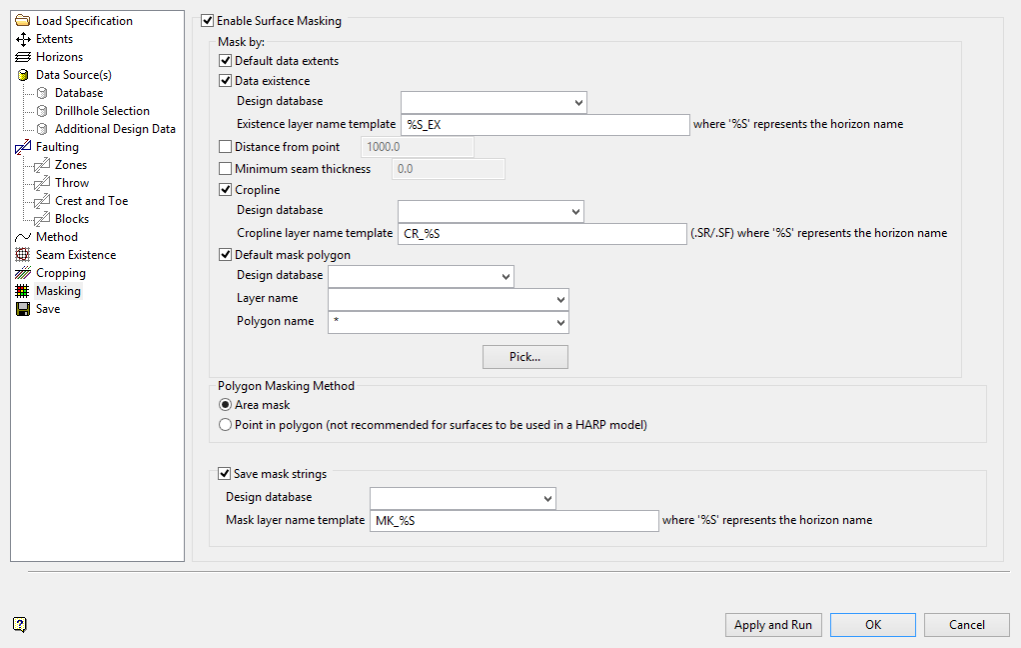
Masking
Masking is optional. If selected, use any or all of the Mask by options in conjunction with each other.
Mask By
Data existence uses existence strings generated in the Seam Existence pane to mask grid nodes.
Note: The Existence layer name template must match the layers generated in the Seam Existence pane.
Distance from point
This masks grid nodes based upon an entered distance from a data point.
|
Tip: The distance from point option is a simple way to obtain measured, indicated, or inferred classification.
|

Example of a grid masked by distance.
Minimum seam thickness
Masks grid nodes when the thickness between the roof and the floor is less than the entered value.
Tip: If there are no splits or nearby seams, Minimum seam thickness could provide a simple run of mine (ROM) result, which is particularly useful for underground coal deposits.
Cropline
Uses crop strings generated in the Cropping pane to mask grid nodes.
Note: To use saved crop strings, the Cropline layer name template must match the layers generated in the Cropping pane.
Default mask polygon
Masks all grids with a single polygon. This is ideal for polygons such as lease boundaries or environmental limits.
Define the polygon using drop-down selections, or click Pick to select a polygon loaded in Vulcan.
-
Clockwise polygons will include grid nodes which fall inside the Plan view projection of polygon extents.
-
Anti-clockwise polygons include grid nodes which fall outside the Plan view projection of polygon extents.
Polygon Masking Method
Area Mask
Select this option to mask the four nodes that make up the grid cell if 50% of the cell area is included in the polygon. The cell is unmasked if more than 50% of the area is excluded by the polygon. The entire cell is taken into account. This option is the only method that considers a cell rather than individual nodes.
Polygon Masking Method
Point in polygon may result in polygons which are not mutually exclusive. HARP models require mutually-exclusive polygons; therefore this option is not suitable when creating HARP models. However, this option may result in nicer grid masking if the end result is not a HARP model.
Save mask strings
This saves mask polygons which represent the interaction of all selections on the panel.
Select the Design database where resulting mask polygons will generate.
The Mask layer name template entry will define the names of layers where polygons will save. The panel default %S_EX, where %S is automatically replaced by the necessary horizon as defined in the horizon list and _EX is a fixed suffix to the called horizon name.
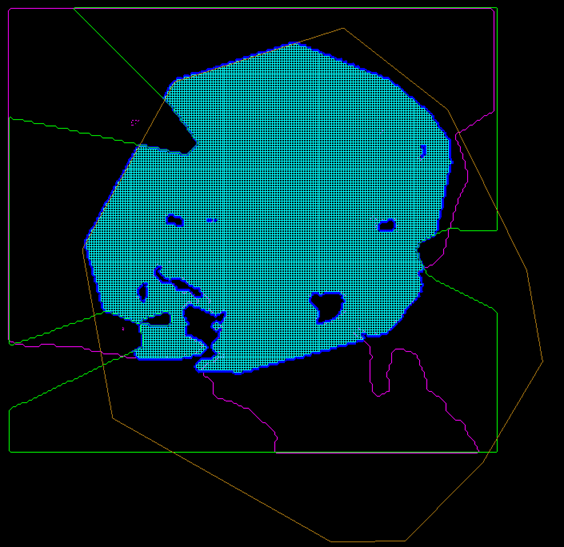
Initial masking polygons and final masking polygon with grid.
In the figure above, the light blue grid is displayed with a final, dark blue, masking polygon. The final polygon was created by the intersection of:
-
A green seam limit polygon. (Data existence)
-
A pink cropping polygon. (Cropline)
-
A brown lease polygon. (Default mask polygon)
Related topics
-
Data Source(s)
-
Faulting

