Cutoff
A cutoff grade is used to define what is to be considered as ore and what is to be considered waste. In addition to a cutoff grade, a head grade can optionally be supplied. If a head grade cutoff is supplied, the average grade of the stope must not only satisfy the cutoff grade, but also a head grade.
Cutoff grade and Head grade value can be set as:
-
Single value: A single cutoff will be applied to all stopes in that optimisation run
-
Cutoff variable: You may select a variable from the block model to supply the cutoff value. This allows for variable cut off values in the same optimisation run.
-
The curve table method can be set up as a relationship between the value and some other variable that relates to the stope dimension, specified as points on a curve. If the mining cost is a function of stope size, then the traditional approach would be to do a run at several different cutoffs and then select the stope size that gives the best result. If the primary dimension controlling the cost is the stope width, which may vary according to orebody width and the number of lenses and included waste proportion, then the new method of specifying the cutoff as a variable will allow the best stope width to be chosen on a local area basis, per level and section as a function of cost. The cutoff or headgrade value is interpolated between the curve points supplies, and otherwise uses the minimum or maximum curve point values if the dimension falls outside the values supplied.
Note: The cutoff grade can be supplied without the head grade, but a head grade cannot be supplied without a cutoff grade.
Requirements
A block model must be selected from the Open Specification page.
Instructions
On the Underground menu, point to Analyse, click Stope Optimiser, and then select Optimisation Control > Cutoff to display the Optimisation Control Cutoff panel.
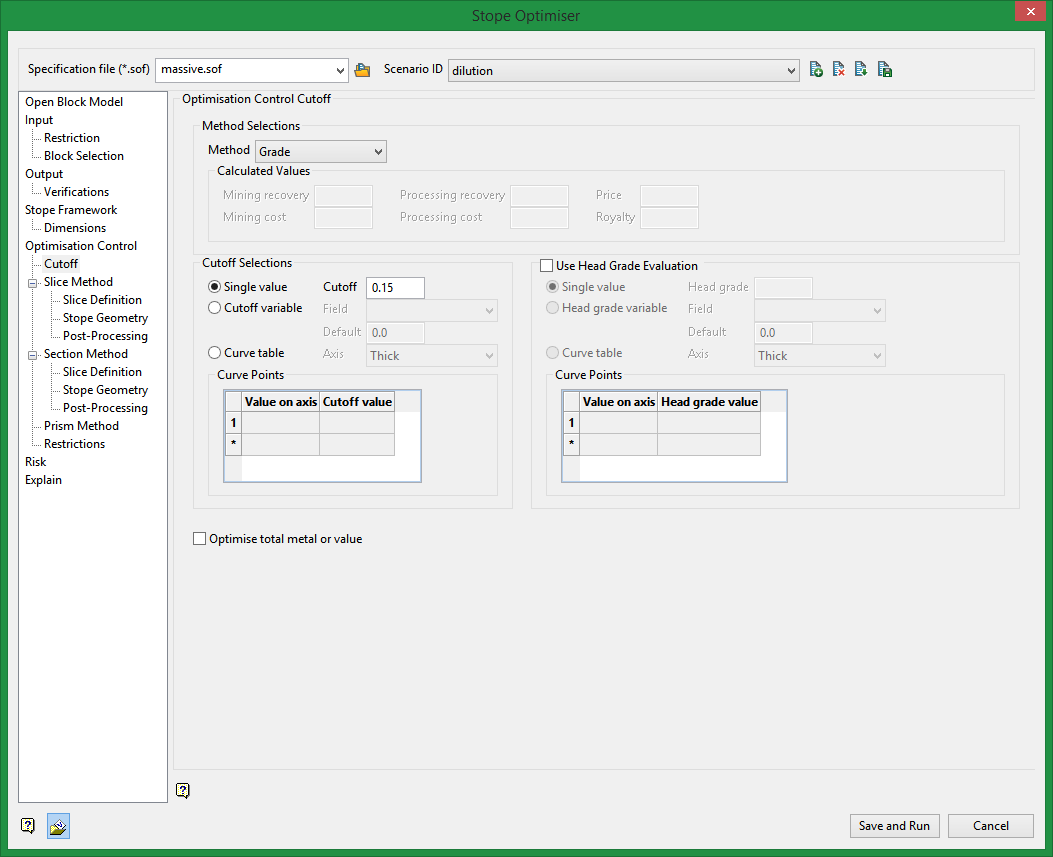
Method Selections
Method
Select Grade, Value, or Calculated from the drop-down menu.
Calculated Values
Select this option to use the calculated method to determine what block, or portions of blocks, contain product defined as being usable.
You will also need to define the desired values for the calculation including:
Mining recovery
Enter a fractional value >0.0.
Mining cost
Enter a numeric value >/= 0.0.
Processing Recovery
Enter a fractional value >0.0
Processing cost
Enter a numeric value >/= 0.0
Price
Enter any numeric value
Royalty
Enter a fractional value >0.0
The calculation may be as follows
value = tonnes* mining recovery * (price * processing recovery * (1.0-royalty) * grade - mining cost - processing cost)
Cutoff Selections
Select one of the following:
Single value
Applies one cutoff to all stopes in an optimisation run.
Cutoff variable
Allows you to specify a block model variable for providing a cutoff value.
Curve table
Allows you to specify the value on axis and cutoff value based on parameters of the stope.
Use Head Grade Evaluation
Select one of the following:
Single value
Applies one head grade cutoff to all stopes in an optimisation run.
Cutoff variable
Allows you to specify a block model variable for providing a cutoff value.
Curve table
Allows you to specify the value on axis and cutoff value based onparameters of the stope.
Optimise total metal or value
Select this option to optimise the total metal or value instead of deducting the cutoff value (or grade). The latter is the normal method as below cutoff material will only be added if the stope width is less than the minimum, or else the added increment to the boundary of the stope is economic.
Related Topics
Section Method Slice Definition
Section Method Post Processing

