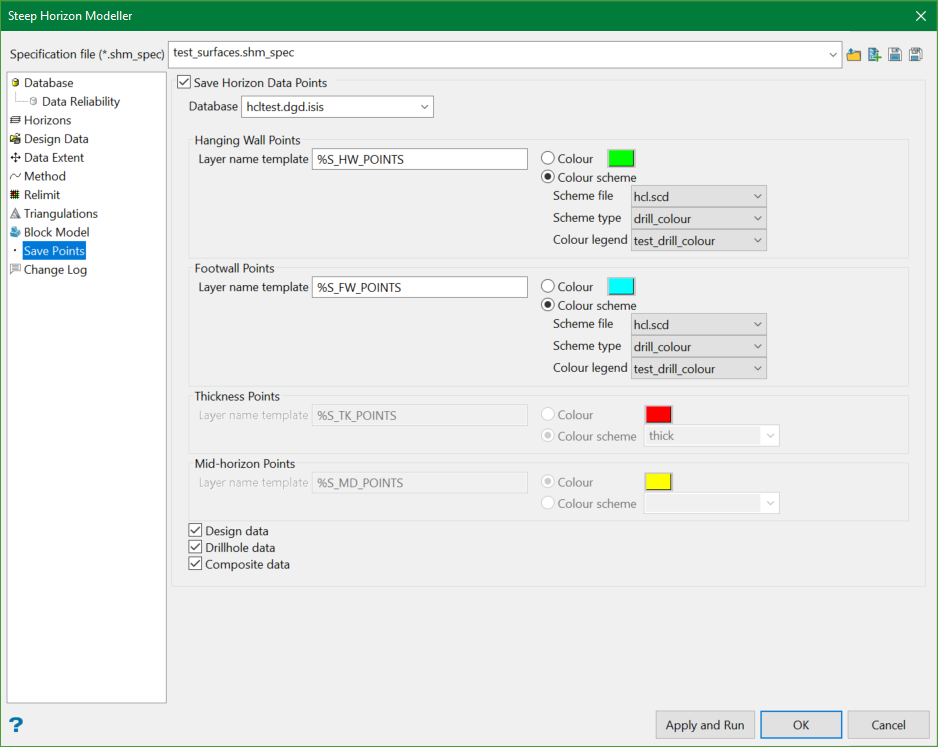
Save Points
This section allows users to save the generated horizon data points into specified layers.
This section is enabled only if the Horizon Surfaces option in the Triangulations section is selected.
Save Horizon Data Points
Select this option if you want to save the input data as design data points into the specified layers.
Database
Choose the database in which the resulting data points will be generated.
Hanging Wall Points/Footwall Points
The Layer name template defines the name of layers where the resultant points will be saved. The panel default is %S_HW_POINTS , where %S is automatically replaced by the necessary horizon name as defined in the horizon list and _HW_POINTS is a fixed suffix assigned to the horizon name for hanging wall points.
Similarly, the panel default for Layer name template is %S_FW_POINTS for footwall points.
Thickness Points/Mid-horizon Points
When choosing the Stacking method in the Method section, the options to save thickness points or mid-horizon points are enabled. The thickness points represent the horizon thickness and the mid-horizon points represent the value between the continuous horizons defined in the horizon list.
The panel default for the Layer name template is %S_TK_POINTS for Thickness Points and %S_MD_POINTS for Mid-horizon Points.
For all of the four points, there are two types of colouring options:
Colour
Select this option for the resulting points to be single coloured. The colours used for the saved points will be selected from the current colour table.
Colour scheme
Select this option for the Vulcan colour scheme to colour the resulting data points.
For hanging wall and footwall points, select the scheme file, type, and colour legend from the respective drop-down lists.
For thickness and mid-horizon points, choose a colour scheme. You don't need to specify colour legend as it comes from the CONTOUR scheme.
Input data
Specify the input data to be saved by selecting one or more of the three databases namely, Design, Drillhole, and Composite.
Related Topics
- Overview
- Database
- Horizons
- Design Data
- Data Extent
- Method
- Relimit
- Triangulations
- Block Model
- Change Log

