Optimisation Control
Use Optimisation Control to select run parameters for the stope Optimiser.
Requirements
A block model must be selected from the Open Specification page.
Instructions
On the Underground menu, point to Analyse, click Stope Optimiser, and then select Optimisation Control from the tree menu on the left to display the Optimisation Control panel.
Model discretisation interval
The values entered into this section indicate how the stope blocks are broken into smaller blocks for analysis. The U axis corresponds with the first axis of your stope orientation plane. The V axis corresponds with your second axis of the stope orientation plane.
The value should be between 0 and 20. The default is 4.
Maximum waste fraction
Enter the maximum fraction of waste material that can be included in any individual stope shape for this optimisation. The value should be between 0 and 1. The default is 1.0.
Stope sequence minimum subset optimisation
Specify the minimum distance to dictate whether different ore lenses are optimised as a whole or subset.
Output sub-economic stopes
Option to output sub-economic stopes. This will include stopes just below the economic parameters specified by the user. These triangulations will be output to the specified stope triangulation output folder.
You will also need to specify a colour for the output triangulations.
Select one of the following options
Fast evaluation, fast reporting
Select this option to have the evaluation proceed and complete in the quickest way possible. This is the default setting.
Fast evaluation, precise reporting
Select this option to add and extra tag (exact_evaluation) to the.xml file. This tag will prompt the optimisation procedure to perform and extra calculation in the block model. This will increase the precision of the evaluation.
Precise evaluation, precise reporting
Select this option to have the evaluation proceed and complete with the most precise return.
Solver Selection
LP Solver
The LP SOLVE solver can solve small test problems, but a commercial solver will be required for large problems.
Note: To use the commercial solvers CPLEX or Gurobi you must have them installed with a valid license.
Time limit hours
Maximum solution time before terminating the solution search.
Presolve
Pre-solve method to simplify and reduce the problem.
Emphasis
Optimal search strategy.
Tuning parameter
Select between integer, double, or string.
Gap relative tolerance
Sets a relative tolerance on the gap between the best integer objective and the objective of the best solution node remaining. When the value falls below the parameter value, the optimization is stopped.
Integrality tolerance
Specifies the amount by which an integer variable can be different from an integer and still be considered feasible.
Advanced Selections
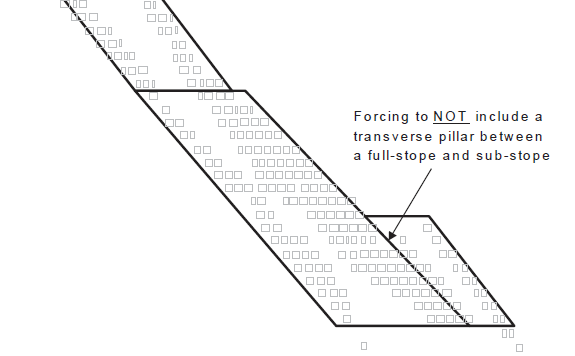
Do not force fullstope substope pillars
Use this in situations where you would want to mine sub-stopes that are adjacent to full stopes in the W-axis (where the normal practice is to require a pillar). An example of this function is depicted in figure below.
Do not force stope split substope pillars
In the Split post-process operation, there are no pillars between split stopes, but at the end of a split sequence the pillar is still required. This switch removes the latter requirement, much like the previous switch.
Disable structure test on seed
If expanding the seed-shape to the structure surface makes the seed-shape sub-economic, you don't otherwise know where a potential stope might have been (unless you do a full run without structure post-processing), so this restricts the expand-to-structure test to only the anneal phase.
Force different dip case corner width tests
The different near/far or hangingwall/footwall seed generation and annealing functions work on width tests at the stope centre, but this means the tests might fail at the corners. This switch forces the tests to also be applied at the corners but the results are only reliable when a single stope is generated for each quad.
Related Topics
Section Method Slice Definition
Section Method Post Processing

