Method
This section allows the selection of horizon modelling methods and parameters.
There are two methods available when creating multiple horizon models:
- Structural Surfaces
- Stacking
Structural Surfaces Method
This method models individual hanging wall and footwall for each horizon.
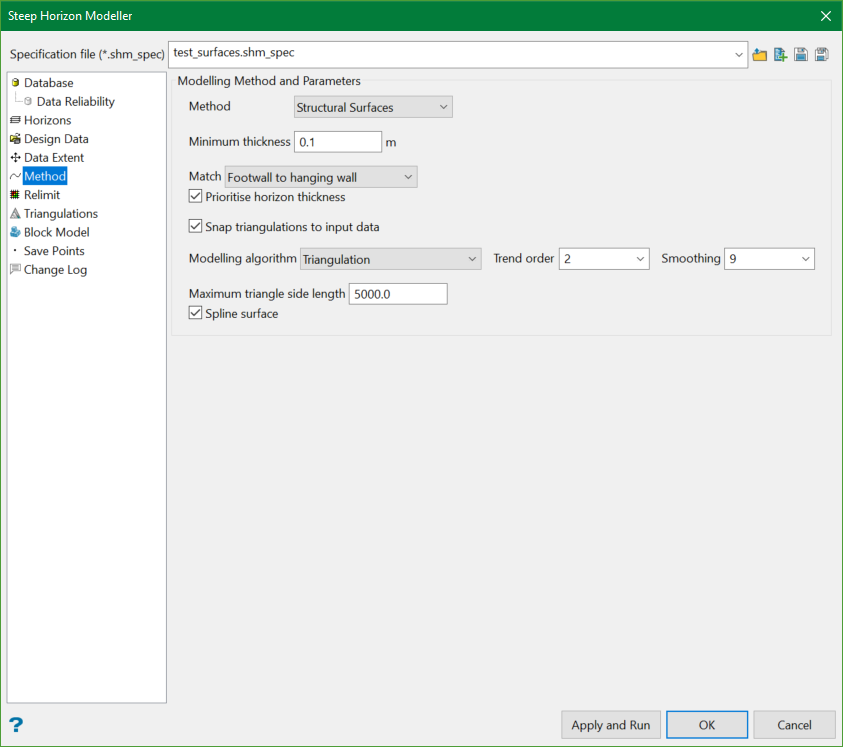
In the above example (screenshot), a triangulation method is used with a 2nd order trend and 9 Smoothing passes. To avoid very long triangle edges, the Maximum triangle side length is limited to 5000.
Note: The Maximum triangle side length field appears on the panel because the Triangulation Modelling algorithm is chosen. Each modelling algorithm has its own required parameters. Selecting different algorithms will populate the panel with unique fields.
Match
Should a horizon cross its neighbour, either the footwall is forced to the hanging wall position or the hanging wall is forced to the footwall position. Control this selection from the drop-down list.
Prioritise horizon thickness
Check this option to maintain the horizon thickness while matching between multiple horizons.
Snap triangulations to input data
Check this option to have the triangulation snapped to the input data points. This option is available for both modelling methods.
Stacking Method
This method creates all horizon models based on one selected structural surface. The selected surface becomes a reference for creating the rest of the models. The remaining surfaces are created by adding and subtracting thickness and mid-horizons from the reference surface.
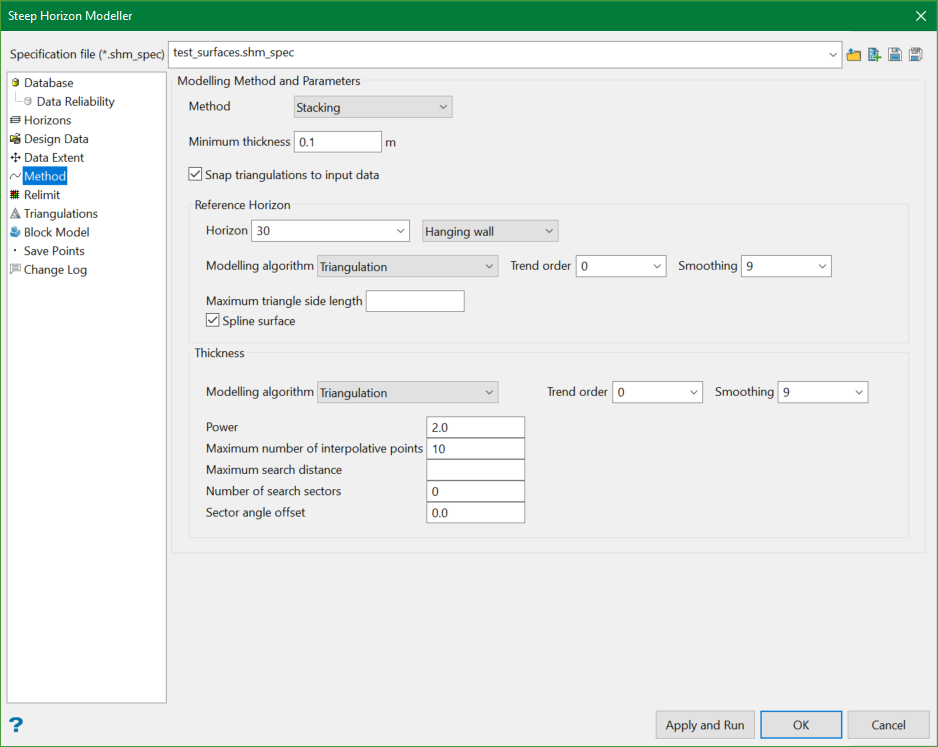
When selecting the Stacking Method, define Modelling algorithms for both the Reference Horizon and the Thickness models.
Reference Horizon
The reference horizon can be selected from the Horizon drop-down list, and is generally the horizon with the most reliable data.
Thickness
It is possible to use a different algorithm when modelling Thickness models.
Note: Each modelling algorithm has its own required parameters. Selecting different algorithms will populate the panel with unique fields.
Related Topics
- Overview
- Database
- Horizons
- Design Data
- Data Extent
- Relimit
- Triangulations
- Block Model
- Save Points
- Change Log

