Seam Existence
This option creates seam limit polygons for each horizon using:
-
All horizons defined in the horizon list. Splitting relationships are honoured.
-
Data location.
-
Automatically-generated total depth mapfiles.
Note: Data existence polygons consider drillholes which do not contain the horizon of interest but are deemed deep enough to have possibly contained the interpolated position of a horizon as indicated by surrounding holes. This data is stored in a TTD mapfile or the TTD horizon in the Mapbase.
For this reason, TTD should not represent a horizon which should be modelled.
Two options are available if Use mapfiles to determine seam existence is selected.
-
- When generating existence polygons for seams with splitting relationships, the default behaviour is to create parent polygons which are mutually exclusive from any associated child polygons. Select Create ‘cumulative’ child existence strings to include the parent horizon extents in the extents of limit polygons for any child seams.
- Honour interpolated mapfile thicknesses includes a seam in the limit polygon boundaries if that seam was given an interpolated thickness during the fixDHD process.
The way horizon splits are modelled varies depending on whether the Structural Surfaces method and or the Stacking method was used to create the grids in the Method pane.
-
Structural Surfaces: The split begins at the drillhole location.
-
Stacking and Hybrid: The split occurs halfway between drillhole locations.
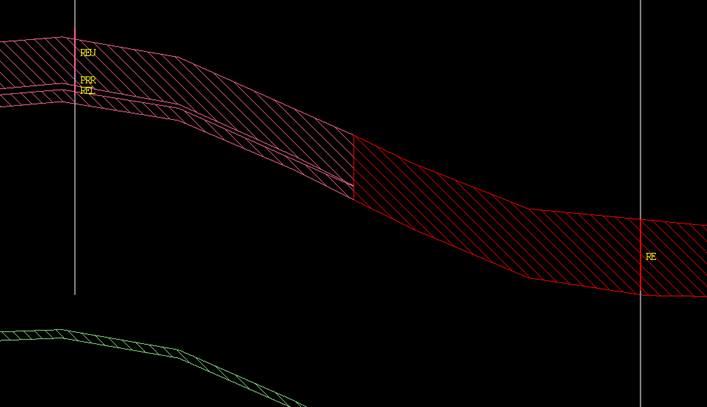
Figure 1 : Stacking Method – split begins half way between bores.
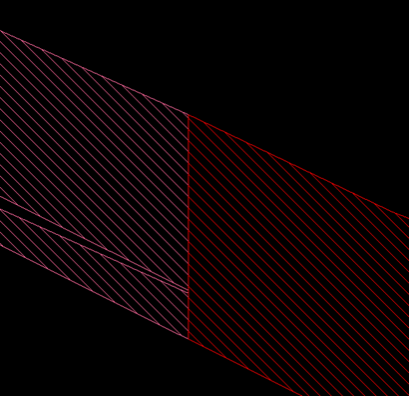
Figure 2 : Detail of split.
The data existence polygons used to mask grids are created in the selected Design database. By default the layer is named %S_EX, where %S is a horizon as defined in the horizon list. For example, the existence polygon for the REU horizon generates to a layer named REU_EX. The existence polygon is always named <horizon>_EX, where horizon is the horizon defined in the horizon list.
Create Seam Existence Strings
Pinch By Seam Existence Strings
Select this check box to force parent and related child models to be mutually exclusive by pinching them to zero thickness where they do not exist and running the parent over the roof of the child or vice versa. This is a useful way to ensure that subsequent reserving is not dependent upon grid masking.
Note: Pinched grids or triangulations should never be used for HARP model creation.
Related topics
-
Data Source(s)
-
Faulting

