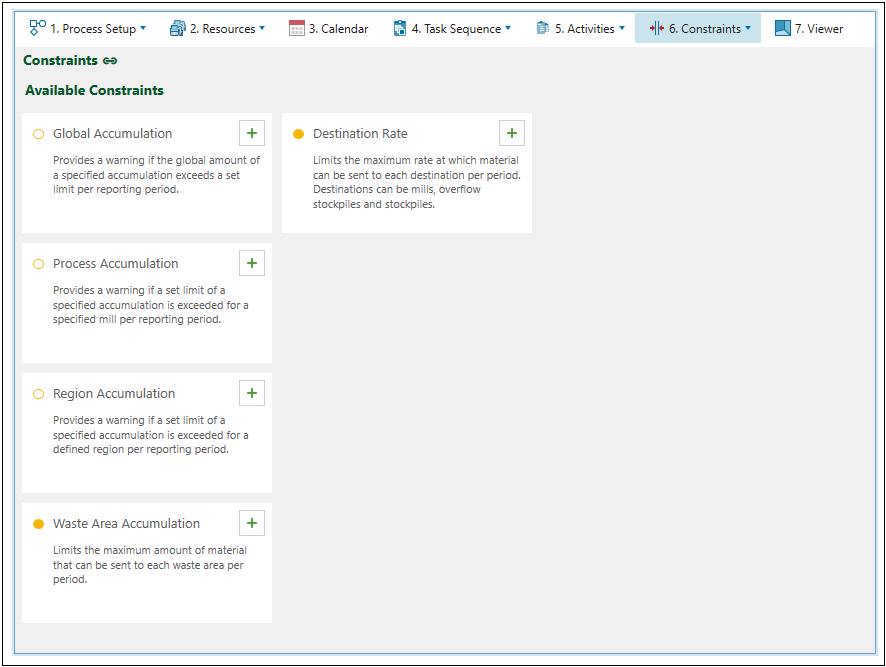
You can enter the screen that shows all constraints available for your setup after selecting ![]() Constraints > Overview from the setup configuration tabs. A short description is given for each constraint.
Constraints > Overview from the setup configuration tabs. A short description is given for each constraint.
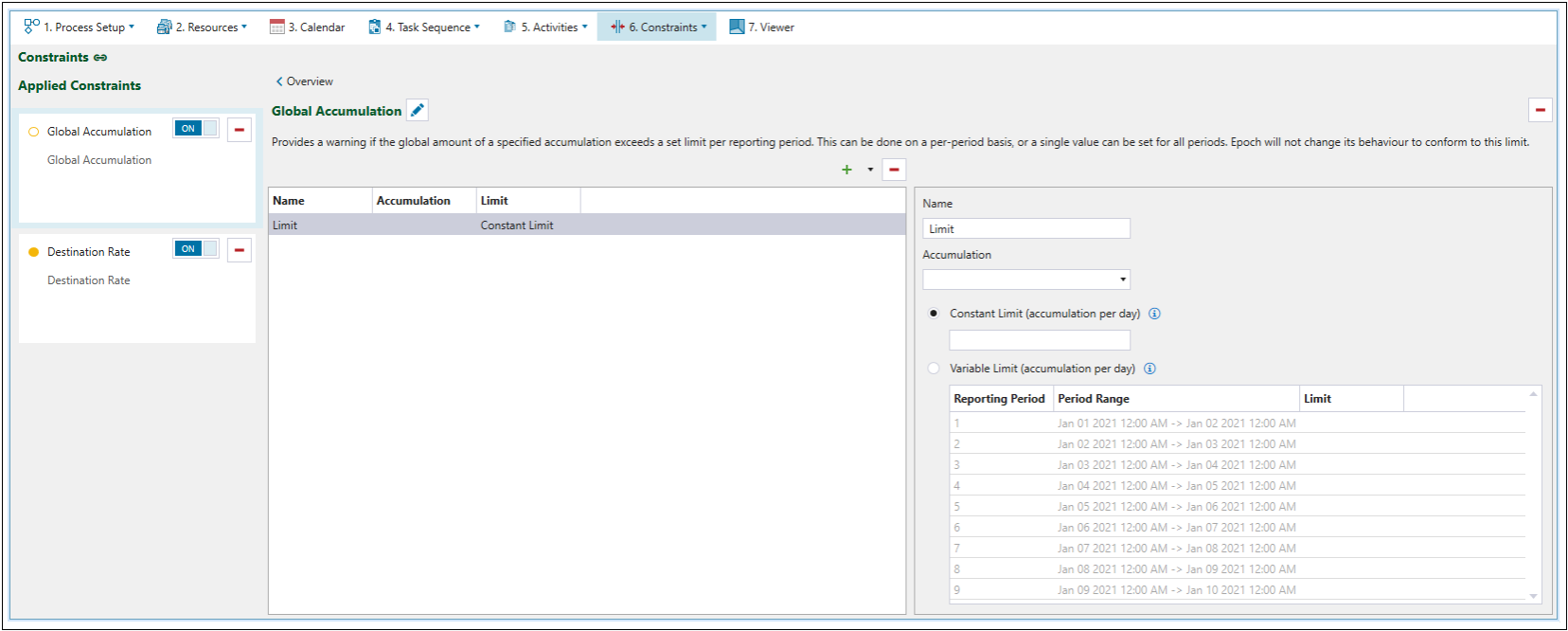
You can apply the required constraints by clicking ![]() (Add new constraint). The constraints applied to your setup will appear on the left side of your screen, as well as under the
(Add new constraint). The constraints applied to your setup will appear on the left side of your screen, as well as under the ![]() Constraints tab drop-down.
Constraints tab drop-down.
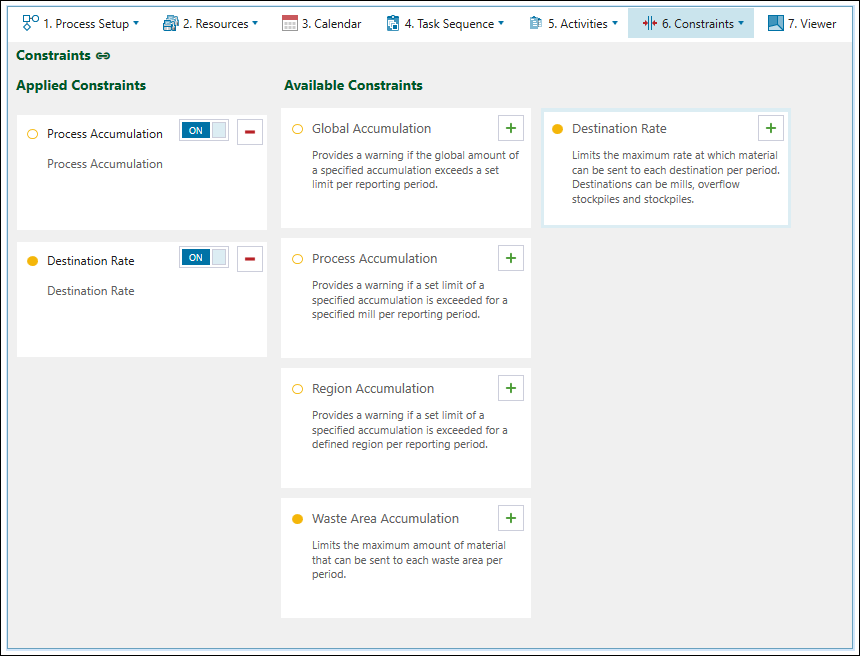
You can select a constraint to configure either by:
-
Clicking on the required constraint in the Applied Constraints list.
Or
-
Selecting the required constraint from the
 Constraints tab drop-down.
Constraints tab drop-down.
The following buttons appear on all constraints to provide unified and simplified ways of operation:
|
|
Enable or disable constraint Toggle button that allows you to enable or disable a constraint in your setup. |
|
|
Delete constraint
Removes constraints from your setup. |
|
|
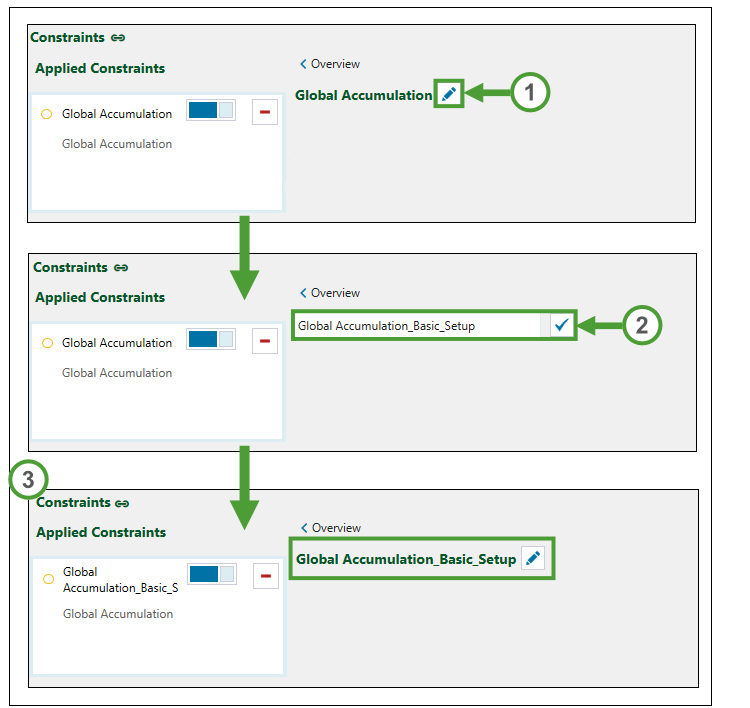
Edit constraint name
To rename a constraint:
|
|
|
Overview
Goes back to the |
Constraints are classified as ![]() Hard and
Hard and ![]() Soft, with the following distinctions:
Soft, with the following distinctions:
-
Hard constraints are mandatory for Evolution when it determines a schedule.
-
Soft constraints are taken into account by Evolution when it determines a schedule, but meeting them is optional.
The following table provides a description of each constraint available in Evolution Epoch setups.
| Constraint | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Global Accumulation | Soft | Limits the maximum amount of material processed in a setup per reporting period. |
| Process Accumulation | Soft | Limits the maximum amount of material that can be sent to a mill per reporting period. |
| Region Accumulation | Soft | Limits the maximum amount of material that can be extracted from a region per reporting period. |
| Waste Area Accumulation | Hard | Limits the maximum amount of material that can be sent to each waste area per period. |
| Destination Rate | Hard | Limits the maximum rate at which material can be sent to each destination (mill, stockpile, and overflow stockpile) per period. |