Blocks
Use the Blocks method to define three-dimensional fault domains in the form of solid triangulations. This method allows the definition of complex 3D fault planes which can model normal, reverse or thrust faulted surfaces.
The triangulations used in Blocks need to be valid, closed and mutually exclusive. The use of the Model > Triangle Utility > Multi-Boolean option to create these solids often makes the process much simpler.
The Blocks method operates as follows.
- The Blocks method creates a fully featured, grid-based integrated Stratigraphic Model in each fault domain.
- Each set of grids is unmasked, triangulated and then clipped exactly to the fault solids resulting in a series of disjointed surfaces representing the roofs and floors of each horizon.
- All the pieces of each horizon's roof and floor are appended to each other to create two faulted surfaces for each horizon - one roof and one floor.
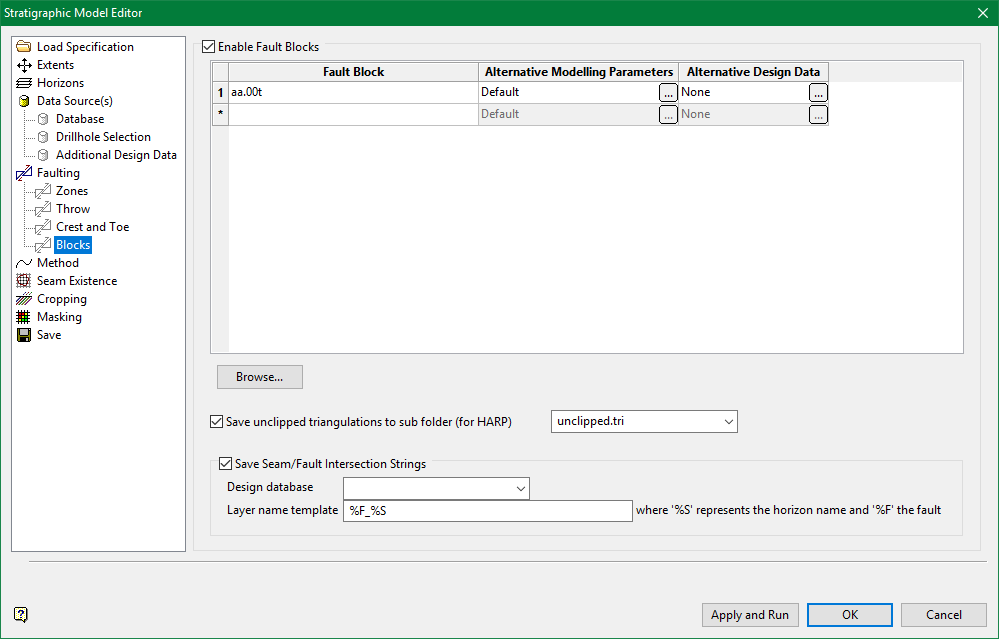
Enable Fault Blocks
Select this check box to use existing solid triangulations to define three-dimensional fault zones.
Note: The Input from existing map file check box, which is located under the Data Source(s) section, must be selected in order to access the available block faulting functionality. If this check box has not been selected, then all options displayed through the Blocks section will be unavailable.
Enter fault block names in the grid. The solids must meet the following requirements:
-
valid closed solid triangulations
-
mutually exclusive
-
cover the area of modelling data
-
contain at least some data on any reference horizons specified.
Alternative Modelling Parameters
Click  to display the Alternative Fault Modelling Parameters panel. Based on the method that you choose in the Method tab, different panels show up.
to display the Alternative Fault Modelling Parameters panel. Based on the method that you choose in the Method tab, different panels show up.
Structural Surfaces
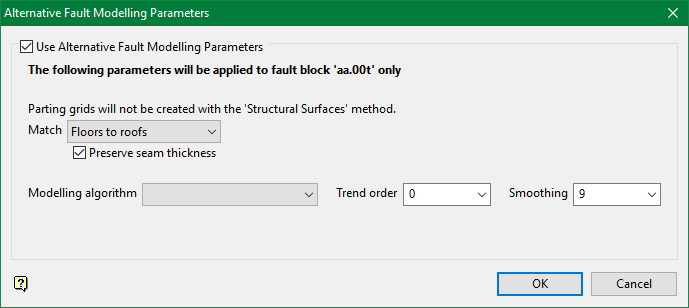
See Structural Surfaces for detailed information.
Stacking
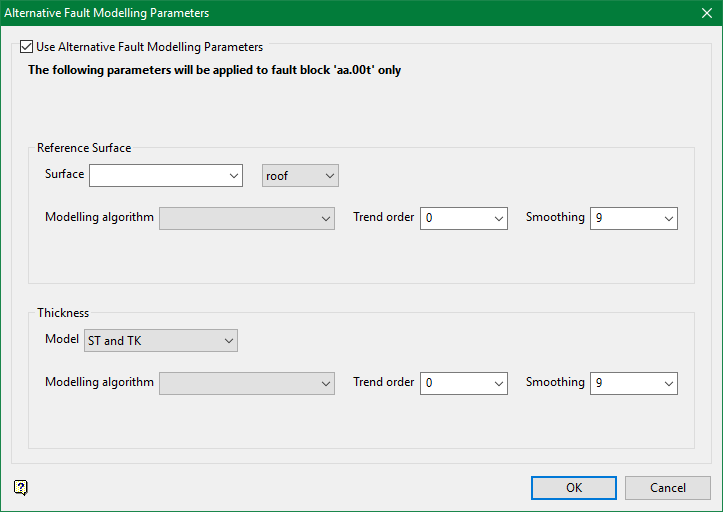
See Stacking for detailed information.
Hybrid
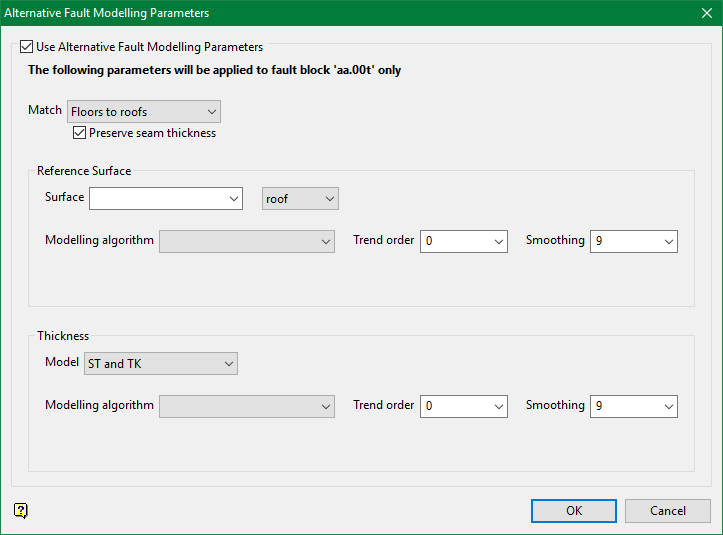
See Hybrid for detailed information.
Alternative Design Data
Click  to display the Alternative Design Data panel.
to display the Alternative Design Data panel.
See Additional Design Data for detailed information.
Save unclipped triangulations to sub folder
Unclipped triangulations are required input for any subsequent HARP or Bstrat block model creation. Unclipped surface triangulations are equivalent to unmasked grids as they exist to the full modelling limit extent.
Select this check box to save the triangulated grids in a nominated directory. When outputting to another location, the.tri and.grid folder extensions are used to display the folder and its contents in the Vulcan Explorer application.
If this check box is not selected, the triangulated grids are treated as temporary files and will be deleted.
Note: In order to save the triangulations, you must nominate a directory in which to save the unclipped faulted triangulations. The saved triangulation file can then be accessed through the Create Harp Model option (under Grid Calc > Integrated Stratigraphic Modelling ).
Save seam/fault intersection strings
Check to automatically save intersections of each horizon and fault plane as strings in a layer. Resulting layers are named using a template defined in the pane. The default Layer name template entry is %F_%S, where %F corresponds to the fault block name and %S corresponds to the horizon name. This template may change as long as the %F and %S variables are included.
Proper Use of Resulting Triangulations
If no fault blocks are supplied, then Grid Calc > Integrated Stratigraphic Modelling > Model Stratigraphy creates unfaulted grid models as output. It is possible to use unfaulted grid models in the creation of HARP or Bstrat block models, but no complex faulting is represented.
If fault blocks are defined, then a series of triangulations representing structure roofs and floors are created. These triangulations are named as follows:
-
Structural roof: <projectcode><horizon>.srt
-
Structural floor: <projectcode><horizon>.sft
Clipped triangulation models are excellent for viewing the structure of faulted models. They are also good for contouring.
Important Do not use clipped triangulation surfaces in the creation of any subsequent HARP or Bstrat block models!
Save unclipped triangulations to a separate directory to avoid accidental deletion during the clean-up process. Unclipped triangulations have a slightly different naming convention which includes the fault block name. Structural roofs are assigned the. srt extension, whereas structural floors receive an. srf extension.
-
Structural roof: <projectcode><horizon><fault block name>.srt
-
Structural floor: <projectcode><horizon><fault block name>.sft
Related topics
-
Data Source(s)
-
Faulting

