Block Selection
On the Underground menu, point to Analyse, click Stope Optimiser, and then select Block Selection from the tree menu on the left to display the Block Selection pane.
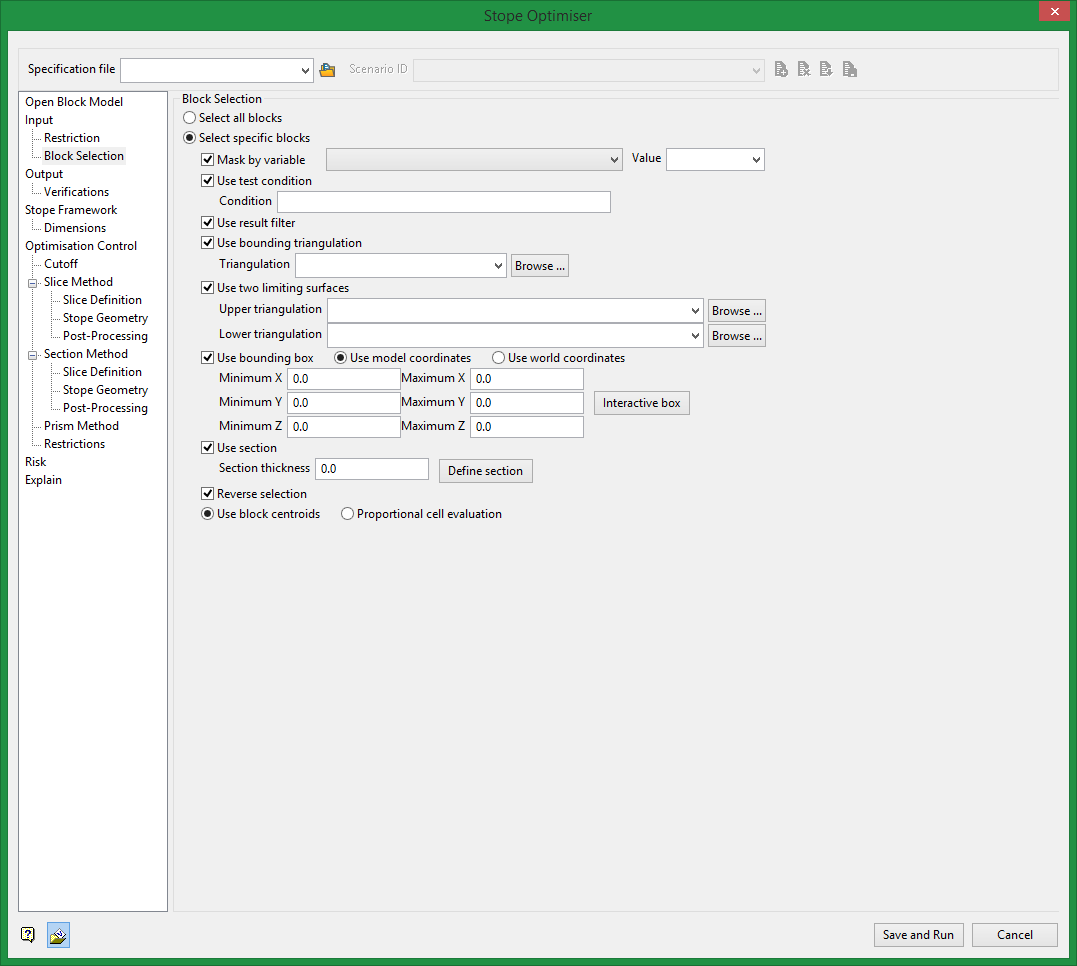
Either all blocks or specific blocks can be selected. If you select Select specific blocks by, then you must enter one or more of the following selection criteria:
Variable
Select this check box to restrict the blocks by a block model variable. You will need to specify the variable, as well as a particular value.
For example, to restrict blocks to those where Material equals Ore, select 'Material' as the variable (from the drop-down list) and enter 'Ore' as the value. However, if you require all blocks thatdo nothave this specified value, then enable the Reverse selection check box. The block model variable may be numeric (for example, the grade variable 'Au') or character (for example, 'Geology') variables.
Use test condition
Select this check box to use a further constraint upon a numeric block model variable, for example, Fe GT 10.0(iron value greater than 10.0). The maximum size of the condition is 132 alphanumeric characters. A list of available operators/functions to use when defining this condition is provided in Appendix B .
Use bounding triangulation
Select this check box to restrict the blocks by a triangulation. This is useful when, for example, you want to evaluate reserves in a particular solid triangulation such as a stope.
To select blocks outside of the bounding triangulation, select the Select blocks outside the solid only option.
You may also select the Use block centroid check box and use it with this restriction.
Note: This option is not applicable to open or 2D triangulations.
Use two limiting surfaces
Select this option to restrict the blocks by bounding surfaces. Browse to or select upper and lower triangulations from the drop down lists. Only blocks that lie in the overlapping sections, as viewed in plan view, of the surfaces are selected.
Use bounding box
Select this check box to restrict the blocks by a box. If you select this option, you must enter the minimum and maximum coordinates for X, Y, and Z in the Block model coordinates. You may also select the Use block centroid check box and use it with this restriction.
Use section
Select this check box to restrict the blocks by a projection plane. You will need to enter its associated thickness. The blocks that are in this thickness will be selected.
The section plane can be selected by line, points or grid coordinates. This information is entered through the Projection Plane panel, which displays by clicking Define Section. You may also select the Use block centroids check box and use it with this restriction.
Reverse selection
Select this check box to select outside the specified regions.
Use block centroids
Select this option to include a block if the block's centroid is in the region. Note the entire block is included. "Block centroid" means that a block is selected or note selected based on the centroid point being inside or outside of the triangulation. The entire block is either selected or rejected, resulting in either the full volume contribution, or a 0 volume contribution. Block centroid is subject to biases.
Example: If the blocks have a height of 10m and the top of a surface is at 116m, the blocks at the top of the surface will be selected because the centres of the blocks along the top are at 115m which is below the surface. This causes a bias since the blocks on top of the surface are only partially inside the solid, but the full volume of the block is contributed to the reserve.
Proportional cell evaluation
Select this option to include those blocks that touch the region. When selecting blocks, all blocks that touch the region are selected. "Proportional" means that the volume of intersection of the solid with the block is computed. If the volume of intersection is 0, then the block is not selected. Otherwise the volume contributed is the volume of intersection, which can range continuously from 0 to the volume of the block. Proportional uses a method of decomposition into prisms, which gives a highly accurate computation of the volume of intersection. For proportional reserves, the sum of the block intersection volumes is the same as the volume of the solid, provided the solid is entirely inside the block model.
Related Topics
Section Method Slice Definition
Section Method Post Processing

